MedBiochem Exam 1, 1998
... 22. All of the statements about Coenzymes are true EXCEPT A. coenzymes are the non-protein portion of an enzyme B. cosubstrates that associate transiently with the active site of the enzyme C. cosubstrates that undergo an alteration following completion of the reaction D. prosthetic groups are the n ...
... 22. All of the statements about Coenzymes are true EXCEPT A. coenzymes are the non-protein portion of an enzyme B. cosubstrates that associate transiently with the active site of the enzyme C. cosubstrates that undergo an alteration following completion of the reaction D. prosthetic groups are the n ...
Firefly Bioluminescence
... As Equations 2 and 3 indicate, the luciferase enzyme functions as a mono-oxygenase, although it does so in a very unusual manner without the apparent involvement of a metal or cofactor. In some way that has not been yet determined, luciferase amino acid residues are recruited to promote the addition ...
... As Equations 2 and 3 indicate, the luciferase enzyme functions as a mono-oxygenase, although it does so in a very unusual manner without the apparent involvement of a metal or cofactor. In some way that has not been yet determined, luciferase amino acid residues are recruited to promote the addition ...
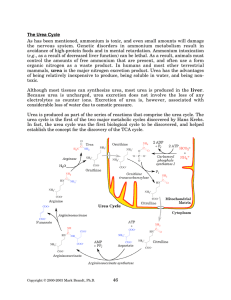
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... glutamine depletes the tissue of glutamate. This is particularly important in the brain, because glutamate is a neurotransmitter, and is the precursor of g-aminobutyric acid (GABA), another neurotransmitter. In addition, synthesis of glutamate requires a-ketoglutarate, and therefore release of gluta ...
... glutamine depletes the tissue of glutamate. This is particularly important in the brain, because glutamate is a neurotransmitter, and is the precursor of g-aminobutyric acid (GABA), another neurotransmitter. In addition, synthesis of glutamate requires a-ketoglutarate, and therefore release of gluta ...
amino acid mixture
... explained if these amino acid residues were absorbed by an alternative peptide transport system which was not shared with glycylglycine. There are 400 possible dipeptides, so that our results cannot with certainty be extrapolated to the normal biological state. Moreover, if there is more than one pe ...
... explained if these amino acid residues were absorbed by an alternative peptide transport system which was not shared with glycylglycine. There are 400 possible dipeptides, so that our results cannot with certainty be extrapolated to the normal biological state. Moreover, if there is more than one pe ...
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle in Thiobacillus
... organisms the tricarboxylic acid cycle is incomplete. In agreement with Taylor, Hoare & Hoare (I 969) we were unable to detect the a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in Thiobacillus denitrijicans. We also failed to demonstrate this enzyme in cell-free extracts from Thiobacillus-A2 when grown autotrophica ...
... organisms the tricarboxylic acid cycle is incomplete. In agreement with Taylor, Hoare & Hoare (I 969) we were unable to detect the a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in Thiobacillus denitrijicans. We also failed to demonstrate this enzyme in cell-free extracts from Thiobacillus-A2 when grown autotrophica ...
Disallowed Ramachandran Conformations of Amino Acid Residues
... cases, with a total of 39 disallowed residues available for comparison. Of these, 33 residues did have the disallowed conformation conserved, while six residues adopted allowed f, c values in some of the related protein structures. On closer examination it was found that in five of these cases c val ...
... cases, with a total of 39 disallowed residues available for comparison. Of these, 33 residues did have the disallowed conformation conserved, while six residues adopted allowed f, c values in some of the related protein structures. On closer examination it was found that in five of these cases c val ...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
... mammalian NaDC1 using a membrane-impermeable sulfonate reagent have shown that the tip of HPout, including its SNT motif, is accessible from the extracellular space 10-12. Such accessibility of the hairpin tip is increased in the presence of Na+ ions, but access to the cysteine labeling is protected ...
... mammalian NaDC1 using a membrane-impermeable sulfonate reagent have shown that the tip of HPout, including its SNT motif, is accessible from the extracellular space 10-12. Such accessibility of the hairpin tip is increased in the presence of Na+ ions, but access to the cysteine labeling is protected ...
biochemistry-lect-4-n-34-amino-acid-and-peptides
... Since amino acids are ampholytes they act as buffers. However, the buffering action of amino acids in the blood is insignificant because of their low concentration. ...
... Since amino acids are ampholytes they act as buffers. However, the buffering action of amino acids in the blood is insignificant because of their low concentration. ...
Initiation, elongation, and termination strategies in polyketide and
... NRPS enzymes. Every carrier protein domain (ArCP, PCP, ACP: aryl, peptidyl and acyl carrier proteins, respectively) must be converted from an inactive apo form to an active holo form by covalent attachment of a Coenzyme-A-derived phosphopantetheine (P-pant) group to a specific serine sidechain found ...
... NRPS enzymes. Every carrier protein domain (ArCP, PCP, ACP: aryl, peptidyl and acyl carrier proteins, respectively) must be converted from an inactive apo form to an active holo form by covalent attachment of a Coenzyme-A-derived phosphopantetheine (P-pant) group to a specific serine sidechain found ...
Novel Substrates for Fluorescence-based Protein Tyrosine Kinase
... Cheng, H.C., Nishio, H., Hatase, O., Ralph, S., and Wang, J.H. (1992) A synthetic peptide derived from p34cdc2 is a specific and efficient substrate of src-family tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem. 267, 9248-56 Garcia, P., Shoelson, S.E., George, S.T., Hinds, D.A., Goldberg, A.R., Miller, W.T. (1993) Ph ...
... Cheng, H.C., Nishio, H., Hatase, O., Ralph, S., and Wang, J.H. (1992) A synthetic peptide derived from p34cdc2 is a specific and efficient substrate of src-family tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem. 267, 9248-56 Garcia, P., Shoelson, S.E., George, S.T., Hinds, D.A., Goldberg, A.R., Miller, W.T. (1993) Ph ...
as a PDF - PubAg
... cDNAs contained a signal peptide, activation peptide, and conserved N-termini (IVGG). Other structural features included His, Asp, and Ser residues for the catalytic amino acid triad of serine proteinase active sites, residues for the binding pocket, and four pairs of cysteine residues for disulfide ...
... cDNAs contained a signal peptide, activation peptide, and conserved N-termini (IVGG). Other structural features included His, Asp, and Ser residues for the catalytic amino acid triad of serine proteinase active sites, residues for the binding pocket, and four pairs of cysteine residues for disulfide ...
Elucidating Substrate and Inhibitor Binding Sites on the Surface of
... Fig. 1. The 89–95 loop defines a substrate binding subsite for GSK-3β. (a) Features of the substrate binding site of GSK-3β. The structure of GSK-3β is based on the available crystal structures,30,40 as described in Ref. 39. The surface of GSK-3β is shown in gray, with the loop 89–95 shown in yellow ...
... Fig. 1. The 89–95 loop defines a substrate binding subsite for GSK-3β. (a) Features of the substrate binding site of GSK-3β. The structure of GSK-3β is based on the available crystal structures,30,40 as described in Ref. 39. The surface of GSK-3β is shown in gray, with the loop 89–95 shown in yellow ...
Chapter 2 Immobilization of Enzymes
... Immobilization of proteins by methods based on the formation of covalent bonds is among the most widely used. An advantage of these methods is that, because of the stable nature of the bonds formed between enzyme and matrix, the enzyme is not released into the solution upon use. However, in order to ...
... Immobilization of proteins by methods based on the formation of covalent bonds is among the most widely used. An advantage of these methods is that, because of the stable nature of the bonds formed between enzyme and matrix, the enzyme is not released into the solution upon use. However, in order to ...
Absorption of Amino Acids from an Amino Acid
... (Holdsworth & Dawson, 1964) and expressed on a percentage basis. The significance of differences between means was assessed by the paired t-test. RESULTS A N D DISCUSSION The results (Fig. 1) show that the extent to which amino acids were absorbed from the amino acid mixture varied considerably, the ...
... (Holdsworth & Dawson, 1964) and expressed on a percentage basis. The significance of differences between means was assessed by the paired t-test. RESULTS A N D DISCUSSION The results (Fig. 1) show that the extent to which amino acids were absorbed from the amino acid mixture varied considerably, the ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.