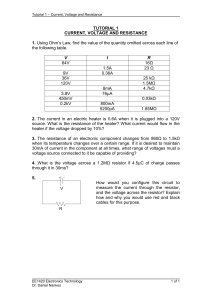
Tutorial 1
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
Exercise 1:
... Exercise 1: Ohm’s Law Begin by reading the material on measuring voltage prepared by Prof E. J. Mastascusa at Bucknell University. Next create the following circuit on your breadboard: ...
... Exercise 1: Ohm’s Law Begin by reading the material on measuring voltage prepared by Prof E. J. Mastascusa at Bucknell University. Next create the following circuit on your breadboard: ...
Series Circuit Lab
... 4. What is the relationship between the voltage drop across the battery and the voltage drops across the resistors? Calculate the theoretical reading that A1, A2, A3, and A4 will read. ...
... 4. What is the relationship between the voltage drop across the battery and the voltage drops across the resistors? Calculate the theoretical reading that A1, A2, A3, and A4 will read. ...
Sample Final Draft. - Information Services and Technology
... is an electrical measuring instrument. We can measure current, voltage and resistor from these multi-meters. There are two kind of multi-meter. First of all an Analog Multi-meter invented. When it invented, it was very huge metal Box. It also got effected easily from its surrounding magnetic fields. ...
... is an electrical measuring instrument. We can measure current, voltage and resistor from these multi-meters. There are two kind of multi-meter. First of all an Analog Multi-meter invented. When it invented, it was very huge metal Box. It also got effected easily from its surrounding magnetic fields. ...
LEP 5.3.04 Band gap of germanium
... On the back of the board is the heating coil, supplied by the alternating voltage output of the power unit. It is recommended that the test piece be warmed up slowly for the measurements, applying firstly 2 V, then 4 V and finally 6 V. The maximum permissible temperature of 175°C must not be exceede ...
... On the back of the board is the heating coil, supplied by the alternating voltage output of the power unit. It is recommended that the test piece be warmed up slowly for the measurements, applying firstly 2 V, then 4 V and finally 6 V. The maximum permissible temperature of 175°C must not be exceede ...
Physics 517/617 Experiment 1 Instrumentation and Resistor Circuits
... 2) Verify Ohm’s law by measuring and then plotting voltage vs. current for a resistor. Fit your graph(s) to extract the measured resistance. Use a resistor of your choice. Repeat the measurement with a resistor of a much higher value (e.g. 10-100X) than your previous choice. Use a DC power supply fo ...
... 2) Verify Ohm’s law by measuring and then plotting voltage vs. current for a resistor. Fit your graph(s) to extract the measured resistance. Use a resistor of your choice. Repeat the measurement with a resistor of a much higher value (e.g. 10-100X) than your previous choice. Use a DC power supply fo ...
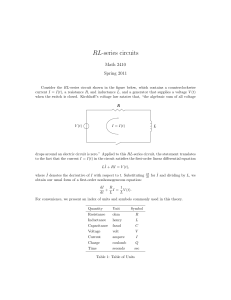
RL-series circuits
... For convenience, we present an index of units and symbols commonly used in this theory. Quantity ...
... For convenience, we present an index of units and symbols commonly used in this theory. Quantity ...
ohms_law
... and the c__________ flowing through the resistor on the a__________ and we record them in the table (next page). For each reading of these two variables we can work out the value of the resistance by using the formula (Ohm’s Law): Resistance (Ohms) = _________________ ...
... and the c__________ flowing through the resistor on the a__________ and we record them in the table (next page). For each reading of these two variables we can work out the value of the resistance by using the formula (Ohm’s Law): Resistance (Ohms) = _________________ ...
AC Voltage (V~) #61-310 Digital Multimeter Instruction Manual
... 23°C±5°C (73.4°F ± 9°F), less than 75% relative humidity. Temperature Coefficient: 0.1 times the applicable accuracy specification from 32°F to 64°F and 82°F to 122°F (0°C to 18°C ; 28°C to 50°C). ...
... 23°C±5°C (73.4°F ± 9°F), less than 75% relative humidity. Temperature Coefficient: 0.1 times the applicable accuracy specification from 32°F to 64°F and 82°F to 122°F (0°C to 18°C ; 28°C to 50°C). ...
Introduction to Photovoltaics Powerpoint
... Electrical Current – how many electrons Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
... Electrical Current – how many electrons Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
CHABOT COLLEGE
... The instructor will check out a multimeter to your team; return it as soon as you finish. Answer all questions shown in italic! Background: A multimeter is a powerful electrical testing tool that can measure resistance levels open/closed circuits (continuity) voltage levels (both AC & DC) The ...
... The instructor will check out a multimeter to your team; return it as soon as you finish. Answer all questions shown in italic! Background: A multimeter is a powerful electrical testing tool that can measure resistance levels open/closed circuits (continuity) voltage levels (both AC & DC) The ...
Ohm`s Law - Blackboard
... Ohm’s Law V= Voltage (V) I = Current in amps (A) R = Resistance in ohm’s (Ω) For voltage use V= I x R ...
... Ohm’s Law V= Voltage (V) I = Current in amps (A) R = Resistance in ohm’s (Ω) For voltage use V= I x R ...
Resistance - UniMAP Portal
... Measurement • The three basic parameters that one may wish to measure in a circuit are voltage ,V, current, I, and resistance, R. • The corresponding meters that can measures these parameters are the voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter respectively. • It is common these days to have a single meter tha ...
... Measurement • The three basic parameters that one may wish to measure in a circuit are voltage ,V, current, I, and resistance, R. • The corresponding meters that can measures these parameters are the voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter respectively. • It is common these days to have a single meter tha ...
Portable Appliance Testing Course Pre-Study Revision
... measurement units. i.e.… voltage (V) measured in volts (V), current (I) measured in Amperes (or amps for short) (A), resistance (R) measured in ohm’s (), power (P) measured in watts (W) The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units ...
... measurement units. i.e.… voltage (V) measured in volts (V), current (I) measured in Amperes (or amps for short) (A), resistance (R) measured in ohm’s (), power (P) measured in watts (W) The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units ...
Electrical Indicating Devices
... A, with an ratings as little as 50µ (internal) wire resistance of less than 1000 Ώ. This makes for a voltmeter with a full-scale rating of ...
... A, with an ratings as little as 50µ (internal) wire resistance of less than 1000 Ώ. This makes for a voltmeter with a full-scale rating of ...
Physics 1.3 - Resistance
... Calculate the resistance of a 12 Volt car stereo that carries a current of 4 A. ...
... Calculate the resistance of a 12 Volt car stereo that carries a current of 4 A. ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.