Quantum networking with single ions J¨ urgen Eschner
... properties (in fact, all properties) are described by distributions that one obtains through repeated measurements. As an example, single photon emission from a single atom may be repeatedly triggered by an exciting laser pulse at time t = 0, and a single-photon detector records an arrival time dist ...
... properties (in fact, all properties) are described by distributions that one obtains through repeated measurements. As an example, single photon emission from a single atom may be repeatedly triggered by an exciting laser pulse at time t = 0, and a single-photon detector records an arrival time dist ...
Theory and simulation of polar and nonpolar polarizable fluids
... molecules that are also polarizable the molecules are modeled as anisotropic Drude oscillators in which the electronic motion along the direction of the permanent dipole and perpendicular to it have different force constants, or equivalently different polarizabilities along the parallel and perpendi ...
... molecules that are also polarizable the molecules are modeled as anisotropic Drude oscillators in which the electronic motion along the direction of the permanent dipole and perpendicular to it have different force constants, or equivalently different polarizabilities along the parallel and perpendi ...
Plasma Process 5 col..
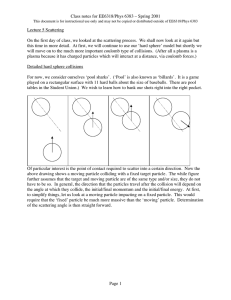
... Of particular interest is the point of contact required to scatter into a certain direction. Now the above drawing shows a moving particle colliding with a fixed target particle. The while figure further assumes that the target and moving particle are of the same type and/or size, they do not have t ...
... Of particular interest is the point of contact required to scatter into a certain direction. Now the above drawing shows a moving particle colliding with a fixed target particle. The while figure further assumes that the target and moving particle are of the same type and/or size, they do not have t ...
Isolated-core excitations in strong electric fields. II. Experimental results in magnesium
... indicate a predominant low-l character. In the 3p channel all states are mixed above 500 V/cm, in striking contrast to the 3s channel where we can clearly distinguish the low-l states in all fields. In order to compare the shakeup starting from various initial states, Fig. 4 shows the autoionization ...
... indicate a predominant low-l character. In the 3p channel all states are mixed above 500 V/cm, in striking contrast to the 3s channel where we can clearly distinguish the low-l states in all fields. In order to compare the shakeup starting from various initial states, Fig. 4 shows the autoionization ...
NON-RELATIVISTIC QUANTUM MECHANICS - Philsci
... come. More than subsequent sections, this section will rely heavily on the material from the mathematical appendix (§7), with references where appropriate. 1.1. The Thought Behind Starting with Formalism. Why begin an account of a physical theory with its formalism? Why not begin, instead, with its ...
... come. More than subsequent sections, this section will rely heavily on the material from the mathematical appendix (§7), with references where appropriate. 1.1. The Thought Behind Starting with Formalism. Why begin an account of a physical theory with its formalism? Why not begin, instead, with its ...
Bipolaron recombination in conjugated polymers Linköping University Post Print
... In organic LEDs, in which the carrier concentration is relatively low, polaron recombination is believed to be the normal electroluminescence channel. However, with the coexistence of polarons and bipolarons in mind, it is straightforward to conjecture a similar process where a negative bipolaron an ...
... In organic LEDs, in which the carrier concentration is relatively low, polaron recombination is believed to be the normal electroluminescence channel. However, with the coexistence of polarons and bipolarons in mind, it is straightforward to conjecture a similar process where a negative bipolaron an ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.