StudyGuide-for-Oceans-2015-key
... 30. A large stream of moving water that flows through an ocean is known as a _Current_.In the 31. Surface currents are caused by _____Wind____. 32. Northern Hemisphere currents curve to the right because of the Coriolis Effect_ 33. A large powerful warm surface current in the Atlantic Ocean that aff ...
... 30. A large stream of moving water that flows through an ocean is known as a _Current_.In the 31. Surface currents are caused by _____Wind____. 32. Northern Hemisphere currents curve to the right because of the Coriolis Effect_ 33. A large powerful warm surface current in the Atlantic Ocean that aff ...
English abstract
... relatively warm and saline waters from the Indian Ocean, transported by the southeast flowing Agulhas Current. Water from the AL are the main component of the upper branch of the AMOC. Because it occupies such a crucial position in the scheme of oceanic currents, the Agulhas system is simultaneously ...
... relatively warm and saline waters from the Indian Ocean, transported by the southeast flowing Agulhas Current. Water from the AL are the main component of the upper branch of the AMOC. Because it occupies such a crucial position in the scheme of oceanic currents, the Agulhas system is simultaneously ...
6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items S6E3c.
... A. sea organisms consume the freshwater. B. the water becomes salty as it enters the ocean. C. water continuously evaporates back out of the ocean.* D. salty glacial water is also evaporating from the ice caps. ...
... A. sea organisms consume the freshwater. B. the water becomes salty as it enters the ocean. C. water continuously evaporates back out of the ocean.* D. salty glacial water is also evaporating from the ice caps. ...
Ocean 11 - Course World
... water bubbling up through fissures known as thermal vents. They occur where plates in the Earth's crust collide and grind. In these black ocean depths, some of the pinnacles resemble stalagmites in a cave while others look like dribble-sand castles on the beach. Ledges, or flanges, of the crusty, fe ...
... water bubbling up through fissures known as thermal vents. They occur where plates in the Earth's crust collide and grind. In these black ocean depths, some of the pinnacles resemble stalagmites in a cave while others look like dribble-sand castles on the beach. Ledges, or flanges, of the crusty, fe ...
Oceans 11 - Course World
... Most vents occur at points where the crust is much younger than a million years old. The water from the vents is relatively cool at 160 degrees. The structures are composed of carbonate minerals and silica. Iron and sulphur-based minerals form most seafloor hot springs deposits. Rocks in the rugged ...
... Most vents occur at points where the crust is much younger than a million years old. The water from the vents is relatively cool at 160 degrees. The structures are composed of carbonate minerals and silica. Iron and sulphur-based minerals form most seafloor hot springs deposits. Rocks in the rugged ...
Lesson 2.1 Continental Drift
... Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
... Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
File - Science by Shaw
... 10. What is the average temperature of the main thermocline? 11. The upward motion of ocean water is called. Currents: 12. What is the “Coriolis Effect”? 13. Wind is deflected to the ______in the Northern Hemisphere and to the ______in the Southern Hemisphere. 14. What is an Ekman spiral? 15. Which ...
... 10. What is the average temperature of the main thermocline? 11. The upward motion of ocean water is called. Currents: 12. What is the “Coriolis Effect”? 13. Wind is deflected to the ______in the Northern Hemisphere and to the ______in the Southern Hemisphere. 14. What is an Ekman spiral? 15. Which ...
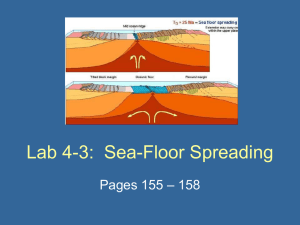
Lab 4-3: Sea-Floor Spreading
... – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
... – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
Drain the Ocean: Video Questions 1. Light can only penetrate a feet
... 2. This area is called the mid-___________ ____________ and runs all of the way around the globe. 3. The Earth’s crust is broken into ______________ plates. 4. Why is Iceland considered so special and exciting to scientists? ...
... 2. This area is called the mid-___________ ____________ and runs all of the way around the globe. 3. The Earth’s crust is broken into ______________ plates. 4. Why is Iceland considered so special and exciting to scientists? ...
Origin and fate of the North Atlantic Current at the Mid
... The NAC is the northward extension of the Gulf Stream and is part of the upper branch of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. The warm, salty water is further transported into the Nordic Seas via the Rockall Trough, into the Denmark Strait and, finally into the Labrador Sea, where it pla ...
... The NAC is the northward extension of the Gulf Stream and is part of the upper branch of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. The warm, salty water is further transported into the Nordic Seas via the Rockall Trough, into the Denmark Strait and, finally into the Labrador Sea, where it pla ...
Oceans Sonar Bathymetry Powerpoint
... a. abyssal plain - flat, featureless region similar to a desert; common in Atlantic and Indian Oceans, rare in the Pacific b. abyssal hill - occur where sediment is not thick enough to cover the underlying rock completely. Usually extinct volcanoes or small formations of rock once extruded in molten ...
... a. abyssal plain - flat, featureless region similar to a desert; common in Atlantic and Indian Oceans, rare in the Pacific b. abyssal hill - occur where sediment is not thick enough to cover the underlying rock completely. Usually extinct volcanoes or small formations of rock once extruded in molten ...
F M2502 PAPER – II EARTH SCIENCES
... Note : Attempt all the questions. Each question carries two (2) marks. ...
... Note : Attempt all the questions. Each question carries two (2) marks. ...
Salt water
... This drives deep ocean currents. They are important to marine animals living in the deep ocean as the retain the oxygen absorbed at the surface as well as the temperature and salinity. ...
... This drives deep ocean currents. They are important to marine animals living in the deep ocean as the retain the oxygen absorbed at the surface as well as the temperature and salinity. ...
Gr.8-Ch.2-Review-Sheet-2014
... 17. _____ has aided the further development of continental drainage systems as material is removed and deposited into the ocean basins. 18. _____ move changing the position of the continents. 19. _____ is a force of erosion in the development of continental drainage systems. 20. Water on earth came ...
... 17. _____ has aided the further development of continental drainage systems as material is removed and deposited into the ocean basins. 18. _____ move changing the position of the continents. 19. _____ is a force of erosion in the development of continental drainage systems. 20. Water on earth came ...
Bodies of Water Notes - Raleigh Charter High School
... i. Lies between Iceland and Norway and is separated from the Atlantic by the Faeroe-Iceland Ridge ii. Kept free of ice by the warm North Atlantic Drift the flows from Scotland Baltic Sea i. Shallow enclosed inland sea with little tide and branches out into Gulf of Bothnia and Gulf of Finland. ii. It ...
... i. Lies between Iceland and Norway and is separated from the Atlantic by the Faeroe-Iceland Ridge ii. Kept free of ice by the warm North Atlantic Drift the flows from Scotland Baltic Sea i. Shallow enclosed inland sea with little tide and branches out into Gulf of Bothnia and Gulf of Finland. ii. It ...
Sea-floor Spreading
... It was possible that molten magma from beneath the earth's crust could ooze up between the plates in the Great Global Rift. As this hot magma cooled in the ocean water, it would expand and push the plates on either side of it -- North and South America to the west and Eurasia and Africa to the east. ...
... It was possible that molten magma from beneath the earth's crust could ooze up between the plates in the Great Global Rift. As this hot magma cooled in the ocean water, it would expand and push the plates on either side of it -- North and South America to the west and Eurasia and Africa to the east. ...
Oceanography - saddlespace.org
... Ch. 17 & 19 1. Oceanography is the study of the world’s oceans. 2. The World Oceans 70% of the Earth’s Surface is covered by Oceans. There are 4 major oceans. Pacific, Atlantic, Indian and Arctic *Possible 5th ocean-Southern Ocean The average depth of the oceans is 4 times deeper than the average he ...
... Ch. 17 & 19 1. Oceanography is the study of the world’s oceans. 2. The World Oceans 70% of the Earth’s Surface is covered by Oceans. There are 4 major oceans. Pacific, Atlantic, Indian and Arctic *Possible 5th ocean-Southern Ocean The average depth of the oceans is 4 times deeper than the average he ...
geology
... 1 Billion Years Ago Excessive heat underneath the Earth’s crust caused the continental crust to split. As the plates moved apart, magma worked its way upward, forming new crust. The Iapetus Ocean was formed between the two plates, one of which contained the Adirondack Mountains that you see across t ...
... 1 Billion Years Ago Excessive heat underneath the Earth’s crust caused the continental crust to split. As the plates moved apart, magma worked its way upward, forming new crust. The Iapetus Ocean was formed between the two plates, one of which contained the Adirondack Mountains that you see across t ...
1 Billion Years Ago 450 Million Years Ago 400 Million Years Ago
... 1 Billion Years Ago Excessive heat underneath the Earth’s crust caused the continental crust to split. As the plates moved apart, magma worked its way upward, forming new crust. The Iapetus Ocean was formed between the two plates, one of which contained the Adirondack Mountains that you see across t ...
... 1 Billion Years Ago Excessive heat underneath the Earth’s crust caused the continental crust to split. As the plates moved apart, magma worked its way upward, forming new crust. The Iapetus Ocean was formed between the two plates, one of which contained the Adirondack Mountains that you see across t ...
draw a diagram of earth`s interior and label each
... OF LITHOSPHERIC PLATES AND WHERE DOES THIS OCCUR? DRAW A DIAGRAM DESCRIBING HOW THIS PROCESS WORKS CONVECTION OCCURS IN THE MANTLE WHEN COOL DENSE MATERIAL SINKS TO THE BOTTOM OF THE MANTLE NEAR THE CORE AND WARM LESS DENSE MATERIAL RISES TO THE TOP OF THE MANTLE TO HEAT EARTH’S SURFACE ...
... OF LITHOSPHERIC PLATES AND WHERE DOES THIS OCCUR? DRAW A DIAGRAM DESCRIBING HOW THIS PROCESS WORKS CONVECTION OCCURS IN THE MANTLE WHEN COOL DENSE MATERIAL SINKS TO THE BOTTOM OF THE MANTLE NEAR THE CORE AND WARM LESS DENSE MATERIAL RISES TO THE TOP OF THE MANTLE TO HEAT EARTH’S SURFACE ...
OCEANOGRAPHY MORE OCEANOGRAPHY
... seawater moves to a less dense area. Cold water moves to warm areas Water with salt is more dense. Evaporation or the formation of ice may cause the salinity of water to increase. Rainfall & melting of ice causes salinity of water to decrease. ...
... seawater moves to a less dense area. Cold water moves to warm areas Water with salt is more dense. Evaporation or the formation of ice may cause the salinity of water to increase. Rainfall & melting of ice causes salinity of water to decrease. ...
Chapter 4: geography and earth questions
... What is the leading factor in outgassing? (volcanic activity) What percent of the freshwater is in the polar ice caps? (69% or 2/3) What is the maximum density of sea water? (2C) Which is more dense: basalt or granite? (basalt) Which type of crust is characteristic of basalt? (oceanic) What process ...
... What is the leading factor in outgassing? (volcanic activity) What percent of the freshwater is in the polar ice caps? (69% or 2/3) What is the maximum density of sea water? (2C) Which is more dense: basalt or granite? (basalt) Which type of crust is characteristic of basalt? (oceanic) What process ...
Chapter 4: geography and earth questions
... What is the leading factor in outgassing? (volcanic activity) What percent of the freshwater is in the polar ice caps? (69% or 2/3) What is the maximum density of sea water? (2C) Which is more dense: basalt or granite? (basalt) Which type of crust is characteristic of basalt? (oceanic) What process ...
... What is the leading factor in outgassing? (volcanic activity) What percent of the freshwater is in the polar ice caps? (69% or 2/3) What is the maximum density of sea water? (2C) Which is more dense: basalt or granite? (basalt) Which type of crust is characteristic of basalt? (oceanic) What process ...