Chapter Three
... FUNCTION. For the first quartile, select Quartile, then insert the cell range like (A1:A15) which is called array in this menu, and then insert the number 1. For the median or second quartile, select Quartile, then insert the array, and then type the number 2. For the third quartile, select Quartile ...
... FUNCTION. For the first quartile, select Quartile, then insert the cell range like (A1:A15) which is called array in this menu, and then insert the number 1. For the median or second quartile, select Quartile, then insert the array, and then type the number 2. For the third quartile, select Quartile ...
1. Under what conditions is the use of the mean preferred? a) for
... 66. The sample should be: a) expressive b) representative c) large d) small e) no requirements --------------------------------------------------------------------67. Designing the sample calls for: a) to determine study units b) to determine number of researchers c) to determine sample size d) sam ...
... 66. The sample should be: a) expressive b) representative c) large d) small e) no requirements --------------------------------------------------------------------67. Designing the sample calls for: a) to determine study units b) to determine number of researchers c) to determine sample size d) sam ...
Topic - University of Oklahoma
... “English” alphabet (such as s for sample standard deviation). However, this is not always true. Some parameters are indicated with “English” characters (such as p for population proportion). Some statistics are indicated with things other than simple “English” characters (such as y for sample mean o ...
... “English” alphabet (such as s for sample standard deviation). However, this is not always true. Some parameters are indicated with “English” characters (such as p for population proportion). Some statistics are indicated with things other than simple “English” characters (such as y for sample mean o ...
Preview Sample 3
... Although the claim is literally true, the data show a wide range of returns for the 29 mutual funds selected by End Run investors. Although 18 funds had positive returns, 11 had negative returns for the five year period. Of the funds having negative returns, many had large losses, with 27.59% having ...
... Although the claim is literally true, the data show a wide range of returns for the 29 mutual funds selected by End Run investors. Although 18 funds had positive returns, 11 had negative returns for the five year period. Of the funds having negative returns, many had large losses, with 27.59% having ...
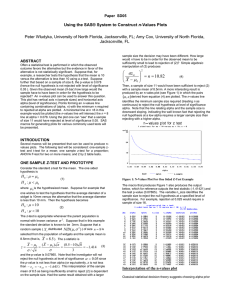
Using the SAS System to Construct n-Values Plots
... plot is based on the null-distribution (whereas the latter is based on various non-null distributions). The n-values plot quantifies statements such as: “The results were nearly significant” by supplying a sample size at which significance would, ceteris paribus, lead to rejection. This approach is ...
... plot is based on the null-distribution (whereas the latter is based on various non-null distributions). The n-values plot quantifies statements such as: “The results were nearly significant” by supplying a sample size at which significance would, ceteris paribus, lead to rejection. This approach is ...
Document
... bands” in previous graphs) • One-sided tests useful if only interested in one limit • Use z1-a or t1-a;n instead of z1-a/2 or t1a/2;n in formulas CS 239, Spring 2007 ...
... bands” in previous graphs) • One-sided tests useful if only interested in one limit • Use z1-a or t1-a;n instead of z1-a/2 or t1a/2;n in formulas CS 239, Spring 2007 ...
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing One-sample test for
... =, ≥, or ≤ notation in the mathematical statement of the hypothesis. A theory about the values of one (or more) population parameter(s). The theory generally represents the status quo, which we accept until it is proven false. Example: H0: µ = 98.6F (average body temperature is 98.6) • Alternative h ...
... =, ≥, or ≤ notation in the mathematical statement of the hypothesis. A theory about the values of one (or more) population parameter(s). The theory generally represents the status quo, which we accept until it is proven false. Example: H0: µ = 98.6F (average body temperature is 98.6) • Alternative h ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.