clash of beliefs and ideals chs. 9-11, gps 9, 10
... The Civil War is one of the key events that formed America’s national character. This unit examines the causes and effects of the conflict and change of the American Civil War. It also provides a rich field for examining the role of individuals, groups and institutions in shaping history. It will al ...
... The Civil War is one of the key events that formed America’s national character. This unit examines the causes and effects of the conflict and change of the American Civil War. It also provides a rich field for examining the role of individuals, groups and institutions in shaping history. It will al ...
Civil War PowerPoint
... • Leader of the Union Army. • General Lee surrendered to him at the Appomattox Court House in 1865 to end the Civil War. • After the Civil War, he was elected the 18th President of the United States. ...
... • Leader of the Union Army. • General Lee surrendered to him at the Appomattox Court House in 1865 to end the Civil War. • After the Civil War, he was elected the 18th President of the United States. ...
Chapter 15
... • "It is difficult at this day to realize the state of public opinion in regard to that unfortunate race which prevailed in the civilized and enlightened portions of the world at the time of the Declaration of Independence, and when the Constitution of the United States was framed and adopted; but t ...
... • "It is difficult at this day to realize the state of public opinion in regard to that unfortunate race which prevailed in the civilized and enlightened portions of the world at the time of the Declaration of Independence, and when the Constitution of the United States was framed and adopted; but t ...
Causes of the Civil War
... -Many feared ending slavery would bankrupt the South. As issue intensified, Southern states threatened to secede, or withdraw, from the Union. ...
... -Many feared ending slavery would bankrupt the South. As issue intensified, Southern states threatened to secede, or withdraw, from the Union. ...
Chapter 15 Notes
... 6. Dec. 20, 1860: South Carolina became the first state to secede 7. Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas joined South Carolina in the secession movement 8. February 1861, the states met in Montgomery, Alabama and formed the Confederate States of America 9. Confederate States ...
... 6. Dec. 20, 1860: South Carolina became the first state to secede 7. Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas joined South Carolina in the secession movement 8. February 1861, the states met in Montgomery, Alabama and formed the Confederate States of America 9. Confederate States ...
Slavery Divides the Nation, 1820–1861
... • Scott could not file a lawsuit because, as an enslaved person, he was not a citizen. • Slaves were considered to be property. • Congress did not have the power to outlaw slavery in any territory. This decision meant the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional. ...
... • Scott could not file a lawsuit because, as an enslaved person, he was not a citizen. • Slaves were considered to be property. • Congress did not have the power to outlaw slavery in any territory. This decision meant the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional. ...
Unit 1 -- Essay #2
... illegal -- that’s why they want more “slave” states and more Rep’s in Congress ! ...
... illegal -- that’s why they want more “slave” states and more Rep’s in Congress ! ...
APUSH - READING GUIDE (CIVIL WAR) CHAPTER 19: Drifting
... 11. Define: secede , secession 12. Which state was the first to secede FOUR DAYS AFTER Abraham Lincoln was elected president? 13. List the 6 states that seceded from the Union in 1860 aside from South Carolina. Please read “Varying Viewpoints” on page 432-433 Chapter 20- Girding for War: The North & ...
... 11. Define: secede , secession 12. Which state was the first to secede FOUR DAYS AFTER Abraham Lincoln was elected president? 13. List the 6 states that seceded from the Union in 1860 aside from South Carolina. Please read “Varying Viewpoints” on page 432-433 Chapter 20- Girding for War: The North & ...
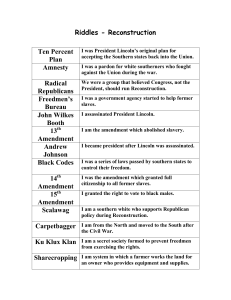
Riddles - Reconstruction Ten Percent Plan Amnesty Radical
... I am the amendment which abolished slavery. I became president after Lincoln was assassinated. I was a series of laws passed by southern states to ...
... I am the amendment which abolished slavery. I became president after Lincoln was assassinated. I was a series of laws passed by southern states to ...
Study Guide Civil War and Reconstruction Prior to the Civil War
... 5. What novel was published in 1852 that depicted slavery as an evil institution? 6. Why was Harriet Tubman known as the “Moses” of her people? 7. What is popular sovereignty? 8. What impact did the Kansas-Nebraska Act have on the Union? 9. What was the civil war that erupted in Kansas of the issue ...
... 5. What novel was published in 1852 that depicted slavery as an evil institution? 6. Why was Harriet Tubman known as the “Moses” of her people? 7. What is popular sovereignty? 8. What impact did the Kansas-Nebraska Act have on the Union? 9. What was the civil war that erupted in Kansas of the issue ...
MSL Study Guide - Public Schools of Robeson County
... Democrat Party split between North and South on slavery issue Republicans: new party, against slavery for territories and new states, formed from Whigs, FreeSoilers, and Northern Democrats Lincoln v. Douglas debates Freeport Doctrine- Douglas’s argument for Popular Sovereignty Lincoln lost e ...
... Democrat Party split between North and South on slavery issue Republicans: new party, against slavery for territories and new states, formed from Whigs, FreeSoilers, and Northern Democrats Lincoln v. Douglas debates Freeport Doctrine- Douglas’s argument for Popular Sovereignty Lincoln lost e ...
US History Chapter 2 Test Review Sheet Terms
... 4. First Battle of Bull Run: significance 5. The war in the West: Grant—goal of capturing Miss. River 6. Battle of Antietam: significance; Emancipation Proclamation: Why issued? Which slaves freed? Result? 7. Gettysburg, Vicksburg: dates, location, events, significance of each 8. Sherman’s March: de ...
... 4. First Battle of Bull Run: significance 5. The war in the West: Grant—goal of capturing Miss. River 6. Battle of Antietam: significance; Emancipation Proclamation: Why issued? Which slaves freed? Result? 7. Gettysburg, Vicksburg: dates, location, events, significance of each 8. Sherman’s March: de ...
Darcey Sweeney
... Johnson informally stipulate that the southern states were to renounce their ordinances of secession, repudiate the Confederate debt, and ratify the proposed 13th Amendment, abolishing slavery. The white elitist regimes in the south tried to prevent blacks from gaining any power at all. The Civil Ri ...
... Johnson informally stipulate that the southern states were to renounce their ordinances of secession, repudiate the Confederate debt, and ratify the proposed 13th Amendment, abolishing slavery. The white elitist regimes in the south tried to prevent blacks from gaining any power at all. The Civil Ri ...
The Civil War and Reconstruction
... wanted to sell in the South. However it was more expensive for the North to produce goods than England because they were better industrialized. •The North wanted a protective tariff placed on imported goods thus raising England’s prices on goods. ©2012, TESCCC ...
... wanted to sell in the South. However it was more expensive for the North to produce goods than England because they were better industrialized. •The North wanted a protective tariff placed on imported goods thus raising England’s prices on goods. ©2012, TESCCC ...
1860 -‐ Abraham Lincoln was elected president of
... On the night that Rosa Parks was arrested Martin Luther King Jr. and other local civil rights leaders planned a citywide bus boycott. The bus boycott was 382 days of walking to work, harassment, v ...
... On the night that Rosa Parks was arrested Martin Luther King Jr. and other local civil rights leaders planned a citywide bus boycott. The bus boycott was 382 days of walking to work, harassment, v ...
history study guide for ch 10
... 1. THE TWO ISSUES SETTLED BY THE CIVIL WAR ARE: NO STATE COULD LEAVE THE UNION AND THE END OF SLAVERY. 2. THE SOUTHERN STATES THAT LEFT THE UNION FORMED THEIR OWN NATION CALLED THE CONFEDERATE STATES OF AMERICA. 3. PEOPLE WHO SPENT MUCH TIME TRYING TO OUTLAW SLAVERY WERE CALLED ABOLITIONISTS. 4. A D ...
... 1. THE TWO ISSUES SETTLED BY THE CIVIL WAR ARE: NO STATE COULD LEAVE THE UNION AND THE END OF SLAVERY. 2. THE SOUTHERN STATES THAT LEFT THE UNION FORMED THEIR OWN NATION CALLED THE CONFEDERATE STATES OF AMERICA. 3. PEOPLE WHO SPENT MUCH TIME TRYING TO OUTLAW SLAVERY WERE CALLED ABOLITIONISTS. 4. A D ...
Civil War and Reconstruction Study Guide
... 1. In the South, after the invention of the cotton gin a. Planters bought more land and fewer enslaved people. b. Planters bought some land and stopped enslaving people. c. Planters bought more land and more enslaved people. 2. Which of the following sentences is true? a. There were more factories ...
... 1. In the South, after the invention of the cotton gin a. Planters bought more land and fewer enslaved people. b. Planters bought some land and stopped enslaving people. c. Planters bought more land and more enslaved people. 2. Which of the following sentences is true? a. There were more factories ...
The Civil War Experience
... Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. In Dixie land where I was born in, Early on a frosty mornin', Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. ...
... Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. In Dixie land where I was born in, Early on a frosty mornin', Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. ...
The Civil War and Reconstruction - Online
... Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. In Dixie land where I was born in, Early on a frosty mornin', Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. ...
... Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. In Dixie land where I was born in, Early on a frosty mornin', Look away, look away, look away, Dixie land. ...
Issues of the American Civil War

Issues of the American Civil War include questions about the name of the war, the tariff, states' rights and the nature of Abraham Lincoln's war goals. For more on naming, see Naming the American Civil War.The question of how important the tariff was in causing the war stems from the Nullification Crisis, which was South Carolina's attempt to nullify a tariff and lasted from 1828 to 1832. The tariff was low after 1846, and the tariff issue faded into the background by 1860 when secession began. States' rights was the justification for nullification and later secession. The most controversial right claimed by Southern states was the alleged right of Southerners to spread slavery into territories owned by the United States.As to the question of the relation of Lincoln's war goals to causes, goals evolved as the war progressed in response to political and military issues, and can't be used as a direct explanation of causes of the war. Lincoln needed to find an issue that would unite a large but divided North to save the Union, and then found that circumstances beyond his control made emancipation possible, which was in line with his ""personal wish that all men everywhere could be free"".