QUANTITATIVE VERSUS QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
... Population: all observations of a particular variable. Example: size of every U.S. city…observe/measure ALL cities for a population. Sample: subset of the population. Example: selecting 50 cities from all US cities. Frequency Distribution, Sampling Distribution, Normal Curve FD is the distribution o ...
... Population: all observations of a particular variable. Example: size of every U.S. city…observe/measure ALL cities for a population. Sample: subset of the population. Example: selecting 50 cities from all US cities. Frequency Distribution, Sampling Distribution, Normal Curve FD is the distribution o ...
Document
... Bayesian approaches and Markov processes One of the most useful numerical techniques for Bayesian analysis involves the use of Markov Chains in an appropriate way to estimate the complex integrals that arise. So we do a quick summary of Markov chains, say something about their ergodic properties, a ...
... Bayesian approaches and Markov processes One of the most useful numerical techniques for Bayesian analysis involves the use of Markov Chains in an appropriate way to estimate the complex integrals that arise. So we do a quick summary of Markov chains, say something about their ergodic properties, a ...
Practice final Math 12 Fall 2013 Please show all work. Are low
... 5. A sample of 146 university students who recently moved off-campus were polled to see whether they agree that off-campus living is preferable to on-campus living. In addition, each was asked how many people live in their current off-campus residence. The results are summarized in the following con ...
... 5. A sample of 146 university students who recently moved off-campus were polled to see whether they agree that off-campus living is preferable to on-campus living. In addition, each was asked how many people live in their current off-campus residence. The results are summarized in the following con ...
Chapter 10 Section 1 (Confidence Intervals)
... unknown or distinctly nonnormal? If n 25, the Central Limit Theorem applies so you may use Normal distribution tools. Otherwise, you need other tools. ...
... unknown or distinctly nonnormal? If n 25, the Central Limit Theorem applies so you may use Normal distribution tools. Otherwise, you need other tools. ...
Homework #7
... abuse by Philadelphia police officers in their treatment of minorities. One study conducted by the American Civil Liberties Union(ACLU), analyzed whether African American drivers were more likely than others in the population to be targeted by police for traffic stops. In this study, they had 262 po ...
... abuse by Philadelphia police officers in their treatment of minorities. One study conducted by the American Civil Liberties Union(ACLU), analyzed whether African American drivers were more likely than others in the population to be targeted by police for traffic stops. In this study, they had 262 po ...
Measures of Spread
... 4. Variance: measure of dispersion that is found by averaging the squares of the deviation (distance from the mean) of each piece of data Calculating Variance: ...
... 4. Variance: measure of dispersion that is found by averaging the squares of the deviation (distance from the mean) of each piece of data Calculating Variance: ...
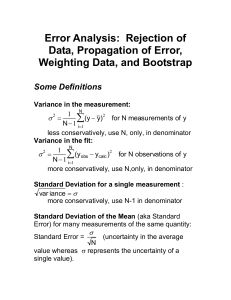
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.