Current #3 - Southgate Schools
... 6. A circuit is wired with a power supply, a resistor and an ammeter. The ammeter reads a current of 24 mA. Determine the new current if the voltage of the power supply was ... g. ... increased by a factor of 2 and the resistance was increased by a factor of 2. h. ... increased by a factor of 3 and ...
... 6. A circuit is wired with a power supply, a resistor and an ammeter. The ammeter reads a current of 24 mA. Determine the new current if the voltage of the power supply was ... g. ... increased by a factor of 2 and the resistance was increased by a factor of 2. h. ... increased by a factor of 3 and ...
GE Infrastructure Universal Temperature Reference
... to about 0.1˚C plus 0.4% of difference between the terminal temperature at calibration and at the time of ...
... to about 0.1˚C plus 0.4% of difference between the terminal temperature at calibration and at the time of ...
FRR Presentation
... A shelf of foam board 10 cm by 12.5 cm with a 6.25 cm by 5cm hole in the center will hold the BalloonSAT. A lidless box of dimensions 6.25 cm by 6.25 cm and 6.25 cm tall will house the batteries and heating element. The box will be sized to fit snuggly into the BalloonSAT shelf in order to keep all ...
... A shelf of foam board 10 cm by 12.5 cm with a 6.25 cm by 5cm hole in the center will hold the BalloonSAT. A lidless box of dimensions 6.25 cm by 6.25 cm and 6.25 cm tall will house the batteries and heating element. The box will be sized to fit snuggly into the BalloonSAT shelf in order to keep all ...
AN1660, Compound Coefficient Pressure Sensor PSPICE Models
... approach, that is usually used, is based upon the assumption that changes are small, and can be modeled with a linear approximation. Using temperature coefficient of resistance as (TCR) as an example, the linear expression takes the form: (2) R(Temp) = R25(1) TCR(Temp - 25)) Provided that the TCR in ...
... approach, that is usually used, is based upon the assumption that changes are small, and can be modeled with a linear approximation. Using temperature coefficient of resistance as (TCR) as an example, the linear expression takes the form: (2) R(Temp) = R25(1) TCR(Temp - 25)) Provided that the TCR in ...
345 - UVa Online Judge
... current flows through a resistor, some of it is converted to heat, thus “resisting”; the flow of the current. The extent to which it does this is indicated by a single positive numeric value, cleverly called the resistance of the resistor. By the way, the units of resistance are Ohms. Here’s what a ...
... current flows through a resistor, some of it is converted to heat, thus “resisting”; the flow of the current. The extent to which it does this is indicated by a single positive numeric value, cleverly called the resistance of the resistor. By the way, the units of resistance are Ohms. Here’s what a ...
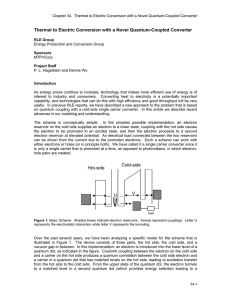
Thermal to Electric Conversion with a Novel Quantum-Coupled Converter
... of the image charge would constitute a surface current, and associated resistive loss as well. Such power dissipation, which could be estimated classically, would provide the rate at which power is dissipated in the hot side by the return current of the cold side converter. If one could develop an a ...
... of the image charge would constitute a surface current, and associated resistive loss as well. Such power dissipation, which could be estimated classically, would provide the rate at which power is dissipated in the hot side by the return current of the cold side converter. If one could develop an a ...
Slide 1
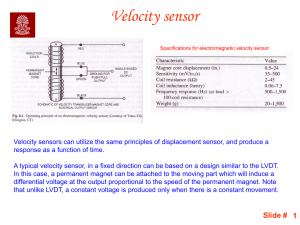
... Acceleration sensor (Accelerometer) CAPACITIVE • In accelerometer there is an inertial or dead mass which is displaced, with respect to the housing, when the there is acceleration • The sensor measures the mass displacement by various means, which is proportional to acceleration for small displacem ...
... Acceleration sensor (Accelerometer) CAPACITIVE • In accelerometer there is an inertial or dead mass which is displaced, with respect to the housing, when the there is acceleration • The sensor measures the mass displacement by various means, which is proportional to acceleration for small displacem ...
Lumped element model
The lumped element model (also called lumped parameter model, or lumped component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems into a topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc.Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the state space of the system to a finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) with a finite number of parameters.