20101-viscera
... 20. The anti-asthmatic effect of Salbutamol is attributed to A. inhibition of intracellular cGMP B. blockade of M-receptor C. activation of adenylate cyclane D. stimulation of β2 receptor E. inhibition of phosphodiesterase Assay questions 1. Please tell the probable adverse reactions after long-time ...
... 20. The anti-asthmatic effect of Salbutamol is attributed to A. inhibition of intracellular cGMP B. blockade of M-receptor C. activation of adenylate cyclane D. stimulation of β2 receptor E. inhibition of phosphodiesterase Assay questions 1. Please tell the probable adverse reactions after long-time ...
Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
... Treatment of chronic inflammation requires use of these agents at doses above those used for analgesia and antipyresis (the incidence of adverse drug effect is increased). 2. Analgesia NSAIDs alleviate mild-to-moderate pain by decreasing PGE and PGF mediated increases pain receptor sensitivity. 3. ...
... Treatment of chronic inflammation requires use of these agents at doses above those used for analgesia and antipyresis (the incidence of adverse drug effect is increased). 2. Analgesia NSAIDs alleviate mild-to-moderate pain by decreasing PGE and PGF mediated increases pain receptor sensitivity. 3. ...
Memantine and Neuroprotection
... Relatively low-affinity, open-channel blocker — only enter channel when it is opened by agonist. Relatively fast off-rate: prevents accumulation in ion channels and interfering with subsequent normal synaptic transmission. ...
... Relatively low-affinity, open-channel blocker — only enter channel when it is opened by agonist. Relatively fast off-rate: prevents accumulation in ion channels and interfering with subsequent normal synaptic transmission. ...
Opioid Use and Maternal Health
... • Partial opioid agonist • Prevents withdrawal symptoms and cravings • Block euphoric effects of other opioids (higher affinity for opioid receptors) • Not a full agonist (less of a high) ...
... • Partial opioid agonist • Prevents withdrawal symptoms and cravings • Block euphoric effects of other opioids (higher affinity for opioid receptors) • Not a full agonist (less of a high) ...
Equine Medications, Forney, 2001
... substance or drug which could affect a horse’s performance or alter its natural conformation or appearance is prohibited except during surgical procedures performed by a duly licensed veterinarian for the sole purpose of protecting the health of the ...
... substance or drug which could affect a horse’s performance or alter its natural conformation or appearance is prohibited except during surgical procedures performed by a duly licensed veterinarian for the sole purpose of protecting the health of the ...
Introduction to Pharmacology
... structure of its receptor, employing at present suitable computer programs. Only few drugs in clinical use at present were developed in this rational way. Most drugs were in the past developed through random testing of chemicals , or modified molecules of known drugs that are known to have some othe ...
... structure of its receptor, employing at present suitable computer programs. Only few drugs in clinical use at present were developed in this rational way. Most drugs were in the past developed through random testing of chemicals , or modified molecules of known drugs that are known to have some othe ...
neuromuscular blocking agents and muscle relaxants
... 4. Therapeutic uses Mild hypertension. In higher doses it is used in endogenous psychoses. 5. Untoward effects Sedation, psychic depression (often results suicide), abdominal cramps and diarrhea, GIT ulceration, increased incidence of brest carcinoma 6. Toxicity Postural hypotension (low doses), se ...
... 4. Therapeutic uses Mild hypertension. In higher doses it is used in endogenous psychoses. 5. Untoward effects Sedation, psychic depression (often results suicide), abdominal cramps and diarrhea, GIT ulceration, increased incidence of brest carcinoma 6. Toxicity Postural hypotension (low doses), se ...
amphetamine sulphate
... Amphetamines are stimulant drugs that work on the central nervous system. They start working within fifteen minutes (faster if injected or smoked.) They cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. They make the user feel more alert, confident and give a sense of increased energy. They reduce ...
... Amphetamines are stimulant drugs that work on the central nervous system. They start working within fifteen minutes (faster if injected or smoked.) They cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. They make the user feel more alert, confident and give a sense of increased energy. They reduce ...
Pharmacologic Principles – Chapter 2
... Enzyme interactions with a drug either inhibit (most common) or enhance (least common) a biochemical reaction within the cell. Nonselective interactions physically alter cell membranes or cell processes. These drugs are most often in the form of antibiotics or cancer drugs. Pharmacotherpeutics - inc ...
... Enzyme interactions with a drug either inhibit (most common) or enhance (least common) a biochemical reaction within the cell. Nonselective interactions physically alter cell membranes or cell processes. These drugs are most often in the form of antibiotics or cancer drugs. Pharmacotherpeutics - inc ...
Management of Behavioural Symptoms of Dementia
... Name……………………………. D.O.B……………………………….. Date of Assessment………………….. Management should focus around early recognition and prevention of behavoural symptoms of dementia, using assessment and non drug management. Antipsychotics should only be prescribed as a last resort and for a defined length of time. T ...
... Name……………………………. D.O.B……………………………….. Date of Assessment………………….. Management should focus around early recognition and prevention of behavoural symptoms of dementia, using assessment and non drug management. Antipsychotics should only be prescribed as a last resort and for a defined length of time. T ...
our fact sheet.
... cells. CDP-choline is a precursor for the synthesis of phospholipids that are essential constituents of cell membranes, including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidyl-ethanolamine. Because cell membranes have a very high turnover rate, these phospholipids must be continuously sy ...
... cells. CDP-choline is a precursor for the synthesis of phospholipids that are essential constituents of cell membranes, including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidyl-ethanolamine. Because cell membranes have a very high turnover rate, these phospholipids must be continuously sy ...
Clinical Trials and Scientific Methods Chapter 0 Enrichment
... science, the plan for performing an experiment is called the procedure. In a clinical trial involving people, it is called a protocol. The protocol includes a description of the type of people who can participate, the schedule, medications, and length of the study. People who take part in a clinical ...
... science, the plan for performing an experiment is called the procedure. In a clinical trial involving people, it is called a protocol. The protocol includes a description of the type of people who can participate, the schedule, medications, and length of the study. People who take part in a clinical ...
The Most-Prescribed Systemic Medications – What Do They Mean in
... decrease dopamine-mediated neurotransmission, which diminishes the distractibility and improves perceptual abilities of schizophrenic patients. Dopamine is not the sole factor, however. Inhibitory interneurons are decreased in number, the enzymes that synthesize the inhibitor neurotransmitter GABA a ...
... decrease dopamine-mediated neurotransmission, which diminishes the distractibility and improves perceptual abilities of schizophrenic patients. Dopamine is not the sole factor, however. Inhibitory interneurons are decreased in number, the enzymes that synthesize the inhibitor neurotransmitter GABA a ...
what are psychoactive drugs? - Florida Alcohol and Drug Abuse
... Stimulants are used primarily to relieve fatigue and increase alertness. The most widely used stimulants are nicotine, which is found in tobacco products, and caffeine, which is found in soft drinks, coffee and tea. Cocaine and amphetamines are more potent stimulants. People who use stimulants build ...
... Stimulants are used primarily to relieve fatigue and increase alertness. The most widely used stimulants are nicotine, which is found in tobacco products, and caffeine, which is found in soft drinks, coffee and tea. Cocaine and amphetamines are more potent stimulants. People who use stimulants build ...
B3.1 L11 Medicinal Plants
... for cuts and bruises. • Lemon balm - soothes nervous tension and anxiety, promotes sleep, and is good for cold sores. • Peppermint - good for digestion, wind and headaches. ...
... for cuts and bruises. • Lemon balm - soothes nervous tension and anxiety, promotes sleep, and is good for cold sores. • Peppermint - good for digestion, wind and headaches. ...
CYP2C9 Master Drug List
... Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) with decreased activity. Still another 28% of people are UltraRapid Metabolizers. Both IMs and PMs exhibit decreased metabolic activity, which puts them at risk for side effects to drugs normally inactivated by 2C19 (e.g.,sertraline, diazepam), or lack of efficacy for ...
... Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) with decreased activity. Still another 28% of people are UltraRapid Metabolizers. Both IMs and PMs exhibit decreased metabolic activity, which puts them at risk for side effects to drugs normally inactivated by 2C19 (e.g.,sertraline, diazepam), or lack of efficacy for ...
494 - The AIDS InfoNet
... interactions can cause a serious, possibly fatal increase in the level of recreational drugs. There is little research on the effects of interactions between ARVs and recreational drugs on the human body. This is because the use of recreational drugs is illegal and they cannot be provided to people ...
... interactions can cause a serious, possibly fatal increase in the level of recreational drugs. There is little research on the effects of interactions between ARVs and recreational drugs on the human body. This is because the use of recreational drugs is illegal and they cannot be provided to people ...
Nuclear Receptor Program Fact Sheet Plexxikon
... processes, including those involved in diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Many important therapeutics, including 12 of the top 100 selling drugs, target nuclear receptors. Plexxikon has focused discovery efforts on novel therapeutics targeting several members of the nuclear recept ...
... processes, including those involved in diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Many important therapeutics, including 12 of the top 100 selling drugs, target nuclear receptors. Plexxikon has focused discovery efforts on novel therapeutics targeting several members of the nuclear recept ...
Neurological and anxiety disorders pp
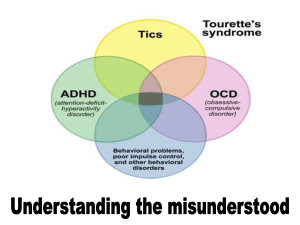
... -specialised brain cells involved in helping regulate the physical movements of the body -higher brain functions such as motivation and decision-making -temporary disruption scrambling decision making - sudden development unconscious motivation to perform an action (the tic) that the conscious mind ...
... -specialised brain cells involved in helping regulate the physical movements of the body -higher brain functions such as motivation and decision-making -temporary disruption scrambling decision making - sudden development unconscious motivation to perform an action (the tic) that the conscious mind ...
No End in Sight: The Abuse of Prescription Narcotics
... There are at least three major sub-types of opioid receptors: mu, delta, and kappa. Each of these, particularly the mu receptor, have multiple sub-types (some estimates put the total number of opioid receptors at 25 to 30). Furthermore, while there is considerable overlap of receptor networks in the ...
... There are at least three major sub-types of opioid receptors: mu, delta, and kappa. Each of these, particularly the mu receptor, have multiple sub-types (some estimates put the total number of opioid receptors at 25 to 30). Furthermore, while there is considerable overlap of receptor networks in the ...
sedation and pain management for routine
... restlessness and anxiety. Opioid drugs are classified as agonists (meaning they stimulate the opioid receptors) or antagonists (meaning they block particular opioid receptors). There are also mixed agonist/antagonist opioids that stimulate some receptors while blocking others as well as partial ...
... restlessness and anxiety. Opioid drugs are classified as agonists (meaning they stimulate the opioid receptors) or antagonists (meaning they block particular opioid receptors). There are also mixed agonist/antagonist opioids that stimulate some receptors while blocking others as well as partial ...
Antidepressant Choices in Primary Care
... tine), and constipation (worse with paroxetine and venlafaxine). Taking the medications with food, starting at one-half of the lowest target dose, and increasing dosages slowly helps to minimize this. Mirtazapine, an atypical antidepressant, generally does not cause these side effects, but may incre ...
... tine), and constipation (worse with paroxetine and venlafaxine). Taking the medications with food, starting at one-half of the lowest target dose, and increasing dosages slowly helps to minimize this. Mirtazapine, an atypical antidepressant, generally does not cause these side effects, but may incre ...
Psychopharmacology

Psychopharmacology (from Greek ψῡχή, psȳkhē, ""breath, life, soul""; φάρμακον, pharmakon, ""drug""; and -λογία, -logia) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain.Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and their receptors is referred to as ""drug action"", and the widespread changes in physiological or psychological function is referred to as ""drug effect"". These drugs may originate from natural sources such as plants and animals, or from artificial sources such as chemical synthesis in the laboratory.