B. True or False/Edit
... type, helpful tips and general suggestions on writing the essay or short-answer questions. Go ahead try this one, and a few of mine that follow! 70. Explain the relationship between an enzyme’s chemical structure and the function of the enzyme, and describe how both structure and function may be alt ...
... type, helpful tips and general suggestions on writing the essay or short-answer questions. Go ahead try this one, and a few of mine that follow! 70. Explain the relationship between an enzyme’s chemical structure and the function of the enzyme, and describe how both structure and function may be alt ...
Cynthia Smith - people.csail.mit.edu
... – Direct negative impact to many enzymes that run our biochemistry as a result of depletion of their nutrient cofactors by glyphosate metabolism ...
... – Direct negative impact to many enzymes that run our biochemistry as a result of depletion of their nutrient cofactors by glyphosate metabolism ...
8)Discuss the roles of cofactors and coenzymes in enzyme activity.
... Enzymes are proteins that are capable of speeding up the chemical reactions. General features of enzymes: 1) Most of the enzymes are proteins, however, recent work has shown that there are RNA molecules which show catalytic activity (RNA enzymes) 2) Enzymes increase the rate of reactions but do not ...
... Enzymes are proteins that are capable of speeding up the chemical reactions. General features of enzymes: 1) Most of the enzymes are proteins, however, recent work has shown that there are RNA molecules which show catalytic activity (RNA enzymes) 2) Enzymes increase the rate of reactions but do not ...
Enzyme
... Stored at high concentration, as lyophilized powders, or in a concentrated (NH4)2SO4 solution Some proteases may go through autolysis during storage. Some enzymes are easier to subject to denaturation at low concentrations. Stored at low temperatures Be careful: freeze-thaw cycles would inac ...
... Stored at high concentration, as lyophilized powders, or in a concentrated (NH4)2SO4 solution Some proteases may go through autolysis during storage. Some enzymes are easier to subject to denaturation at low concentrations. Stored at low temperatures Be careful: freeze-thaw cycles would inac ...
File - John Robert Warner
... Two important AIDS-fighting drugs are enzyme inhibitors. The first, AZT (azidothymidine, also called zidovudine), resembles a molecule essential to reproduction of the AIDS-causing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AZT is accepted by an HIV enzyme as a substrate and prevents the virus from produci ...
... Two important AIDS-fighting drugs are enzyme inhibitors. The first, AZT (azidothymidine, also called zidovudine), resembles a molecule essential to reproduction of the AIDS-causing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AZT is accepted by an HIV enzyme as a substrate and prevents the virus from produci ...
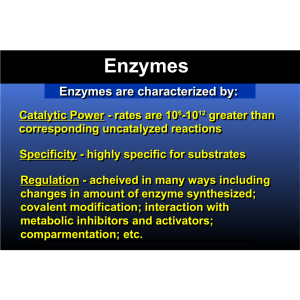
Enzymes Enzymes are characterized by
... to the name of the substrate or a phrase describing the catalytic reaction. Urease - catalyzes the hyrolysis of urea Alcohol dehydrogenase - catalyzes the oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes ...
... to the name of the substrate or a phrase describing the catalytic reaction. Urease - catalyzes the hyrolysis of urea Alcohol dehydrogenase - catalyzes the oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes ...
Enzymes
... catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the same reaction in parallel; this can allow more complex regulation: with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzym ...
... catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the same reaction in parallel; this can allow more complex regulation: with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzym ...
Energetics and Enzymes
... Other inhibitors do not act directly with the active site – These bind somewhere else and change the shape of the enzyme so that the substrate will no longer fit the active site ...
... Other inhibitors do not act directly with the active site – These bind somewhere else and change the shape of the enzyme so that the substrate will no longer fit the active site ...
Peptide microarrays for detailed, high-throughput
... was used for real-time detection of protein kinase A (PKA) for substrate identification and kinetic characterization of PKA (figure 1). Figure 2 shows a time course of peptide phosphorylation over 50 minutes. In this assay the IC50 of three PKA inhibitors, AMP–PNP, staurosporin, and PKA inhibitor pe ...
... was used for real-time detection of protein kinase A (PKA) for substrate identification and kinetic characterization of PKA (figure 1). Figure 2 shows a time course of peptide phosphorylation over 50 minutes. In this assay the IC50 of three PKA inhibitors, AMP–PNP, staurosporin, and PKA inhibitor pe ...
Brookfield Academy Upper School SMART Team
... the catalytic region, containing both the PLP and the heme cofactor, while the C-terminal domain is the regulatory region, binding SAM. Upon binding with SAM, the C-terminal domain is removed, and the enzyme functions as a homodimer. The PLP is covalently attached to CBS by lysine 119, while the hem ...
... the catalytic region, containing both the PLP and the heme cofactor, while the C-terminal domain is the regulatory region, binding SAM. Upon binding with SAM, the C-terminal domain is removed, and the enzyme functions as a homodimer. The PLP is covalently attached to CBS by lysine 119, while the hem ...
Chapter 14 Review Question Answers
... enzymes needed for the glucuronidation of many drug molecules). Inhibition of epoxide hydrolase by valproate prolongs the biological half-life of the arene oxide intermediate and thus increases phenytoin-induced idiosyncratic toxicities. The formation of catechol metabolites from p-HPPH or m-HPPH in ...
... enzymes needed for the glucuronidation of many drug molecules). Inhibition of epoxide hydrolase by valproate prolongs the biological half-life of the arene oxide intermediate and thus increases phenytoin-induced idiosyncratic toxicities. The formation of catechol metabolites from p-HPPH or m-HPPH in ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... describe the basic structure of an enzyme. define the terms substrate and active site. describe the lock and key hypothesis of enzyme function and explain why this hypothesis is no longer considered correct. describe the induced fit model of enzyme function. (This is the currently accepted explanati ...
... describe the basic structure of an enzyme. define the terms substrate and active site. describe the lock and key hypothesis of enzyme function and explain why this hypothesis is no longer considered correct. describe the induced fit model of enzyme function. (This is the currently accepted explanati ...
Case Study #1 Use of bioinformatics in drug development
... receptors. •Drug may be classified as: substrates/inhibitors (for enzymes) agonists/antagonists (for receptors) •Ligands for receptors normally bind via a non-covalent reversible binding. ...
... receptors. •Drug may be classified as: substrates/inhibitors (for enzymes) agonists/antagonists (for receptors) •Ligands for receptors normally bind via a non-covalent reversible binding. ...
7.016 Problem Set 1 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... Esterases hydrolyze ester bonds. For simplicity, only the amino acids whose side-chains interact with the substrate are shown. Each circled interaction is important for the binding of the substrate to the enzyme. ...
... Esterases hydrolyze ester bonds. For simplicity, only the amino acids whose side-chains interact with the substrate are shown. Each circled interaction is important for the binding of the substrate to the enzyme. ...
elisa - WordPress.com
... (conjugated) to horseradish peroxidase (HRP) • Enzyme substrate: 3,3’,5,5’ – tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) – a colorless solution that when oxidized by HRP turns yellow. A substrate is a compound or substance that undergoes change. – Substrates bind to active sites on the surface of enzymes and are con ...
... (conjugated) to horseradish peroxidase (HRP) • Enzyme substrate: 3,3’,5,5’ – tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) – a colorless solution that when oxidized by HRP turns yellow. A substrate is a compound or substance that undergoes change. – Substrates bind to active sites on the surface of enzymes and are con ...
Chap 4 Study Guide
... let me guide you through one possible answer. Watch for key terms in bold-face type, helpful tips and general suggestions on writing the essay or short-answer questions. Go ahead try this one, and a few of mine that follow! 70. Explain the relationship between an enzyme’s chemical structure and the ...
... let me guide you through one possible answer. Watch for key terms in bold-face type, helpful tips and general suggestions on writing the essay or short-answer questions. Go ahead try this one, and a few of mine that follow! 70. Explain the relationship between an enzyme’s chemical structure and the ...
File
... 7. Effect of pH on Enzymes Enzymes work best within a range of pH depending on the type of enzyme. The pH that the enzymes works best at is called it’s Optimum pH If the pH is too high, the enzymes active site changes shape (denatured) What is the optimum pH of this enzyme ? ...
... 7. Effect of pH on Enzymes Enzymes work best within a range of pH depending on the type of enzyme. The pH that the enzymes works best at is called it’s Optimum pH If the pH is too high, the enzymes active site changes shape (denatured) What is the optimum pH of this enzyme ? ...
Polymer Molecules
... All proteins contain the elements C,O,H, N. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body cannot make every type of amino acids that it needs. So our diet ...
... All proteins contain the elements C,O,H, N. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body cannot make every type of amino acids that it needs. So our diet ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... • Such mutual recognition is the basis for specificity. The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site 3. Regulation • Although the enormous catalytic potential is essential, it does pose a problem: if it was not regulated, all reactions in a ce ...
... • Such mutual recognition is the basis for specificity. The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site 3. Regulation • Although the enormous catalytic potential is essential, it does pose a problem: if it was not regulated, all reactions in a ce ...
Sample%20Exam%20Protein%20ANSWERS
... 5. How is ligand binding in the extracellular domain communicated to the transmembrane unit? Loop 7 and loop 2 act together like a caliper to hold pro8 in the trans conformation. Ligand binding (5HT3 for example) in the extracellular binding domain moves Trp138 (shown in the center of the extracellu ...
... 5. How is ligand binding in the extracellular domain communicated to the transmembrane unit? Loop 7 and loop 2 act together like a caliper to hold pro8 in the trans conformation. Ligand binding (5HT3 for example) in the extracellular binding domain moves Trp138 (shown in the center of the extracellu ...
Human carboxylesterase 1: from drug metabolism to drug discovery
... and a large, flexible region [24]. The small ester linkages of cocaine and heroin pack into the small, rigid pocket, whereas the large, flexible pocket accommodates the structurally distinct tropine and morphine rings of cocaine and heroin respectively. These structural results, elucidated from the ...
... and a large, flexible region [24]. The small ester linkages of cocaine and heroin pack into the small, rigid pocket, whereas the large, flexible pocket accommodates the structurally distinct tropine and morphine rings of cocaine and heroin respectively. These structural results, elucidated from the ...
Enzyme Lab
... bases are frequently used catalysts in organic chemistry and can accelerate reactions thousands of times. The biological catalysts known as enzymes catalyze the great majority of chemical reactions in the cell. Enzymes can accelerate reactions 1014 to 1020 times, amounts that are far greater than an ...
... bases are frequently used catalysts in organic chemistry and can accelerate reactions thousands of times. The biological catalysts known as enzymes catalyze the great majority of chemical reactions in the cell. Enzymes can accelerate reactions 1014 to 1020 times, amounts that are far greater than an ...
Q1. Babies find it difficult to digest proteins in their food. Baby food
... (40oC is) optimum / best temperature allow near to 37oC / body temperature where enzymes work best ...
... (40oC is) optimum / best temperature allow near to 37oC / body temperature where enzymes work best ...
allosteric activator
... change of enzyme synthesis and degradation so that ultimately determine enzyme level at any point in time. In many instances, transcriptional regulation determines the concentrations of specific enzyme, with enzyme proteins degradation playing a minor role. In other instances, protein synthesis is c ...
... change of enzyme synthesis and degradation so that ultimately determine enzyme level at any point in time. In many instances, transcriptional regulation determines the concentrations of specific enzyme, with enzyme proteins degradation playing a minor role. In other instances, protein synthesis is c ...
Document
... Two important AIDS-fighting drugs are enzyme inhibitors. The first, AZT (azidothymidine, also called zidovudine), resembles a molecule essential to reproduction of the AIDS-causing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AZT is accepted by an HIV enzyme as a substrate and prevents the virus from produci ...
... Two important AIDS-fighting drugs are enzyme inhibitors. The first, AZT (azidothymidine, also called zidovudine), resembles a molecule essential to reproduction of the AIDS-causing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AZT is accepted by an HIV enzyme as a substrate and prevents the virus from produci ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.