chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules
... ° Sanger used chemical methods to determine the sequence of amino acids in the small fragments. ° He then searched for overlapping regions among the pieces obtained by hydrolyzing with the different agents. ° After years of effort, Sanger was able to reconstruct the complete primary structure of ins ...
... ° Sanger used chemical methods to determine the sequence of amino acids in the small fragments. ° He then searched for overlapping regions among the pieces obtained by hydrolyzing with the different agents. ° After years of effort, Sanger was able to reconstruct the complete primary structure of ins ...
No Slide Title
... 1.messenger RNA (mRNA) single chain copy of gene that describes sequence in which aa should bond together to for protein 2.transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up appropriate aa and transfers it to ribosome contains ANTICODON complementary to mRNA codon 3.ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 4. Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) - p ...
... 1.messenger RNA (mRNA) single chain copy of gene that describes sequence in which aa should bond together to for protein 2.transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up appropriate aa and transfers it to ribosome contains ANTICODON complementary to mRNA codon 3.ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 4. Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) - p ...
Protein Phosphorylation in Rhodomicrobium vmnielii
... From the pattern of phosphopolypeptides from a continuously labelled culture, it is clear that at least 25 distinct phosphorylated species were present, with particularly abundant species of M , 88000,66000,55000 and 12700 (Fig. 1). The profile was unaffected by the stage of growth of the culture. T ...
... From the pattern of phosphopolypeptides from a continuously labelled culture, it is clear that at least 25 distinct phosphorylated species were present, with particularly abundant species of M , 88000,66000,55000 and 12700 (Fig. 1). The profile was unaffected by the stage of growth of the culture. T ...
Gene predictions: structural, discovery, functional part 1
... of genes known (or believed) to be real to nucleotide patterns of ORFs in the whole genome. ORFs with patterns similar to the patterns in the training genes are considered real themselves. • Using Glimmer is a two-part process • Train Glimmer with genes from organism that was sequenced, which are kn ...
... of genes known (or believed) to be real to nucleotide patterns of ORFs in the whole genome. ORFs with patterns similar to the patterns in the training genes are considered real themselves. • Using Glimmer is a two-part process • Train Glimmer with genes from organism that was sequenced, which are kn ...
Document
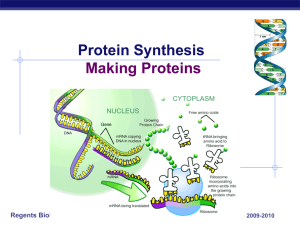
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... Passing on DNA information Need to get DNA gene information from nucleus to cytoplasm ...
DNA - EPFL
... DNA Replication, ctd • DNA synthesis occurs in the chemical direction 5’3’ • Nucleic acid chains are assembled from 5’ triphosphates of deoxyribonucleosides (the triphosphates supply energy) • DNA polymerases are enzymes that copy (replicate) DNA • DNA polymerases require a short preexisting DNA s ...
... DNA Replication, ctd • DNA synthesis occurs in the chemical direction 5’3’ • Nucleic acid chains are assembled from 5’ triphosphates of deoxyribonucleosides (the triphosphates supply energy) • DNA polymerases are enzymes that copy (replicate) DNA • DNA polymerases require a short preexisting DNA s ...
ProteinStructurePredictionTalk
... • Future. – Secondary structure is also based on the environment the protein is folded in. – Including this metadata to attempt to improve methods. ...
... • Future. – Secondary structure is also based on the environment the protein is folded in. – Including this metadata to attempt to improve methods. ...
1st lecture CELLS
... According to the Cell Theory, all living things are composed of one or more cells. Cells fall into prokaryotic and eukaryotic types. Prokaryotic cells are smaller (as a general rule) and lack much of the internal compartmentalization and complexity of eukaryotic cells. No matter which type of cell w ...
... According to the Cell Theory, all living things are composed of one or more cells. Cells fall into prokaryotic and eukaryotic types. Prokaryotic cells are smaller (as a general rule) and lack much of the internal compartmentalization and complexity of eukaryotic cells. No matter which type of cell w ...
Document
... • Medium that contains nutrients for bacterial growth and gene expression – Carbohydrates – Amino acids – Nucleotides – Salts – Vitamins ...
... • Medium that contains nutrients for bacterial growth and gene expression – Carbohydrates – Amino acids – Nucleotides – Salts – Vitamins ...
17_Learning_Objectives
... initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can produce i ...
... initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can produce i ...
Transcription Coactivator Family Proteins
... general transcription factors. While direct contacts between activators and general factors have been demonstrated in vitro, an additional class of proteins, termed coactivators, appear to be required for transcriptional activation of some genes. For example, transcription of class II genes depends ...
... general transcription factors. While direct contacts between activators and general factors have been demonstrated in vitro, an additional class of proteins, termed coactivators, appear to be required for transcriptional activation of some genes. For example, transcription of class II genes depends ...
Anne Ye - A Critical Review of Computational Protein Design Strategies: Progress, Limitations, and Improvements
... of functional groups and propose a transition state for the reaction. Based on this, quantum mechanical calculations are used to generate a theoretical active site, or a theozyme, in which amino acids with the key functional groups are built into the geometry predicted to best stabilize the transiti ...
... of functional groups and propose a transition state for the reaction. Based on this, quantum mechanical calculations are used to generate a theoretical active site, or a theozyme, in which amino acids with the key functional groups are built into the geometry predicted to best stabilize the transiti ...
Bio 301, Biochemistry I
... 14. Which of the following is an accurate statement regarding the relationship between primers and nucleic acid synthesis? a. Primase catalyzes the de novo polymerization of DNA. b. RNA polymerase II initiates RNA synthesis by elongation of a DNA primer. c. During DNA replication, every Okazaki frag ...
... 14. Which of the following is an accurate statement regarding the relationship between primers and nucleic acid synthesis? a. Primase catalyzes the de novo polymerization of DNA. b. RNA polymerase II initiates RNA synthesis by elongation of a DNA primer. c. During DNA replication, every Okazaki frag ...
Section 3.3: Carbon Compounds Building Blocks of Cells • The parts
... What are biomolecules and what are they made up of? ...
... What are biomolecules and what are they made up of? ...
PPT - FLI - Leibniz Institute for Age Research
... There is a particular propensity for Aminoisobutyric acid (Aib). The chain has an alkyl N terminus (usually acetyl) and a hydroxy-amino acid at the C terminus. Peptaibols generally exhibit antimicrobial activity and are referred to as antibiotic peptides. The main sources of the peptaibols known to ...
... There is a particular propensity for Aminoisobutyric acid (Aib). The chain has an alkyl N terminus (usually acetyl) and a hydroxy-amino acid at the C terminus. Peptaibols generally exhibit antimicrobial activity and are referred to as antibiotic peptides. The main sources of the peptaibols known to ...
CH. 12.3 : DNA, RNA, and Protein
... • The sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains information. • This information is put to work through the production of proteins. • Proteins fold into complex, three-dimensional shapes to become key cell structures and regulators of cell functions. • Thus, by encoding the instructions for making prot ...
... • The sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains information. • This information is put to work through the production of proteins. • Proteins fold into complex, three-dimensional shapes to become key cell structures and regulators of cell functions. • Thus, by encoding the instructions for making prot ...
Protein
... • Derived proteins are of two types, primarily derived proteins and secondary derived proteins. Primary derived proteins are derivatives of proteins, in which the size of the protein molecule is not altered materially, while in secondary derived proteins, hydrolysis occurs, as a result the molecules ...
... • Derived proteins are of two types, primarily derived proteins and secondary derived proteins. Primary derived proteins are derivatives of proteins, in which the size of the protein molecule is not altered materially, while in secondary derived proteins, hydrolysis occurs, as a result the molecules ...
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
... specific solubilization of the additional cell envelope protein or of another cell envelope protein. The additional cell envelope protein is not heatmodifiable as the same electrophoretic mobility was observed after preincubation in sample buffer for 2 h at 37°C and after boiling for 5 min. Thus a p ...
... specific solubilization of the additional cell envelope protein or of another cell envelope protein. The additional cell envelope protein is not heatmodifiable as the same electrophoretic mobility was observed after preincubation in sample buffer for 2 h at 37°C and after boiling for 5 min. Thus a p ...
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening (also known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the binding domain (BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the domain responsible for binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation assay.