Unit 4
... e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation. f. Explain the importance of the growing economic disparity between the North and the South through an examination of population, functioning railroads, and industrial output. SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and socia ...
... e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation. f. Explain the importance of the growing economic disparity between the North and the South through an examination of population, functioning railroads, and industrial output. SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and socia ...
The Unknown Battle of the Civil War It looked like a pool of white
... with red blood and many had fallen to the ground. But why was there not any blackness in this pale pool? Why was it so white? This pool of white was a common scene during the Civil War. Of these men fighting in the first two years of the war, there were no African Americans because of the negative p ...
... with red blood and many had fallen to the ground. But why was there not any blackness in this pale pool? Why was it so white? This pool of white was a common scene during the Civil War. Of these men fighting in the first two years of the war, there were no African Americans because of the negative p ...
Minnesota`s attitude toward the Southern case for secession [by] F
... the enactment by some of the States of the 'Personal Liberty Bills,' and yet not one, poor, panting negro has ever escaped from their clutches in consequence of any of them. They know as well as we do, that these legislative provisions were passed by the several States for the protection of their ow ...
... the enactment by some of the States of the 'Personal Liberty Bills,' and yet not one, poor, panting negro has ever escaped from their clutches in consequence of any of them. They know as well as we do, that these legislative provisions were passed by the several States for the protection of their ow ...
annotated bibliography of recent Civil War era articles
... How can the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade Database be used to “contrast the number of African slaves coming to United States with those going to Central and South America” and how can this be a way to “examine the areas of Africa from which slaves originated and the number of voyages originating in the ...
... How can the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade Database be used to “contrast the number of African slaves coming to United States with those going to Central and South America” and how can this be a way to “examine the areas of Africa from which slaves originated and the number of voyages originating in the ...
The Coming of the Civil War
... National political parties no longer existed. Voters in the North chose between Northern Democrat Stephen Douglas and Republican Abraham Lincoln, while Southerners voted for Southern Democrat J.C. Breckinridge or John Bell of the newly formed Constitutional Union Party. While votes in the Border Sta ...
... National political parties no longer existed. Voters in the North chose between Northern Democrat Stephen Douglas and Republican Abraham Lincoln, while Southerners voted for Southern Democrat J.C. Breckinridge or John Bell of the newly formed Constitutional Union Party. While votes in the Border Sta ...
Did You Know? - Dalton Local Schools
... could vote for measures they agreed with and vote against parts they did see any without such thing? not support rejecting the whole plan. Congress passed the Too series of five separate bills in August and September John C. Calhoun ill to deliver it himself, so it was read by another senator with C ...
... could vote for measures they agreed with and vote against parts they did see any without such thing? not support rejecting the whole plan. Congress passed the Too series of five separate bills in August and September John C. Calhoun ill to deliver it himself, so it was read by another senator with C ...
secession
... – Lincoln stood for ideas that Northerners liked: free land out west, higher tariffs to protect American jobs, no slavery in western territories, and an increase in industry and railroads – Saw secession of southern states as unnecessary and against the law. – Goal was to “preserve the Union” at wha ...
... – Lincoln stood for ideas that Northerners liked: free land out west, higher tariffs to protect American jobs, no slavery in western territories, and an increase in industry and railroads – Saw secession of southern states as unnecessary and against the law. – Goal was to “preserve the Union” at wha ...
Scalawags Among Us: Alamance County Among the
... that period would be a year and three months, from March 1867 to July 1868. Basically, Johnson‟s Southern policy had left power in the hands of people who had run things before and during the Civil War. That was certainly true in North Carolina, including Alamance County. Now, in 1867, after about t ...
... that period would be a year and three months, from March 1867 to July 1868. Basically, Johnson‟s Southern policy had left power in the hands of people who had run things before and during the Civil War. That was certainly true in North Carolina, including Alamance County. Now, in 1867, after about t ...
short Chapterwalk18
... order to be readmitted into the Union? Ans: Loyalty oath; support for abolition; revised state constitutions; election of new state officials, representatives, and senators Section 2: The Fight over Reconstruction Page 626 The Black Codes 38. How were southern African Americans treated after the Civ ...
... order to be readmitted into the Union? Ans: Loyalty oath; support for abolition; revised state constitutions; election of new state officials, representatives, and senators Section 2: The Fight over Reconstruction Page 626 The Black Codes 38. How were southern African Americans treated after the Civ ...
Transforming Fire: The Civil War, 1861–1865
... dedication to a common task forged bonds among soldiers that they cherished for years. The last two years of the war brought increasing antigovernment sentiment in both South and North. More widespread in the South, such sentiment involved the planters—who seemed committed only to their own selfish ...
... dedication to a common task forged bonds among soldiers that they cherished for years. The last two years of the war brought increasing antigovernment sentiment in both South and North. More widespread in the South, such sentiment involved the planters—who seemed committed only to their own selfish ...
bowen TAHP1 paper (2)
... American Civil War as it infused more tension between the North and the South around the issue of slavery. In looking at the reasons that motivated the withdrawal of the Confederate states and the beginning of the Civil war, it can be noted that the abolition movement played a significant role by be ...
... American Civil War as it infused more tension between the North and the South around the issue of slavery. In looking at the reasons that motivated the withdrawal of the Confederate states and the beginning of the Civil war, it can be noted that the abolition movement played a significant role by be ...
Chapter 16 The Civil War 1861–1865
... Communities all over the North rallied to make up for the army’s shortcomings with supplies and assistance. The efforts of women on the local level to make clothing for the men from their communities who had gone off to war soon took on national dimensions. The Women’s Central Association of Relief, ...
... Communities all over the North rallied to make up for the army’s shortcomings with supplies and assistance. The efforts of women on the local level to make clothing for the men from their communities who had gone off to war soon took on national dimensions. The Women’s Central Association of Relief, ...
thesis development worksheet information
... was the leader of the United States during a period of great national conflict. His leadership, through the critical decisions of the Emancipation Proclamation, not only freed slaves but also changed the course of the Civil War. 9. What was the impact or historical significance? The lasting legacy o ...
... was the leader of the United States during a period of great national conflict. His leadership, through the critical decisions of the Emancipation Proclamation, not only freed slaves but also changed the course of the Civil War. 9. What was the impact or historical significance? The lasting legacy o ...
Goal 1: The New Nation The New Nation: Federalist ERA (George
... Battle of Fallen Timbers Washington sent the US army to the Northwest Territory (Ohio River Valley) to defeat Native American’s . Treaty of Greenville: o Ended the Battle of Fallen Timbers o Native American’s forced to cede the Ohio River Valley (Northwest Territory) o Native American’s within ...
... Battle of Fallen Timbers Washington sent the US army to the Northwest Territory (Ohio River Valley) to defeat Native American’s . Treaty of Greenville: o Ended the Battle of Fallen Timbers o Native American’s forced to cede the Ohio River Valley (Northwest Territory) o Native American’s within ...
FINAL Revised December 9, 2013 The Civil War: A
... role proportional to their number in state legislatures, but as the states gradually escaped from what they described as “carpetbagger” government, the black freedmen were systematically disenfranchised and prevented from voting by organized campaigns of violence, murder, and lynching, in which the ...
... role proportional to their number in state legislatures, but as the states gradually escaped from what they described as “carpetbagger” government, the black freedmen were systematically disenfranchised and prevented from voting by organized campaigns of violence, murder, and lynching, in which the ...
The 1850 Sectional Crisis
... David Wilmot is a “free soiler” who wanted northern whites to benefit from new terrirtories. His proviso was part of a finance bill for the Mexican- American war. House of Representatives passed this bill- 83 YES 64 NO. The Senate prevent this becoming law; ...
... David Wilmot is a “free soiler” who wanted northern whites to benefit from new terrirtories. His proviso was part of a finance bill for the Mexican- American war. House of Representatives passed this bill- 83 YES 64 NO. The Senate prevent this becoming law; ...
The War for Southern Independence
... does not follow, however, that slavery was therefore the issue. (If it was so critical, why not fight over it in 1800? 1828? 1856?) Rather, the issue over which war came was the independence of the newly organized Confederacy. As William Appleman Williams says, "the cause of the Civil War was the re ...
... does not follow, however, that slavery was therefore the issue. (If it was so critical, why not fight over it in 1800? 1828? 1856?) Rather, the issue over which war came was the independence of the newly organized Confederacy. As William Appleman Williams says, "the cause of the Civil War was the re ...
Civil War Guide1
... Guide students through the activity. Ask them why it was important for the North to cut the Confederate states off from outside suppliers. Explain that, because the South had a small industrial base, it had to import much of the weaponry, ammunition, medicines and painkillers, and other war material ...
... Guide students through the activity. Ask them why it was important for the North to cut the Confederate states off from outside suppliers. Explain that, because the South had a small industrial base, it had to import much of the weaponry, ammunition, medicines and painkillers, and other war material ...
Welcome! We hope you enjoy our presentation! Jackie Brown Paul
... •On the morning of April 9th the final battle is fought •In the afternoon of April 9th Robert E. Lee ...
... •On the morning of April 9th the final battle is fought •In the afternoon of April 9th Robert E. Lee ...
How did the War with Mexico lead to conflict between the North and
... Compromise of 1820. The Missouri Compromise had stated that NO new territories would become slave states. The Kansas – Nebraska Act, however, allowed each state that formed from the new territories to decide for itself. Northerners were outraged – Southerners elated. ...
... Compromise of 1820. The Missouri Compromise had stated that NO new territories would become slave states. The Kansas – Nebraska Act, however, allowed each state that formed from the new territories to decide for itself. Northerners were outraged – Southerners elated. ...
Chapter 5 Reconstruction - Doral Academy Preparatory
... 1876: Due process and equal protection clauses only protected citizens from the actions of the state, not other citizens. The Cold RivalWar Plans Begins for Reconstruction ...
... 1876: Due process and equal protection clauses only protected citizens from the actions of the state, not other citizens. The Cold RivalWar Plans Begins for Reconstruction ...
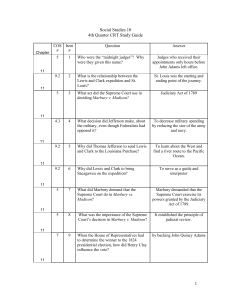
Social Studies, 4th 9 weeks
... restrictions placed on the rights and opportunities of freedmen, including racial segregation and Jim Crow laws. ...
... restrictions placed on the rights and opportunities of freedmen, including racial segregation and Jim Crow laws. ...
Chapter 10 PP
... Brown, many northern abolitionists considered him a martyr. • Southerners were outraged that a man who had planned a slave revolt was hailed as a hero. ...
... Brown, many northern abolitionists considered him a martyr. • Southerners were outraged that a man who had planned a slave revolt was hailed as a hero. ...
Social Studies 10
... It made the Civil War a war against slavery, and the British did not intervene on the side of the Confederacy. ...
... It made the Civil War a war against slavery, and the British did not intervene on the side of the Confederacy. ...
Redeemers

In United States history, the Redeemers were a white political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction era that followed the Civil War. Redeemers were the southern wing of the Bourbon Democrats, the conservative, pro-business faction in the Democratic Party, who pursued a policy of Redemption, seeking to oust the Radical Republican coalition of freedmen, ""carpetbaggers"", and ""scalawags"". They generally were led by the rich landowners, businessmen and professionals, and dominated Southern politics in most areas from the 1870s to 1910.During Reconstruction, the South was under occupation by federal forces and Southern state governments were dominated by Republicans. Republicans nationally pressed for the granting of political rights to the newly freed slaves as the key to their becoming full citizens. The Thirteenth Amendment (banning slavery), Fourteenth Amendment (guaranteeing the civil rights of former slaves and ensuring equal protection of the laws), and Fifteenth Amendment (prohibiting the denial of the right to vote on grounds of race, color, or previous condition of servitude) enshrined such political rights in the Constitution.Numerous educated blacks moved to the South to work for Reconstruction, and some blacks attained positions of political power under these conditions. However, the Reconstruction governments were unpopular with many white Southerners, who were not willing to accept defeat and continued to try to prevent black political activity by any means. While the elite planter class often supported insurgencies, violence against freedmen and other Republicans was often carried out by other whites; insurgency took the form of the secret Ku Klux Klan in the first years after the war.In the 1870s, secret paramilitary organizations, such as the White League in Louisiana and Red Shirts in Mississippi and North Carolina undermined the opposition. These paramilitary bands used violence and threats to undermine the Republican vote. By the presidential election of 1876, only three Southern states – Louisiana, South Carolina, and Florida – were ""unredeemed"", or not yet taken over by white Democrats. The disputed Presidential election between Rutherford B. Hayes (the Republican governor of Ohio) and Samuel J. Tilden (the Democratic governor of New York) was allegedly resolved by the Compromise of 1877, also known as the Corrupt Bargain. In this compromise, it was claimed, Hayes became President in exchange for numerous favors to the South, one of which was the removal of Federal troops from the remaining ""unredeemed"" Southern states; this was however a policy Hayes had endorsed during his campaign. With the removal of these forces, Reconstruction came to an end.

![Minnesota`s attitude toward the Southern case for secession [by] F](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012889783_1-11e33f252f72ae9447535d34b559408b-300x300.png)