Chapter 11 Section 5 Notes Thirteenth Amendment – amends the
... Military Strategy: Did not need to attack or conquer the North; had only to avoid defeat to win the war ...
... Military Strategy: Did not need to attack or conquer the North; had only to avoid defeat to win the war ...
Ch7 Key Terms
... Carolina. He peered out his bedroom window and a wave of terror rushed over him. Thirty men in white robes and hoods stood around the house. Many held shotguns. They were members of the Ku Klux Klan, an organization that used violence and intimidation to force African Americans and white Republicans ...
... Carolina. He peered out his bedroom window and a wave of terror rushed over him. Thirty men in white robes and hoods stood around the house. Many held shotguns. They were members of the Ku Klux Klan, an organization that used violence and intimidation to force African Americans and white Republicans ...
Freedom`s Main Line - Teaching Tolerance
... Before the Civil War, there had been no stateenforced separation of blacks and whites in public places in the South. From white Southerners’ perspective, there had been no need. The institution of slavery clearly placed blacks at the bottom rung of society and established white supremacy. But follow ...
... Before the Civil War, there had been no stateenforced separation of blacks and whites in public places in the South. From white Southerners’ perspective, there had been no need. The institution of slavery clearly placed blacks at the bottom rung of society and established white supremacy. But follow ...
The Union in Peril - Plain Local Schools
... save the Union and alienated his abolitionist supporters John C. Calhoun (SC): argued against compromise and for states’ rights William H. Seward (NY): against the compromise and argued that there was a higher law than the Constitution Stephen A. Douglas (IL): prepared the components of the co ...
... save the Union and alienated his abolitionist supporters John C. Calhoun (SC): argued against compromise and for states’ rights William H. Seward (NY): against the compromise and argued that there was a higher law than the Constitution Stephen A. Douglas (IL): prepared the components of the co ...
Study Guide: 1844-1877 (from the College Board) After reading the
... A. Although citizenship, equal protection of the laws, and voting rights were granted to African Americans in the 14th and 15th Amendments, these rights were progressively stripped away through segregation, violence, Supreme Court decisions, and local political tactics. B. The women’s rights movemen ...
... A. Although citizenship, equal protection of the laws, and voting rights were granted to African Americans in the 14th and 15th Amendments, these rights were progressively stripped away through segregation, violence, Supreme Court decisions, and local political tactics. B. The women’s rights movemen ...
Unit 5 Civil War
... • Assassination of President Lincoln (1865) – Five days after the confederate surrender, Confederate sympathizer John Wilkes Booth assassinates President Lincoln on April 15, 1865. VII. Reconstruction • The time of rebuilding the nation after the Civil War. Federal troops went to the South to make s ...
... • Assassination of President Lincoln (1865) – Five days after the confederate surrender, Confederate sympathizer John Wilkes Booth assassinates President Lincoln on April 15, 1865. VII. Reconstruction • The time of rebuilding the nation after the Civil War. Federal troops went to the South to make s ...
SS5H2 - Effingham County Schools
... 1. After the Civil War ended in 1865, the country began the process of bringing the South back into the Union. This period of time was called A. Reconstruction. B. the Great Depression. C. Emancipation. D. the Industrial Revolution. 2. What was the biggest problem facing the United States at the end ...
... 1. After the Civil War ended in 1865, the country began the process of bringing the South back into the Union. This period of time was called A. Reconstruction. B. the Great Depression. C. Emancipation. D. the Industrial Revolution. 2. What was the biggest problem facing the United States at the end ...
Practice test Chapter 17
... ____ 21. Whom did white southerners call “carpetbaggers”? a. former slaves living in the north who voted with the Republicans b. northern-born Republican office-holders in the South c. African American Republicans who took over Confederate seats ____ 22. Hiram Revels was the first African American t ...
... ____ 21. Whom did white southerners call “carpetbaggers”? a. former slaves living in the north who voted with the Republicans b. northern-born Republican office-holders in the South c. African American Republicans who took over Confederate seats ____ 22. Hiram Revels was the first African American t ...
Federal Civil Rights Policy Summary and Overview
... acts to enforce the Thirteenth, Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments, allowing the federal government to impose heavy penalties for violations. The Civil Rights Act of 1866: This act granted black citizens equal rights to contract, to sue and be sued, to marry, travel, and own property. It made all c ...
... acts to enforce the Thirteenth, Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments, allowing the federal government to impose heavy penalties for violations. The Civil Rights Act of 1866: This act granted black citizens equal rights to contract, to sue and be sued, to marry, travel, and own property. It made all c ...
2005 – 2006 - Suffolk Public Schools Blog
... The Fourteenth Amendment guaranteed all citizens equality before the law The Fifteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution gave male citizens the right to vote regardless of race, color, or former status as a slave. Later methods of depriving citizens of their 15th Amendment rights included poll taxe ...
... The Fourteenth Amendment guaranteed all citizens equality before the law The Fifteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution gave male citizens the right to vote regardless of race, color, or former status as a slave. Later methods of depriving citizens of their 15th Amendment rights included poll taxe ...
The battle was done, the buglers silent. Bone
... Black churches grew robustly. The 150,000-member black Baptist Church of 1850 reached 500,000 by 1870, while the African Methodist Episcopal Church quadrupled in size from 100,000 to 400,000 in the first decade after emancipation. These churches formed the bedrock of black community life, and they s ...
... Black churches grew robustly. The 150,000-member black Baptist Church of 1850 reached 500,000 by 1870, while the African Methodist Episcopal Church quadrupled in size from 100,000 to 400,000 in the first decade after emancipation. These churches formed the bedrock of black community life, and they s ...
Reconstruction Powerpoint
... South to help freedmen, called “carpetbaggers” by Southern Democrats ...
... South to help freedmen, called “carpetbaggers” by Southern Democrats ...
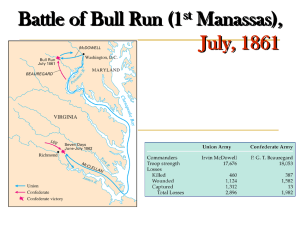
Battle of Bull Run (1 st Manassas)
... The McLean family, who had moved from Manassas Junction after two major battles destroyed their farm in northeastern Virginia, started a new life in the quiet western Virginia town of Appomattox Court House. They still could not escape the war. On April 9, 1865 . . . ...
... The McLean family, who had moved from Manassas Junction after two major battles destroyed their farm in northeastern Virginia, started a new life in the quiet western Virginia town of Appomattox Court House. They still could not escape the war. On April 9, 1865 . . . ...
Causes of the Civil War
... Northerners did not support states’ rights. They believed the national government had final power. ...
... Northerners did not support states’ rights. They believed the national government had final power. ...
Quiz 4 - Civil War and Reconstruction
... 6. ______________________________________ failed attempt in 1846 to prohibit slavery in any territory acquired as a result of the Mexican War, caused split on issue of slavery in territories. 7. _____________________________________ election where Democratic party split, Abraham Lincoln elected U.S. ...
... 6. ______________________________________ failed attempt in 1846 to prohibit slavery in any territory acquired as a result of the Mexican War, caused split on issue of slavery in territories. 7. _____________________________________ election where Democratic party split, Abraham Lincoln elected U.S. ...
Name: :______Date
... 8. What event in 1860 led the Southern states to secede? A. The election of Republican Abraham Lincoln to the Presidency. B. The passage of an anti-slavery amendment to the Constitution. C. A Supreme Court declaration that slavery was unconstitutional. D. The Dred Scott decision. 9. Southern states ...
... 8. What event in 1860 led the Southern states to secede? A. The election of Republican Abraham Lincoln to the Presidency. B. The passage of an anti-slavery amendment to the Constitution. C. A Supreme Court declaration that slavery was unconstitutional. D. The Dred Scott decision. 9. Southern states ...
Reconstruction - Trimble County Schools
... http://encarta.msn.com/media_461520820/ Cartoon_of_the_Carpetbaggers.html ...
... http://encarta.msn.com/media_461520820/ Cartoon_of_the_Carpetbaggers.html ...
The Politics of Reconstruction
... an amendment that their legislators had little to do with. The amendment was not ratified until 1868. The Radical Republicans won numerous seats in the 1866 Congressional elections. They now had enough votes in Congress to take control of Reconstruction. In 1867, the new Congress passed the Reconstr ...
... an amendment that their legislators had little to do with. The amendment was not ratified until 1868. The Radical Republicans won numerous seats in the 1866 Congressional elections. They now had enough votes in Congress to take control of Reconstruction. In 1867, the new Congress passed the Reconstr ...
SOL 9b: States` Rights and Slavery
... would DECIDE about slavery (popular sovereignty). 3) Kansas-Nebraska Act: People in each state would decided the SLAVERY issue (popular sovereignty) ...
... would DECIDE about slavery (popular sovereignty). 3) Kansas-Nebraska Act: People in each state would decided the SLAVERY issue (popular sovereignty) ...
Unit Six PPT 3 - Henry County Schools
... South to help freedmen, called “carpetbaggers” by Southern Democrats ...
... South to help freedmen, called “carpetbaggers” by Southern Democrats ...
Redeemers

In United States history, the Redeemers were a white political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction era that followed the Civil War. Redeemers were the southern wing of the Bourbon Democrats, the conservative, pro-business faction in the Democratic Party, who pursued a policy of Redemption, seeking to oust the Radical Republican coalition of freedmen, ""carpetbaggers"", and ""scalawags"". They generally were led by the rich landowners, businessmen and professionals, and dominated Southern politics in most areas from the 1870s to 1910.During Reconstruction, the South was under occupation by federal forces and Southern state governments were dominated by Republicans. Republicans nationally pressed for the granting of political rights to the newly freed slaves as the key to their becoming full citizens. The Thirteenth Amendment (banning slavery), Fourteenth Amendment (guaranteeing the civil rights of former slaves and ensuring equal protection of the laws), and Fifteenth Amendment (prohibiting the denial of the right to vote on grounds of race, color, or previous condition of servitude) enshrined such political rights in the Constitution.Numerous educated blacks moved to the South to work for Reconstruction, and some blacks attained positions of political power under these conditions. However, the Reconstruction governments were unpopular with many white Southerners, who were not willing to accept defeat and continued to try to prevent black political activity by any means. While the elite planter class often supported insurgencies, violence against freedmen and other Republicans was often carried out by other whites; insurgency took the form of the secret Ku Klux Klan in the first years after the war.In the 1870s, secret paramilitary organizations, such as the White League in Louisiana and Red Shirts in Mississippi and North Carolina undermined the opposition. These paramilitary bands used violence and threats to undermine the Republican vote. By the presidential election of 1876, only three Southern states – Louisiana, South Carolina, and Florida – were ""unredeemed"", or not yet taken over by white Democrats. The disputed Presidential election between Rutherford B. Hayes (the Republican governor of Ohio) and Samuel J. Tilden (the Democratic governor of New York) was allegedly resolved by the Compromise of 1877, also known as the Corrupt Bargain. In this compromise, it was claimed, Hayes became President in exchange for numerous favors to the South, one of which was the removal of Federal troops from the remaining ""unredeemed"" Southern states; this was however a policy Hayes had endorsed during his campaign. With the removal of these forces, Reconstruction came to an end.