9 electricity test - circuits
... a) Place four switches in the circuit so each switch only controls one light bulb. Label each switch with the letter of the bulb it controls. b) Insert a switch that will turn off only three bulbs. Label it E c) Insert a switch that will turn off all the bulbs. Label it F ...
... a) Place four switches in the circuit so each switch only controls one light bulb. Label each switch with the letter of the bulb it controls. b) Insert a switch that will turn off only three bulbs. Label it E c) Insert a switch that will turn off all the bulbs. Label it F ...
electricity - chapter 1 quiz
... 12. A thermocouple produces electrical energy from heat energy. 13. A photocell produces electrical energy from light energy. 14. In an electrochemical cell, the difference in charges between the positive and negative terminals is called the potential – difference. 15. A circuit is a complete path f ...
... 12. A thermocouple produces electrical energy from heat energy. 13. A photocell produces electrical energy from light energy. 14. In an electrochemical cell, the difference in charges between the positive and negative terminals is called the potential – difference. 15. A circuit is a complete path f ...
LA 35-NP
... In order to avoid over-heating, it is necessary that the recommended primary connections be followed (see table page 2). Pollution class 2 Measurement carried out after 15 mn functioning The result of the coercive field of the magnetic circuit With a di/dt of 100 A/µs. ...
... In order to avoid over-heating, it is necessary that the recommended primary connections be followed (see table page 2). Pollution class 2 Measurement carried out after 15 mn functioning The result of the coercive field of the magnetic circuit With a di/dt of 100 A/µs. ...
Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculation
... Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculations Introduction Regardless of circuit complexity, circuit designers as well as users need to be able to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experienc ...
... Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculations Introduction Regardless of circuit complexity, circuit designers as well as users need to be able to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experienc ...
Alternating Current * Learning Outcomes
... current with time. Use an oscilloscope to show a.c. Discuss the use of a.c. in the national grid. HL: Solve problems about peak and rms values of voltage and current. ...
... current with time. Use an oscilloscope to show a.c. Discuss the use of a.c. in the national grid. HL: Solve problems about peak and rms values of voltage and current. ...
Transformer Equivalent Circuit -- Lab Review Sheet
... The short circuit test gives R1, X1, R2 and X2. This test is performed by applying rated current to the high voltage side and shorting the low voltage side. The high voltage side corresponds to the low current side, applying the test current to the low current side is done for safety reasons. With t ...
... The short circuit test gives R1, X1, R2 and X2. This test is performed by applying rated current to the high voltage side and shorting the low voltage side. The high voltage side corresponds to the low current side, applying the test current to the low current side is done for safety reasons. With t ...
ACD-10 Pro and ACD-10 TRMS Pro Product Manual
... Inputs are made through the test leads terminals. Slide-switch on defaults at Ω. Press Diode test function. Normal forward SELECT button momentarily 2 times to select voltage drop (forward biased) for a good silicon diode is between 0.400V to 0.900V. A reading higher than that indicates a leaky diod ...
... Inputs are made through the test leads terminals. Slide-switch on defaults at Ω. Press Diode test function. Normal forward SELECT button momentarily 2 times to select voltage drop (forward biased) for a good silicon diode is between 0.400V to 0.900V. A reading higher than that indicates a leaky diod ...
Voltage - Madison County Schools
... Ohm concluded that conductors and most other devices have a constant resistance regardless of the applied voltage. ...
... Ohm concluded that conductors and most other devices have a constant resistance regardless of the applied voltage. ...
PHYS1120ExamIIReview.. - University of Colorado Boulder
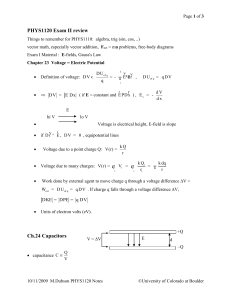
... Ohm's Law: V I R (where R = constant) lo V hi V ...
... Ohm's Law: V I R (where R = constant) lo V hi V ...
Electric Current and Electric Circuits
... VOLTAGE ( V ) Potential Difference - energy available to move electrons from objects of high potential to objects of low potential energy. measures amount of work electrons can do if they move between two points. unit: volt (V) 1 volt = 1Joule/1 coulomb High voltage greater potential to do work. Low ...
... VOLTAGE ( V ) Potential Difference - energy available to move electrons from objects of high potential to objects of low potential energy. measures amount of work electrons can do if they move between two points. unit: volt (V) 1 volt = 1Joule/1 coulomb High voltage greater potential to do work. Low ...
START-DET PMT-Base-H..
... A Fluke model 89 IV multimeter was used to measure the voltage drop across the 100 K ohm resistor (the meter’s voltage measurement resolution is 1 uV and accuracy of better than 0.1%). Two Bertan model 313A high voltage power supplies were used to supply positive and negative voltages to the board. ...
... A Fluke model 89 IV multimeter was used to measure the voltage drop across the 100 K ohm resistor (the meter’s voltage measurement resolution is 1 uV and accuracy of better than 0.1%). Two Bertan model 313A high voltage power supplies were used to supply positive and negative voltages to the board. ...
Lecture 11
... • An ammeter A is connected between points a and b in the circuit below, in which the four resistors are identical. The current through the ammeter is ...
... • An ammeter A is connected between points a and b in the circuit below, in which the four resistors are identical. The current through the ammeter is ...
1. introduction to analog electronics laboratory
... keep the power density under control. Since the source of power can be a battery, it is important to ensure long battery life through techniques such as clock gating, power gating, etc. The Power Management block is responsible for these functions. ...
... keep the power density under control. Since the source of power can be a battery, it is important to ensure long battery life through techniques such as clock gating, power gating, etc. The Power Management block is responsible for these functions. ...
Protective earth resistance meter RMO60E
... operation) test current for the preset test duration (equal or exceeding 1 minute) - gives an user possibility to easily check the protective bonding/grounding of the equipment. The full load voltage of 12 V assures that the measurement is executed properly and that the result obtained (pass fail cl ...
... operation) test current for the preset test duration (equal or exceeding 1 minute) - gives an user possibility to easily check the protective bonding/grounding of the equipment. The full load voltage of 12 V assures that the measurement is executed properly and that the result obtained (pass fail cl ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. For v3 and v4, we know the total voltage across the two is v4 + v3. From the given equation, we know that v4 = 2*v3 because their ratio is 2:1. Set our equation equal to 6 V. So v3 should be 6/3 = 2 V. This means that v4 = vs – v3 = 6-2 = 4 ...
... This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. For v3 and v4, we know the total voltage across the two is v4 + v3. From the given equation, we know that v4 = 2*v3 because their ratio is 2:1. Set our equation equal to 6 V. So v3 should be 6/3 = 2 V. This means that v4 = vs – v3 = 6-2 = 4 ...
I - אתר מורי הפיזיקה
... Learning Goals: Students will be able to Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits Build circuits from schematic drawings Use voltmeters and ammeters to take readings in circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements in circuits. ...
... Learning Goals: Students will be able to Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits Build circuits from schematic drawings Use voltmeters and ammeters to take readings in circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements in circuits. ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.