Circuitry, meters, and Ohm`s law
... electrode surfaces in a battery, electrons are deposited at one electrode to flow to the other electrode through a wire. Ohm's law states that the voltage difference V between two points in a conducting medium is proportional to the current I between those points. That is, ...
... electrode surfaces in a battery, electrons are deposited at one electrode to flow to the other electrode through a wire. Ohm's law states that the voltage difference V between two points in a conducting medium is proportional to the current I between those points. That is, ...
Intro to Electric Circuits
... Current Current is the movement of electrical charge - the flow of electrons through the electronic circuit. In our analogy, current would be the flow of water moving through the tube (wire). ...
... Current Current is the movement of electrical charge - the flow of electrons through the electronic circuit. In our analogy, current would be the flow of water moving through the tube (wire). ...
Elecrtonics_L1
... b) What is the circuit arrangement below called? If A and C are connected across a 6 V battery, calculate the voltage at B if the variable resistor is set to (i) 5 kΩ (ii) 40 k Ω A 10 k ...
... b) What is the circuit arrangement below called? If A and C are connected across a 6 V battery, calculate the voltage at B if the variable resistor is set to (i) 5 kΩ (ii) 40 k Ω A 10 k ...
Testing, Measurement, and Troubleshooting
... Precise resistor inserted in current path Typical values 0.1 to 1 Voltage drop across shunt measured Coil of wire wrapped around conductor Measure induced voltage Resistance Resistance measured several ways Very accurately using bridge type circuits Apply known current to resistor Measure voltage ...
... Precise resistor inserted in current path Typical values 0.1 to 1 Voltage drop across shunt measured Coil of wire wrapped around conductor Measure induced voltage Resistance Resistance measured several ways Very accurately using bridge type circuits Apply known current to resistor Measure voltage ...
Lecture 14
... Current is analogous to flow, and is measure in amperes or amps for short. Direct current (DC) is a constant voltage, e.g. a single C or D battery produces 1.5 volts. Alternating Current (AC) is a voltage that reverse rapidly, at 60 cycles/second in the US. An electrical outlet gives 110 volts ...
... Current is analogous to flow, and is measure in amperes or amps for short. Direct current (DC) is a constant voltage, e.g. a single C or D battery produces 1.5 volts. Alternating Current (AC) is a voltage that reverse rapidly, at 60 cycles/second in the US. An electrical outlet gives 110 volts ...
Testing, Measurement, and Troubleshooting
... Precise resistor inserted in current path Typical values 0.1 to 1 Voltage drop across shunt measured Coil of wire wrapped around conductor Measure induced voltage Resistance Resistance measured several ways Very accurately using bridge type circuits Apply known current to resistor Measure voltage ...
... Precise resistor inserted in current path Typical values 0.1 to 1 Voltage drop across shunt measured Coil of wire wrapped around conductor Measure induced voltage Resistance Resistance measured several ways Very accurately using bridge type circuits Apply known current to resistor Measure voltage ...
Tutorial 1
... 4. An average value of a set of voltage measurement is 30.15V. Calculate the precision of the measurement if one of the measurement readings is 29.9V. 5. A voltmeter has an accuracy of 98% in full-scale measurement readings. a. If the voltmeter gives measurement reading of 175V at range of 300V, cal ...
... 4. An average value of a set of voltage measurement is 30.15V. Calculate the precision of the measurement if one of the measurement readings is 29.9V. 5. A voltmeter has an accuracy of 98% in full-scale measurement readings. a. If the voltmeter gives measurement reading of 175V at range of 300V, cal ...
Lec #10 ppt
... Why is Single-Frequency Excitation Important? • Some circuits are driven by a single-frequency sinusoidal source. • Some circuits are driven by sinusoidal sources whose frequency changes slowly over time. • You can express any periodic electrical signal as a sum of single-frequency sinusoids – so y ...
... Why is Single-Frequency Excitation Important? • Some circuits are driven by a single-frequency sinusoidal source. • Some circuits are driven by sinusoidal sources whose frequency changes slowly over time. • You can express any periodic electrical signal as a sum of single-frequency sinusoids – so y ...
Chapter 7 Review
... Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the components. Components connected in parallel are connected so the same voltage is applied to each component. In a series circuit, every device must function for the circuit to be complete a ...
... Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the components. Components connected in parallel are connected so the same voltage is applied to each component. In a series circuit, every device must function for the circuit to be complete a ...
Sleep Sound3
... Prototyping involved using strain gages attached to a mattress, pressure measurements and weight scales. The final prototype uses a variable inductance oscillator circuit in a strap. This will be attached to infant sleepwear. ...
... Prototyping involved using strain gages attached to a mattress, pressure measurements and weight scales. The final prototype uses a variable inductance oscillator circuit in a strap. This will be attached to infant sleepwear. ...
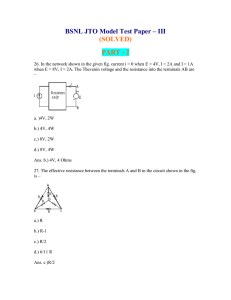
BSNL JTO Model Test Paper – III
... In an ideal transmission line with matched load, the voltage standing wave ratio and reflection coefficient are respectively a. ) 1 and 1 b ). infinity and 1 c ) infinity and 0 d. ) 1 and 0 When an electric charge of 100 coulombs is enclosed in sphere of radius 100 m then the electric displacement d ...
... In an ideal transmission line with matched load, the voltage standing wave ratio and reflection coefficient are respectively a. ) 1 and 1 b ). infinity and 1 c ) infinity and 0 d. ) 1 and 0 When an electric charge of 100 coulombs is enclosed in sphere of radius 100 m then the electric displacement d ...
MeasurementsG11ES
... The analog voltmeter measures voltage by deflecting a needle against a scale.The most accurate reading is taken from the range which gives the biggest deflection. A digital voltmeter displays the voltage value in digits. Voltage may also be measured using a digital multimeter (DMM) which is shown in ...
... The analog voltmeter measures voltage by deflecting a needle against a scale.The most accurate reading is taken from the range which gives the biggest deflection. A digital voltmeter displays the voltage value in digits. Voltage may also be measured using a digital multimeter (DMM) which is shown in ...
Ohms Law and Basic Circuit Theory
... Q1) On your worksheet sketch the circuit. Set the resistance to 140 ohms. Complete the table on your worksheet. As you increase the voltage the number of batteries will increase in 1.5-volt increments. Note hat the simulation shows current flow not electron flow. Current flows from positive to negat ...
... Q1) On your worksheet sketch the circuit. Set the resistance to 140 ohms. Complete the table on your worksheet. As you increase the voltage the number of batteries will increase in 1.5-volt increments. Note hat the simulation shows current flow not electron flow. Current flows from positive to negat ...
Multimeter
A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (Volt-Ohm meter or Volt-Ohm-milliammeter ), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter would include basic features such as the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter whose pointer moves over a scale calibrated for all the different measurements that can be made. Digital multimeters (DMM, DVOM) display the measured value in numerals, and may also display a bar of a length proportional to the quantity being measured. Digital multimeters are now far more common but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value. A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work, or a bench instrument which can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.Multimeters are available in a wide range of features and prices. Cheap multimeters can cost less than US$10, while laboratory-grade models with certified calibration can cost more than US$5,000.