Click to the presentation
... •Maximum achievable yield to 3HP from glucose during anaerobic growth matches commercial pathway •Slightly reduced maximum achievable intracellular activity at which 3HP can be produced •Numerous other attractive candidates ...
... •Maximum achievable yield to 3HP from glucose during anaerobic growth matches commercial pathway •Slightly reduced maximum achievable intracellular activity at which 3HP can be produced •Numerous other attractive candidates ...
nature of polyethyleneimine-glucose oxidase interactions
... Based on the best docked energies: -5.8 and -4.5 kcal/mol, two sites were differentiated on the protein body, which show the best affinity to PEI (Table 1). In the first case, the ligand is bound to amino acids inside of the protein area (LIG1, Figure 5), while in the second case the binding takes p ...
... Based on the best docked energies: -5.8 and -4.5 kcal/mol, two sites were differentiated on the protein body, which show the best affinity to PEI (Table 1). In the first case, the ligand is bound to amino acids inside of the protein area (LIG1, Figure 5), while in the second case the binding takes p ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2003 - Second Exam:
... 5. Which of the statements regarding enzymes is false? a) Enzymes are usually proteins that function as catalysts. b) Enzymes are usually specific. c) Enzymes may be used many times for a specific reaction. d) The active site of an enzyme remains rigid and does not change shape. 6. The nucleophile t ...
... 5. Which of the statements regarding enzymes is false? a) Enzymes are usually proteins that function as catalysts. b) Enzymes are usually specific. c) Enzymes may be used many times for a specific reaction. d) The active site of an enzyme remains rigid and does not change shape. 6. The nucleophile t ...
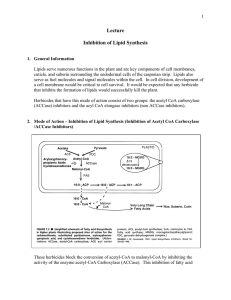
Lecture Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis
... and ICI Plant Protection (Zeneca/Syngenta) and was first tested in the U.S. in 1981. Sethoxydim was discovered by Nippon Soda Co. and was developed by BASF in the U.S. where it was first tested in 1978. Clethodim was not discovered until 1987. 7. Mode of Action – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhib ...
... and ICI Plant Protection (Zeneca/Syngenta) and was first tested in the U.S. in 1981. Sethoxydim was discovered by Nippon Soda Co. and was developed by BASF in the U.S. where it was first tested in 1978. Clethodim was not discovered until 1987. 7. Mode of Action – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhib ...
Mechanisms of catalysis
... • rate enhancement cannot only be explained with above mechanisms and • we know that enzymes are conformationally dynamic ...
... • rate enhancement cannot only be explained with above mechanisms and • we know that enzymes are conformationally dynamic ...
Mechanisms of catalysis
... • rate enhancement cannot only be explained with above mechanisms and • we know that enzymes are conformationally dynamic ...
... • rate enhancement cannot only be explained with above mechanisms and • we know that enzymes are conformationally dynamic ...
Quiz - Columbus Labs
... catalyzes GDP-GTP exchange on the α -subunit of the heterotrimer G protein (Gαβγ ), replacing GDP with GTP. The Gα -subunit with GTP bound dissociates from the βγ -subunits and binds to adenylyl cyclase (AC). AC becomes active upon association with Gα :GTP and catalyzes the formation of cAMP from AT ...
... catalyzes GDP-GTP exchange on the α -subunit of the heterotrimer G protein (Gαβγ ), replacing GDP with GTP. The Gα -subunit with GTP bound dissociates from the βγ -subunits and binds to adenylyl cyclase (AC). AC becomes active upon association with Gα :GTP and catalyzes the formation of cAMP from AT ...
1 Biology 205 Exam 1 4/21/16 1. Geography quiz
... 7. A mutation in a particular enzyme causes the enzyme to form more hydrogen bonds with its substrate. What effect do you think this might have on the enzyme’s function? Start your answer by defining KM, Vmax and turnover number and then answer the question in terms of KM, Vmax and turnover number. ...
... 7. A mutation in a particular enzyme causes the enzyme to form more hydrogen bonds with its substrate. What effect do you think this might have on the enzyme’s function? Start your answer by defining KM, Vmax and turnover number and then answer the question in terms of KM, Vmax and turnover number. ...
D-Glucose is a carbohydrate which can be classified as which of the
... Since it binds the active site, it is clearly a competitive inhibitor. Thus, it will have no effect on Vmax but the Km will increase. ...
... Since it binds the active site, it is clearly a competitive inhibitor. Thus, it will have no effect on Vmax but the Km will increase. ...
yes - Learnblock
... A. Any region could be used as the solution can be made to any pH no. Some very reactive B. No region would be suitable as the pH changes with the addition of H+ counter intuitive! C. Region C, as it is in the middle of the pH range a disaster ...
... A. Any region could be used as the solution can be made to any pH no. Some very reactive B. No region would be suitable as the pH changes with the addition of H+ counter intuitive! C. Region C, as it is in the middle of the pH range a disaster ...
Introduction to Winemaking Part 2: Must Additions
... How much is necessary? • From 25 mg/L to 75 mg/L SO2 required to inhibit from 75 to 97% of PPO enzyme. • Laccase a more potent oxidative enzyme found in Botryized fruit requires 150 mg/L (too much). • 0.825 mg/L molecular SO2 is necessary to reduce viable cell population by an order of magnitude (1 ...
... How much is necessary? • From 25 mg/L to 75 mg/L SO2 required to inhibit from 75 to 97% of PPO enzyme. • Laccase a more potent oxidative enzyme found in Botryized fruit requires 150 mg/L (too much). • 0.825 mg/L molecular SO2 is necessary to reduce viable cell population by an order of magnitude (1 ...
Bio_Ch2_ Enzymes_2009
... • Increase Concentration of Enzyme – More enzyme available to make contact with more substrate molecules – Speeds up reaction rate up to a point – Reaction rate decreases as substrate is converted into product ...
... • Increase Concentration of Enzyme – More enzyme available to make contact with more substrate molecules – Speeds up reaction rate up to a point – Reaction rate decreases as substrate is converted into product ...
What happened to my cousin Patrick O’Neill?
... • Enzymes (usually proteins) are biological catalysts, highly specific for their substrates (reactants). • Enzymes change reactants into products through ...
... • Enzymes (usually proteins) are biological catalysts, highly specific for their substrates (reactants). • Enzymes change reactants into products through ...
Unit: Enzymes I
... UNIT: Enzymes I (Colorimetric/Turbidimetric/End-point) (continued) technician should suspect high enzyme activity causing substrate depletion. Continuous monitoring is used most commonly with those enzymes in which changes in NADH or NADPH are measured but can also be used for the determination of ...
... UNIT: Enzymes I (Colorimetric/Turbidimetric/End-point) (continued) technician should suspect high enzyme activity causing substrate depletion. Continuous monitoring is used most commonly with those enzymes in which changes in NADH or NADPH are measured but can also be used for the determination of ...
AP Biology Chapter 8 Introduction to Metabolism Guided Notes
... Catalysis in the Enzyme’s Active Site • In an enzymatic reaction, the __________binds to the __________ ______of the enzyme • The active site can lower an EA barrier by ...
... Catalysis in the Enzyme’s Active Site • In an enzymatic reaction, the __________binds to the __________ ______of the enzyme • The active site can lower an EA barrier by ...
1. A. Name each enzyme present in the citric acid cycle and specify
... serves to carry H from a donor to an acceptor in a reaction catalyzed by a single enzyme. B. In "designing" a metabolic pathway you find it necessary to extend a carbon chain by 1 carbon atom. Would you select an enzyme which uses thiamin pyrophosphate as prosthetic group or one that uses biotin? Wh ...
... serves to carry H from a donor to an acceptor in a reaction catalyzed by a single enzyme. B. In "designing" a metabolic pathway you find it necessary to extend a carbon chain by 1 carbon atom. Would you select an enzyme which uses thiamin pyrophosphate as prosthetic group or one that uses biotin? Wh ...
Enzymes for Pharma Applications
... fats, which is then acted upon by the lipase in pancreatin secreted by pancreas. Bile salts are either glyvine or taurine conjugates of polyhydroxy steroidal acid. Ox bile is the most important commercial source of these acids and contains primarily cholic acid with less amount of deoxycholic acid. ...
... fats, which is then acted upon by the lipase in pancreatin secreted by pancreas. Bile salts are either glyvine or taurine conjugates of polyhydroxy steroidal acid. Ox bile is the most important commercial source of these acids and contains primarily cholic acid with less amount of deoxycholic acid. ...
hemoglobin - MBBS Students Club
... Uroporphyrin- acetate and propionate Coproporphyrin- methyl and propionate Protoporphyrin IX- vinyl, methyl and propionate ...
... Uroporphyrin- acetate and propionate Coproporphyrin- methyl and propionate Protoporphyrin IX- vinyl, methyl and propionate ...
... orders of the enzyme structure without disrupting its primary structure. When the pH is reverted to 7.4 the primary structure tries to fold on itself to acquire the active 3D-conformation but fails to do so. Hence the enzyme cannot renature and thus remains inactive. d) You isolate a mutant version ...
rational drug design
... ion is also found in the active site) 6. Charged ions are often required to assist an enzyme to do its job. These ions are cofactors. Which cofactor seems to be involved in the functioning of amylase (is in the active site)? Cl7. Sugar units often form a ring shape. How many sugar units are there in ...
... ion is also found in the active site) 6. Charged ions are often required to assist an enzyme to do its job. These ions are cofactors. Which cofactor seems to be involved in the functioning of amylase (is in the active site)? Cl7. Sugar units often form a ring shape. How many sugar units are there in ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Was the first B vitamin identified. Is part of the coenzyme thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP). Is used to decarboxylate -keto carboxylic acids. RDA is 2 mg; deficiencies include fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss, nerve degeneration, heart failure Sources are liver, yeast, whole grains, cereal ...
... Was the first B vitamin identified. Is part of the coenzyme thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP). Is used to decarboxylate -keto carboxylic acids. RDA is 2 mg; deficiencies include fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss, nerve degeneration, heart failure Sources are liver, yeast, whole grains, cereal ...
One of the most famous examples
... Substrates & products Chemical kinetics Enzyme specificity Substrates and products Chemical kinetics Enzyme kinetics Michaelis - Menten equation Vo, Vmax, Km, turnover number ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------PROSTHETIC GROUPS: There are some NON ...
... Substrates & products Chemical kinetics Enzyme specificity Substrates and products Chemical kinetics Enzyme kinetics Michaelis - Menten equation Vo, Vmax, Km, turnover number ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------PROSTHETIC GROUPS: There are some NON ...
Nadine Noelting
... superfamily. This is roughly located between amino acids 120 and 420. The mutations associated with my gene are found in this conserved domain. The family consists of nonheme, iron (II)- dependent enzymes, including phenylalanine hydroxylase, eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase, and eukaryotic tryptopha ...
... superfamily. This is roughly located between amino acids 120 and 420. The mutations associated with my gene are found in this conserved domain. The family consists of nonheme, iron (II)- dependent enzymes, including phenylalanine hydroxylase, eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase, and eukaryotic tryptopha ...
The effects of calcium ions on the activites of hexokinase
... sarcoplasmic reticulum. The dependence of muscular contraction on a supply of ATP from catabolic processes (particularly glycolysis) suggested the possibility that the increased sarcoplasmic concentration of Ca2+ might stimulate the activities of the regulatory enzymes of glycolysis, or modify the b ...
... sarcoplasmic reticulum. The dependence of muscular contraction on a supply of ATP from catabolic processes (particularly glycolysis) suggested the possibility that the increased sarcoplasmic concentration of Ca2+ might stimulate the activities of the regulatory enzymes of glycolysis, or modify the b ...
Enzyme inhibitor

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used in pesticides. Not all molecules that bind to enzymes are inhibitors; enzyme activators bind to enzymes and increase their enzymatic activity, while enzyme substrates bind and are converted to products in the normal catalytic cycle of the enzyme.The binding of an inhibitor can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. Inhibitor binding is either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible inhibitors usually react with the enzyme and change it chemically (e.g. via covalent bond formation). These inhibitors modify key amino acid residues needed for enzymatic activity. In contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and different types of inhibition are produced depending on whether these inhibitors bind to the enzyme, the enzyme-substrate complex, or both.Many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors, so their discovery and improvement is an active area of research in biochemistry and pharmacology. A medicinal enzyme inhibitor is often judged by its specificity (its lack of binding to other proteins) and its potency (its dissociation constant, which indicates the concentration needed to inhibit the enzyme). A high specificity and potency ensure that a drug will have few side effects and thus low toxicity.Enzyme inhibitors also occur naturally and are involved in the regulation of metabolism. For example, enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products. This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Other cellular enzyme inhibitors are proteins that specifically bind to and inhibit an enzyme target. This can help control enzymes that may be damaging to a cell, like proteases or nucleases. A well-characterised example of this is the ribonuclease inhibitor, which binds to ribonucleases in one of the tightest known protein–protein interactions. Natural enzyme inhibitors can also be poisons and are used as defences against predators or as ways of killing prey.