Dopamin
... • Drug affinities of most neuroleptics for the D2 receptor reflect their potencies in treating schizophrenia. • The various receptors show different anatomic distributions. • The D4 receptor binds the atypical neuroleptic clozapine with an affinity ten times higher than that of D2 sites. ...
... • Drug affinities of most neuroleptics for the D2 receptor reflect their potencies in treating schizophrenia. • The various receptors show different anatomic distributions. • The D4 receptor binds the atypical neuroleptic clozapine with an affinity ten times higher than that of D2 sites. ...
Document
... Adrenergic Receptor Agonists • Termed sympathomimetic drugs • Divided into three groups • Direct-acting agonists – Catecholamines – Noncatecholamines ...
... Adrenergic Receptor Agonists • Termed sympathomimetic drugs • Divided into three groups • Direct-acting agonists – Catecholamines – Noncatecholamines ...
Summary overview: Gi and Gs G-protein coupled receptors - Di-Et-Tri
... - Receptors : macromolecules including enzymes, transporters, structures on cell membranes, transcription factors, nucleotides etc. - Receptors are mostly normal regulatory structures playing a role in the physiology of the organism. - Natural ligands: neurotransmitters, hormones or other signalling ...
... - Receptors : macromolecules including enzymes, transporters, structures on cell membranes, transcription factors, nucleotides etc. - Receptors are mostly normal regulatory structures playing a role in the physiology of the organism. - Natural ligands: neurotransmitters, hormones or other signalling ...
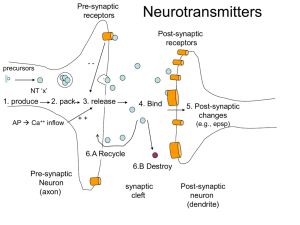
1. Neurotransmitter released from the pre
... 13. Ways by which the effects on the postsynaptic cell can be enhanced are: a. Presynaptic facilitation b. High frequency of action potentials in the presynaptic terminal c. Adding an agonist for the receptors on the postsynaptic cell d. Blocking the reuptake of NT into the presynaptic terminal e. ...
... 13. Ways by which the effects on the postsynaptic cell can be enhanced are: a. Presynaptic facilitation b. High frequency of action potentials in the presynaptic terminal c. Adding an agonist for the receptors on the postsynaptic cell d. Blocking the reuptake of NT into the presynaptic terminal e. ...
Document
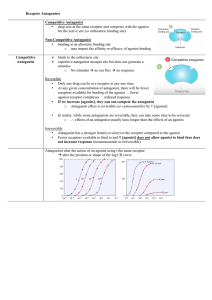
... A small # of drugs produce their physiological effect without interacting with receptors. Examples: Drugs that bind to enzymes interfere with the normal activity of the enzyme in one of 2 ways CompetitiveNon-competitiveDrugs can also bind to membrane transport proteins (competitively and non-compet ...
... A small # of drugs produce their physiological effect without interacting with receptors. Examples: Drugs that bind to enzymes interfere with the normal activity of the enzyme in one of 2 ways CompetitiveNon-competitiveDrugs can also bind to membrane transport proteins (competitively and non-compet ...
Serotonin (5-HT) - Addiction Science Network
... bodies, slows firing rate of serotonergic neurons Current theories focus on glutamate release in thalamocortical terminals, causing dissociation between sensory relay and cortical output ...
... bodies, slows firing rate of serotonergic neurons Current theories focus on glutamate release in thalamocortical terminals, causing dissociation between sensory relay and cortical output ...
Drugs - BIDD - National University of Singapore
... 1-Adrenoceptor agonists: These can be used to treat hypotension through vasoconstriction, leading to increased blood pressure and cardiac arrhythmias through activation of vagal reflexes. Also valuable adjuncts to local anaesthetics, as vasoconstriction can slow the systemic dispersal of the ...
... 1-Adrenoceptor agonists: These can be used to treat hypotension through vasoconstriction, leading to increased blood pressure and cardiac arrhythmias through activation of vagal reflexes. Also valuable adjuncts to local anaesthetics, as vasoconstriction can slow the systemic dispersal of the ...
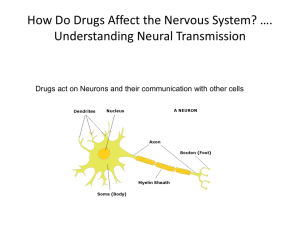
Neural Transmission - People Server at UNCW
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. • Implicated in relaxation/anti-anxiety ...
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. • Implicated in relaxation/anti-anxiety ...
Non-depolarizing blocking agents
... motoneurons. At this point, full neuromuscular block has been achieved. The prototypical depolarizing blocking drug is succinylcholine (suxamethonium). It is the only such drug used clinically. It has a rapid onset (30 seconds) but very short duration of action (5–10 minutes) because of hydrolysis b ...
... motoneurons. At this point, full neuromuscular block has been achieved. The prototypical depolarizing blocking drug is succinylcholine (suxamethonium). It is the only such drug used clinically. It has a rapid onset (30 seconds) but very short duration of action (5–10 minutes) because of hydrolysis b ...
HST-151
... neurons, the release of glutamate (an excitatory neurotransmitter) from cells in the CNS (hippocampus), and even the release of norepinephrine from the endings of postganglionic sympathetic fibers in the heart and vasculature. The ionic basis for these inhibitory effects is not established, but both ...
... neurons, the release of glutamate (an excitatory neurotransmitter) from cells in the CNS (hippocampus), and even the release of norepinephrine from the endings of postganglionic sympathetic fibers in the heart and vasculature. The ionic basis for these inhibitory effects is not established, but both ...
Pharmacology Objectives 2
... iii. Difference in action of stereoisomers, e.g. dextrophan(-) and levophranol(+). iv. Competitive antagonists block specific targets, e.g. atropine blocks acetylcholine but not norepinephrine or other neurotransmitters. v. Biochemical radioligand studies show specific sites binding certain drugs. v ...
... iii. Difference in action of stereoisomers, e.g. dextrophan(-) and levophranol(+). iv. Competitive antagonists block specific targets, e.g. atropine blocks acetylcholine but not norepinephrine or other neurotransmitters. v. Biochemical radioligand studies show specific sites binding certain drugs. v ...
parasympathomimetic drugs
... Acetylcholine & other Choline esters have a permanently charged quaternary ammonium group in their structure All are hydrolysed in the GIT ...
... Acetylcholine & other Choline esters have a permanently charged quaternary ammonium group in their structure All are hydrolysed in the GIT ...
Specific NT systems
... – Increase the effect of neurotransmitter X (agonist) – Decrease the effect of neurotransmitter X (antagonist) Thus, in order to understand the action of a ‘drug Y’, we need to understand the neurochemical system it interacts with. In other words, we need to understand how Neurotransmitter X - is pr ...
... – Increase the effect of neurotransmitter X (agonist) – Decrease the effect of neurotransmitter X (antagonist) Thus, in order to understand the action of a ‘drug Y’, we need to understand the neurochemical system it interacts with. In other words, we need to understand how Neurotransmitter X - is pr ...
Nicotinic agonist

A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine.Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine.