Statistical Inference with SCILAB
... A population constitutes the collection of all conceivable results of a random process, while a sample is a sub-set of a population. Typically, it is very difficult or impractical to evaluate the entire population for a given parameter. Therefore, we select one or more samples out of the population ...
... A population constitutes the collection of all conceivable results of a random process, while a sample is a sub-set of a population. Typically, it is very difficult or impractical to evaluate the entire population for a given parameter. Therefore, we select one or more samples out of the population ...
Title of slide
... Summarize pdf of parameter of interest with, e.g., mean, median, standard deviation, etc. Although numerical values of answer here same as in frequentist case, interpretation is different (sometimes unimportant?) G. Cowan ...
... Summarize pdf of parameter of interest with, e.g., mean, median, standard deviation, etc. Although numerical values of answer here same as in frequentist case, interpretation is different (sometimes unimportant?) G. Cowan ...
local copy
... So, I bet (either by this point in the day or out of sheer frustration) that you want to know what to do with the command prompt (i.e., >). The first thing that you could do is write a comment - something that helps you understand the code but which is not parsed by the machine. Comments always foll ...
... So, I bet (either by this point in the day or out of sheer frustration) that you want to know what to do with the command prompt (i.e., >). The first thing that you could do is write a comment - something that helps you understand the code but which is not parsed by the machine. Comments always foll ...
homework4_2010_key
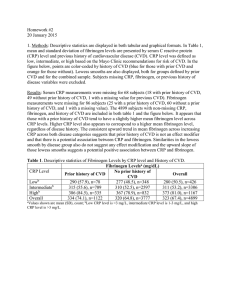
... /*Question 2: Descriptives for Ran and didn't run*/ title "Descriptives for those who ran and didn't run"; proc means data=b510.allgroups; class ran; format ran ranfmt.; run; /*Question 3: Side-by-side boxplots for HR1 and HR2*/ title "Boxplots for those who ran and didn't run"; proc sgplot data=b51 ...
... /*Question 2: Descriptives for Ran and didn't run*/ title "Descriptives for those who ran and didn't run"; proc means data=b510.allgroups; class ran; format ran ranfmt.; run; /*Question 3: Side-by-side boxplots for HR1 and HR2*/ title "Boxplots for those who ran and didn't run"; proc sgplot data=b51 ...
Download PDF
... from forty years ago might have little bearing on returns this year, so parameters are not likely to be stationary over long periods of time. However, using only very recent data to estimate model parameters exposes the model to estimation errors. Even if the process that generates returns is statio ...
... from forty years ago might have little bearing on returns this year, so parameters are not likely to be stationary over long periods of time. However, using only very recent data to estimate model parameters exposes the model to estimation errors. Even if the process that generates returns is statio ...
Solutions and Applications Manual
... The coefficient vector is b = (X′X)-1X′y = (-.0727985, .235622, -.00364866)′. The total sum of squares is y′y = .63652, so we can obtain e′e = y′y - b′X′y. X′y is given in the top row of the matrix. Making the substitution, we obtain e′e = .63652 - .63291 = .00361. To compute R2, we require Σi (xi - ...
... The coefficient vector is b = (X′X)-1X′y = (-.0727985, .235622, -.00364866)′. The total sum of squares is y′y = .63652, so we can obtain e′e = y′y - b′X′y. X′y is given in the top row of the matrix. Making the substitution, we obtain e′e = .63652 - .63291 = .00361. To compute R2, we require Σi (xi - ...
Statistics Using R with Biological Examples
... that it completely free, making it wonderfully accessible to students and researchers. The structure of the R software is a base program, providing basic program functionality, which can be added onto with smaller specialized program modules called packages. One of the biggest growth areas in contri ...
... that it completely free, making it wonderfully accessible to students and researchers. The structure of the R software is a base program, providing basic program functionality, which can be added onto with smaller specialized program modules called packages. One of the biggest growth areas in contri ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.