InAConchShell - some tryout study material
... seiche: standing wave; tsunami: seismic sea waves Wind-generated waves controlled by 4 factors: wind velocity, wind duration, fetch (area wind blows over), and original sea state. Fully developed sea: name says what it means; significant wave height: average of top 1/3. ...
... seiche: standing wave; tsunami: seismic sea waves Wind-generated waves controlled by 4 factors: wind velocity, wind duration, fetch (area wind blows over), and original sea state. Fully developed sea: name says what it means; significant wave height: average of top 1/3. ...
Waves Fact Sheet Anything that causes water to move can produce
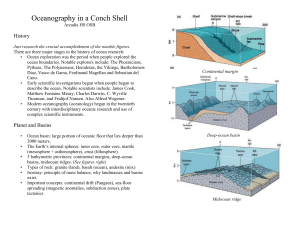
... By Margaret Olsen, Southeast COSEE Education Specialist ...
... By Margaret Olsen, Southeast COSEE Education Specialist ...
Earthquake Definitions - Red Hook Central Schools
... As the Earth’s plates move past one another, friction causes the plates to get “stuck”. · Stress and pressure builds up and causes the plate to become deformed (bend) as it continues to try and move (the plates are elastic-they can change shape). · Eventually, the pressure is great enough to over ...
... As the Earth’s plates move past one another, friction causes the plates to get “stuck”. · Stress and pressure builds up and causes the plate to become deformed (bend) as it continues to try and move (the plates are elastic-they can change shape). · Eventually, the pressure is great enough to over ...
Marine Processes - G. Lombardo Radice
... Trough: The low area in between two waves. Wavelength: The distance between two crests or two troughs. Wave height: The distance between the crest and the trough. Wave Frequency: The number of waves per minute. Velocity: The speed that a wave is traveling. It is influenced by the wind, fetch (distan ...
... Trough: The low area in between two waves. Wavelength: The distance between two crests or two troughs. Wave height: The distance between the crest and the trough. Wave Frequency: The number of waves per minute. Velocity: The speed that a wave is traveling. It is influenced by the wind, fetch (distan ...
Science Chapter Two Landforms and Constructive/Destructive
... another Ocean waves change and wear down cliffs Ocean waves change beaches Rain that freezes in small cracks can expand and break down rock Flowing water makes rocks tumble together, which smoothes their edges ...
... another Ocean waves change and wear down cliffs Ocean waves change beaches Rain that freezes in small cracks can expand and break down rock Flowing water makes rocks tumble together, which smoothes their edges ...
Study Guide: Ch 16 - Dynamic Ocean
... 14. The smallest daily tidal range occurs during which type of tide (spring tide or neap tide)? 15. Which tidal pattern has two high tides and two low tides each day? 16. The movement of water that parallels the shore within the surf zone is called ____. 17. The accumulation of sediment found along ...
... 14. The smallest daily tidal range occurs during which type of tide (spring tide or neap tide)? 15. Which tidal pattern has two high tides and two low tides each day? 16. The movement of water that parallels the shore within the surf zone is called ____. 17. The accumulation of sediment found along ...
Earth Quakes
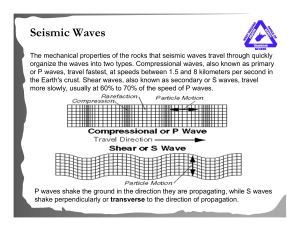
... waves: the slowest type of waves which only travel along the Earth’s surface, not the interior like the S and P body waves. Surface waves usually cause the most destruction because they move the ground and take the longest time to pass. The point where the waves originate is where the rock fails ...
... waves: the slowest type of waves which only travel along the Earth’s surface, not the interior like the S and P body waves. Surface waves usually cause the most destruction because they move the ground and take the longest time to pass. The point where the waves originate is where the rock fails ...
Oceans - acpsd
... flat step of rock formed in an exposed windy area where the waves pound hard against the shore. • Over time the waves cut out, or erode, a steep cliff. • Marine terraces are common along the Pacific Coast. ...
... flat step of rock formed in an exposed windy area where the waves pound hard against the shore. • Over time the waves cut out, or erode, a steep cliff. • Marine terraces are common along the Pacific Coast. ...
Waves and Tides
... When the trough of a wave gets close to land, it starts to drag while the crest moves on, getting higher and higher until it tumbles over. ...
... When the trough of a wave gets close to land, it starts to drag while the crest moves on, getting higher and higher until it tumbles over. ...
Tsunami - Meaning,Safety
... Tsunami is a Japanese word meaning ‘Harbour Wave’. In the past the scientific community sometimes referred to them as ‘tidal waves’ or ‘seismic sea waves’. Tsunamis are the hydrosphere’s most destructive force. They are giant waves that are caused by sudden movement of the seabed during an earthquak ...
... Tsunami is a Japanese word meaning ‘Harbour Wave’. In the past the scientific community sometimes referred to them as ‘tidal waves’ or ‘seismic sea waves’. Tsunamis are the hydrosphere’s most destructive force. They are giant waves that are caused by sudden movement of the seabed during an earthquak ...
A mechanical wave is created when a source of energy causes a
... A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels. ...
... A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels. ...
Waves DR Worksheet Ch. 14 Section 3
... _____ 16. the bubbles in the crest of a breaking wave _____ 17. long rolling waves that move steadily and at long distances across the ocean _____ 18. a giant ocean wave that forms after a volcanic eruption, submarine earthquake, or landslide _____ 19. a local rise in sea level near the shore, cause ...
... _____ 16. the bubbles in the crest of a breaking wave _____ 17. long rolling waves that move steadily and at long distances across the ocean _____ 18. a giant ocean wave that forms after a volcanic eruption, submarine earthquake, or landslide _____ 19. a local rise in sea level near the shore, cause ...
14.3 Directed Reading A
... _____ 16. the bubbles in the crest of a breaking wave _____ 17. long rolling waves that move steadily and at long distances across the ocean _____ 18. a giant ocean wave that forms after a volcanic eruption, submarine earthquake, or landslide _____ 19. a local rise in sea level near the shore, cause ...
... _____ 16. the bubbles in the crest of a breaking wave _____ 17. long rolling waves that move steadily and at long distances across the ocean _____ 18. a giant ocean wave that forms after a volcanic eruption, submarine earthquake, or landslide _____ 19. a local rise in sea level near the shore, cause ...
Name Oceanography Video Worksheet Waves and Erosion 1. Most
... Waves and Erosion 1. Most ocean waves are created by? ...
... Waves and Erosion 1. Most ocean waves are created by? ...
Surf break

A surf break (also break, shore break, or big wave break) is a permanent (or semi permanent) obstruction such as a coral reef, rock, shoal, or headland that causes a wave to break, forming a barreling wave or other wave that can be surfed, before it eventually collapses. The topography of the seabed determines the shape of the wave and type of break. Since shoals can change size and location, affecting the break, it takes commitment and skill to find good breaks. Some surf breaks are quite dangerous, since the surfer can collide with a reef or rocks below the water. Surf breaks may be defended vehemently by surfers, as human activities and constructions can have unintended and unpredictable consequences which can be either positive, negative, or unknown. In 2008, surfers and environmentalists opposed a toll road project in Orange County, California that would have changed sediment patterns and affected the world-class Trestles surf break north of San Onofre State Beach which attracted 400,000 surfers in 2007.In 2007, the NSW Geographical Names Register began formally recognizing names of surf breaks in Australia, defining a surf break as a ""permanent obstruction such as a reef, headland, bombora, rock or sandbar, which causes waves to break"".One of the largest surf breaks in the world is the Jaws surf break in Maui, Hawaii, with waves that reach a maximum height of 40–60 feet (12–18 m).