Homework set 5
... The empirical quantile function. Just as we can produce in R an approximate density function for the given data, we can also obtain the quantiles using the R-function quantile(). Here is an example, where we obtain the first quartile (or 25th percentile) of data vector x: ...
... The empirical quantile function. Just as we can produce in R an approximate density function for the given data, we can also obtain the quantiles using the R-function quantile(). Here is an example, where we obtain the first quartile (or 25th percentile) of data vector x: ...
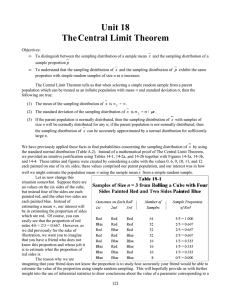
Unit 18 TheCentral Limit Theorem
... from n = 3 rolls of the cube. As we have emphasized previously, a parameter such as λ is always a fixed, single value that we are trying to estimate, because we do not know its value, and a statistic such as p is a random value which depends on the sample we happen to have selected. Let us now retur ...
... from n = 3 rolls of the cube. As we have emphasized previously, a parameter such as λ is always a fixed, single value that we are trying to estimate, because we do not know its value, and a statistic such as p is a random value which depends on the sample we happen to have selected. Let us now retur ...
ppt session 9
... stationary, they tend to produce regressions with high R-squared statistics and low DW statistics, indicating high levels of autocorrelation. This is caused by the drift in the variables often being related, but not directly accounted for in the regression, hence the omitted variable effect. ...
... stationary, they tend to produce regressions with high R-squared statistics and low DW statistics, indicating high levels of autocorrelation. This is caused by the drift in the variables often being related, but not directly accounted for in the regression, hence the omitted variable effect. ...
Steps in Hypothesis Testing
... that the groups have different means. If you don’t reject H0, assume the means are equal. If you find that there is a difference between groups using ANOVA, find the right Q in (table = , column =c and row n-c) and use the TUKEY-KRAMER in PHSTAT to find which groups are different. ...
... that the groups have different means. If you don’t reject H0, assume the means are equal. If you find that there is a difference between groups using ANOVA, find the right Q in (table = , column =c and row n-c) and use the TUKEY-KRAMER in PHSTAT to find which groups are different. ...
Solutions for Exam 2 Study Guide
... Let R be the continuous random variable giving the error in a geologist's estimate for the value of a lease. Experience allows us to assume that R is normal, with R = 0 and R = 10 million dollars. Suppose that the 15 companies form 3 bidding rings of equal sizes. Let M be the random variable givin ...
... Let R be the continuous random variable giving the error in a geologist's estimate for the value of a lease. Experience allows us to assume that R is normal, with R = 0 and R = 10 million dollars. Suppose that the 15 companies form 3 bidding rings of equal sizes. Let M be the random variable givin ...
The Null Hypothesis
... – relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about population characteristics that are inferred from observations made with a sample – asserts that observed differences or relationships merely result from chance errors inherent in the sampling process If the researcher rejects the n ...
... – relates to a statistical method of interpreting conclusions about population characteristics that are inferred from observations made with a sample – asserts that observed differences or relationships merely result from chance errors inherent in the sampling process If the researcher rejects the n ...
descriptive methods for categorical and numeric variables
... category. It is called a 3 X 3 table because there are 3 rows and 3 columns in the table corresponding to the three different levels of taste and type respectively. The second number in each “cell” of the table is the Row % which gives the percent of hotdogs in each taste category within type. The T ...
... category. It is called a 3 X 3 table because there are 3 rows and 3 columns in the table corresponding to the three different levels of taste and type respectively. The second number in each “cell” of the table is the Row % which gives the percent of hotdogs in each taste category within type. The T ...
What`s the Point (Estimate)?
... “What will happen” is the same as the first die, equal chances of 1 through 6 The expected has equally likely chances of being 2.67, 3.50, or 4.33 If you set your reserve at the “average” both have the same average, 3.5, the true average is within 0.83 of this amount with 100% confidence There is a ...
... “What will happen” is the same as the first die, equal chances of 1 through 6 The expected has equally likely chances of being 2.67, 3.50, or 4.33 If you set your reserve at the “average” both have the same average, 3.5, the true average is within 0.83 of this amount with 100% confidence There is a ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.