1. Pre-Lab Introduction
... Make sure before you apply an input signal to a circuit, all connections are correct, and no shorted wires exist. Do not short the function generator signal and ground connections together Do not touch the circuit wiring while power is applied to it Ensure you connect the correct terminal of the tra ...
... Make sure before you apply an input signal to a circuit, all connections are correct, and no shorted wires exist. Do not short the function generator signal and ground connections together Do not touch the circuit wiring while power is applied to it Ensure you connect the correct terminal of the tra ...
To read a diagram, we must understand a circuit. Here is Dictionary
... The open button completes the circuit but it does not have to be held for the unit to keep going open. Also remember that when the start switch in the motor drops out or opens, the IR relay looses power. What keeps the unit running open is a “latching circuit.” This is done using the 13 and 14 NO c ...
... The open button completes the circuit but it does not have to be held for the unit to keep going open. Also remember that when the start switch in the motor drops out or opens, the IR relay looses power. What keeps the unit running open is a “latching circuit.” This is done using the 13 and 14 NO c ...
D N IAGNOSTIC EWS
... CT’s have an accuracy rating. CT’s used for metering are far more accurate (for example 0.3%) than CT’s used for protection (for example 2.5%). A metering CT need only maintain its accuracy in the range of 10% to 125% of rated nominal current. However, the protection must maintain its accuracy for a ...
... CT’s have an accuracy rating. CT’s used for metering are far more accurate (for example 0.3%) than CT’s used for protection (for example 2.5%). A metering CT need only maintain its accuracy in the range of 10% to 125% of rated nominal current. However, the protection must maintain its accuracy for a ...
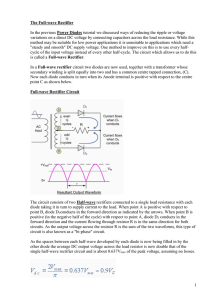
The Full-wave Rectifier
... given load and a smaller reservoir or smoothing capacitor than an equivalent half-wave rectifier. Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice that of the AC supply frequency (100Hz) where for the half-wave rectifier it is exactly equal to the supply frequency (50Hz). The amou ...
... given load and a smaller reservoir or smoothing capacitor than an equivalent half-wave rectifier. Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice that of the AC supply frequency (100Hz) where for the half-wave rectifier it is exactly equal to the supply frequency (50Hz). The amou ...
Voltage Sag Ride Through Mitigation
... contactors and relays are readily available. A DC contactor or relay is stronger because the flux is constant. A rectifier is required to change AC to DC. A small storage capacitor could be added to DC contactor to extend ride-through energy. Disadvantage of DC is increased arcing due to lack of zer ...
... contactors and relays are readily available. A DC contactor or relay is stronger because the flux is constant. A rectifier is required to change AC to DC. A small storage capacitor could be added to DC contactor to extend ride-through energy. Disadvantage of DC is increased arcing due to lack of zer ...
Generadores Indar
... even under the most adverse conditions. As a result of this process of impregnation, the magnetic package, the coils, the wedges, the fastenings and the supports of the head make up a compact unit that is capable of supporting all the mechanical and electrical stresses the machine can be subjected t ...
... even under the most adverse conditions. As a result of this process of impregnation, the magnetic package, the coils, the wedges, the fastenings and the supports of the head make up a compact unit that is capable of supporting all the mechanical and electrical stresses the machine can be subjected t ...
New or Revised Definitions #5 - pes-psrc
... (usually “on” - “off” power line carrier) is used to block tripping at the remote terminal for external faults. Tripping is accomplished by forward overreaching elements in the absence of a blocking signal from the remote terminal. See: directional comparison protection. Directional comparison unblo ...
... (usually “on” - “off” power line carrier) is used to block tripping at the remote terminal for external faults. Tripping is accomplished by forward overreaching elements in the absence of a blocking signal from the remote terminal. See: directional comparison protection. Directional comparison unblo ...
Lecture 9 - PIV, Filters and Multiple Diodes
... The turns ratio of the primary to each secondary winding is The PIV of each diode: 2vs (peak) - V = 2(9.6) - 0.6 = 19.2 - 0.6 = 18.6 V ...
... The turns ratio of the primary to each secondary winding is The PIV of each diode: 2vs (peak) - V = 2(9.6) - 0.6 = 19.2 - 0.6 = 18.6 V ...
experiment 1 - UniMAP Portal
... Substations are integral parts of a power system and form important link between the generating stations, transmission systems, distribution systems and the load points such as Figure 1. The substation’s function is to support the system, providing points of delivery in the transmission system. Subs ...
... Substations are integral parts of a power system and form important link between the generating stations, transmission systems, distribution systems and the load points such as Figure 1. The substation’s function is to support the system, providing points of delivery in the transmission system. Subs ...
III. UPQC - Academic Science,International Journal of Computer
... The healthcare environment comprises of various combination of sensitive electronic loads and other commercial loads. Hence maintaining quality power is essential and critical. Power quality is the term used for overall voltage quality, current quality and nature of output waveform which directly or ...
... The healthcare environment comprises of various combination of sensitive electronic loads and other commercial loads. Hence maintaining quality power is essential and critical. Power quality is the term used for overall voltage quality, current quality and nature of output waveform which directly or ...
Comprehensive Study of Forward and Fly Back Converter for
... discussion also leads to conclude that the switch voltage stress of the proposed converter is somewhat higher than that of the conventional one due to the balanced capacitor voltage Vcb. This also helps in improvement in individual performance of converter. Since the proposed converter merges the fo ...
... discussion also leads to conclude that the switch voltage stress of the proposed converter is somewhat higher than that of the conventional one due to the balanced capacitor voltage Vcb. This also helps in improvement in individual performance of converter. Since the proposed converter merges the fo ...
Distributed generation and voltage changes in a distribution network
... and reactive power output. In this case, the impact of the DG is brought down to decreasing of the total power load at the connection point. The node at which the DG is connected can be represented as a PQ node, whereas the DG can be modelled as a negative power load. 2) The DG injects active power ...
... and reactive power output. In this case, the impact of the DG is brought down to decreasing of the total power load at the connection point. The node at which the DG is connected can be represented as a PQ node, whereas the DG can be modelled as a negative power load. 2) The DG injects active power ...
Recommendation 6A
... The oil conservator shall be positioned as shown in Appendix B2. Its capacity shall correspond to at least 10% of the oil volume to which it is connected. The capacity of the sump shall be 5…10% of the oil conservator volume. The sump shall be provided with a top cover and drainage system. In transf ...
... The oil conservator shall be positioned as shown in Appendix B2. Its capacity shall correspond to at least 10% of the oil volume to which it is connected. The capacity of the sump shall be 5…10% of the oil conservator volume. The sump shall be provided with a top cover and drainage system. In transf ...
Transformer

A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Commonly, transformers are used to increase or decrease the voltages of alternating current in electric power applications.A varying current in the transformer's primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer core and a varying magnetic field impinging on the transformer's secondary winding. This varying magnetic field at the secondary winding induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in the secondary winding. Making use of Faraday's Law in conjunction with high magnetic permeability core properties, transformers can thus be designed to efficiently change AC voltages from one voltage level to another within power networks.Since the invention of the first constant potential transformer in 1885, transformers have become essential for the transmission, distribution, and utilization of alternating current electrical energy. A wide range of transformer designs are encountered in electronic and electric power applications. Transformers range in size from RF transformers less than a cubic centimeter in volume to units interconnecting the power grid weighing hundreds of tons.

![Dynamic VAR`s [D-VAR]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008161131_1-082e6e1fddaf6a197897b251ba053ae1-300x300.png)