Teaching DNA, Proteins, and Protein Synthesis
... Learn about amino acid side chains and construct primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein structures with the LEGO amino acids. ...
... Learn about amino acid side chains and construct primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protein structures with the LEGO amino acids. ...
Cell Membrane
... a) primary active transport b) secondary active transport 3- Osmosis Diffusion Random movement of substance either through the membrane directly or in combination with carrier protein down an electrochemical gradient 1- Simple diffusion 2- Active diffusion Simple Diffusion Non carrier mediated tra ...
... a) primary active transport b) secondary active transport 3- Osmosis Diffusion Random movement of substance either through the membrane directly or in combination with carrier protein down an electrochemical gradient 1- Simple diffusion 2- Active diffusion Simple Diffusion Non carrier mediated tra ...
Cell Membrane
... a) primary active transport b) secondary active transport 3- Osmosis Diffusion Random movement of substance either through the membrane directly or in combination with carrier protein down an electrochemical gradient 1- Simple diffusion 2- Active diffusion Simple Diffusion Non carrier mediated tra ...
... a) primary active transport b) secondary active transport 3- Osmosis Diffusion Random movement of substance either through the membrane directly or in combination with carrier protein down an electrochemical gradient 1- Simple diffusion 2- Active diffusion Simple Diffusion Non carrier mediated tra ...
the ubiquitin system and a putative stimulatory role
... Among eukaryotes, ubiquitin is highly conserved, meaning that the amino acid sequence does not differ much when very different organisms are compared. Ub is a heat-stable protein that folds up into a compact globular structure. It is found throughout the cell and can exist either in free form or as ...
... Among eukaryotes, ubiquitin is highly conserved, meaning that the amino acid sequence does not differ much when very different organisms are compared. Ub is a heat-stable protein that folds up into a compact globular structure. It is found throughout the cell and can exist either in free form or as ...
Lh6Ch04bProt
... 1. hydrophobic interactions contribute strongly to protein folding and stabilization ultimately burring hydrophobic R groups with at least two layers of secondary structure covering them up to exclude water. 2. alpha and beta structures are usually in different layers. Their R-groups generally do ...
... 1. hydrophobic interactions contribute strongly to protein folding and stabilization ultimately burring hydrophobic R groups with at least two layers of secondary structure covering them up to exclude water. 2. alpha and beta structures are usually in different layers. Their R-groups generally do ...
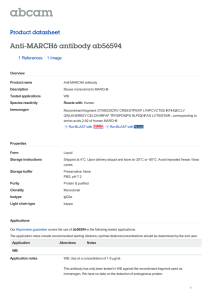
Anti-MARCH6 antibody ab56594 Product datasheet 1 References 1 Image
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
Recombinant Expression Systems
... Autographa californica (multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus AcMNPV). •The baculovirus genome contains the gene, encoding polyhedrin, an abundant viral protein. This protein accumulates in the insect cell towards the end of the infectious cycle and is the major constituent of a protein matrix, contai ...
... Autographa californica (multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus AcMNPV). •The baculovirus genome contains the gene, encoding polyhedrin, an abundant viral protein. This protein accumulates in the insect cell towards the end of the infectious cycle and is the major constituent of a protein matrix, contai ...
ABSTRACT - University of Colorado
... To reduce the likelihood of cross-linking, phenylalanine (F) was substituted for tyrosine at the same sites. We examined aggregate formation and neurotoxic effects of these constructs in a rat dopaminergic cell line (N27 cells) by transient transfection. Results showed that expression of Y39C or Y12 ...
... To reduce the likelihood of cross-linking, phenylalanine (F) was substituted for tyrosine at the same sites. We examined aggregate formation and neurotoxic effects of these constructs in a rat dopaminergic cell line (N27 cells) by transient transfection. Results showed that expression of Y39C or Y12 ...
PROTEINS Dr Mervat Salah Dept of Nutrition
... (2) Net protein, utilization (NPU) = Nitrogen retained by the body ...
... (2) Net protein, utilization (NPU) = Nitrogen retained by the body ...
Powerpoint
... • They are called essential AA because it's essential that you get them from the foods you eat. ...
... • They are called essential AA because it's essential that you get them from the foods you eat. ...
Protein PowerPoint - Bowdle FACS
... • They are called essential AA because it's essential that you get them from the foods you eat. ...
... • They are called essential AA because it's essential that you get them from the foods you eat. ...
Aminoacids
... – Two ends of the amino acid the amino terminal end and the carboxy terminal end. Abbreviated N and C Same idea with the peptide ...
... – Two ends of the amino acid the amino terminal end and the carboxy terminal end. Abbreviated N and C Same idea with the peptide ...
New Ligands of CRABP2 Suggest a Role for this Protein in
... proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis by binding to the RA receptor (RAR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimers. The cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 (CRABP2) is involved in the transport of RA from the cytosol to specific RA receptors in the nucleus, acting as a coactivator of n ...
... proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis by binding to the RA receptor (RAR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimers. The cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 (CRABP2) is involved in the transport of RA from the cytosol to specific RA receptors in the nucleus, acting as a coactivator of n ...
Protein Structure and Bioinformatics
... • What are the primary secondary structures? • How are protein structures determined experimentally? • How can structures be predicted in silico? ...
... • What are the primary secondary structures? • How are protein structures determined experimentally? • How can structures be predicted in silico? ...
New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentation
... • They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. • Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. ...
... • They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. • Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. ...
CellTransport
... plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell. ...
... plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell. ...