PDF - Pediatric Neurology Briefs
... proximal shunt failure is most commonly caused by over-drainage of CSF and collapse of the ventricular walls around the catheter. The valve and DRS system are replaced. 3) Normal volume hydrocephalus with symptoms of ICP and headaches developing in the morning and progressing, a common problem with ...
... proximal shunt failure is most commonly caused by over-drainage of CSF and collapse of the ventricular walls around the catheter. The valve and DRS system are replaced. 3) Normal volume hydrocephalus with symptoms of ICP and headaches developing in the morning and progressing, a common problem with ...
can - Austin Community College
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
can - Austin Community College
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
Functional Classification
... Prevalence- approximately 60 per 100,000 births; Prevalences higher among Latino and female offspring. The causes- both environmental and genetic factors Exposure to alcohol Valproic acid, carbamazepine, or isotretinoin hyperthermia Malnutrition (especially folate deficiency) Diabetes and obesity My ...
... Prevalence- approximately 60 per 100,000 births; Prevalences higher among Latino and female offspring. The causes- both environmental and genetic factors Exposure to alcohol Valproic acid, carbamazepine, or isotretinoin hyperthermia Malnutrition (especially folate deficiency) Diabetes and obesity My ...
Magnetic resonance imaging indicators of blood
... Results: In nonhydrocephalic rats, water content decreased progressively from age 3 to 7 weeks. T1 and T2 and apparent diffusion coefficients did not exhibit parallel changes and there was no evidence of BBB permeability to tracers. The cerebral ventricles enlarged progressively in the weeks followi ...
... Results: In nonhydrocephalic rats, water content decreased progressively from age 3 to 7 weeks. T1 and T2 and apparent diffusion coefficients did not exhibit parallel changes and there was no evidence of BBB permeability to tracers. The cerebral ventricles enlarged progressively in the weeks followi ...
Ch 28 CNS Money [5-11
... o elderly and infants at risk o lysis growth of fibroblasts into hematoma early development of hyalinized CT, o fresh clotted blood on brain surface; underlying brain flattened o chronic subdural hematomas = repeat episodes of bleeding (greatest risk after 1st hemorrhage) o most common over late ...
... o elderly and infants at risk o lysis growth of fibroblasts into hematoma early development of hyalinized CT, o fresh clotted blood on brain surface; underlying brain flattened o chronic subdural hematomas = repeat episodes of bleeding (greatest risk after 1st hemorrhage) o most common over late ...
Erin Hardie
... other ocular findings were attributed to her newly discovered neurological maldevelopment and the patient was educated on the findings. Her clinical presentation was considered a combination of both hydrocephalus and a absence of the posterior corpus callosum. Below is a review of the pathogenesis, ...
... other ocular findings were attributed to her newly discovered neurological maldevelopment and the patient was educated on the findings. Her clinical presentation was considered a combination of both hydrocephalus and a absence of the posterior corpus callosum. Below is a review of the pathogenesis, ...
ASAL USUL
... gross and fine motor functions, balance, control, reflexes, posture. Oral motor dysfunction, such as swallowing and feeding difficulties, speech impairment, and poor muscle tone in the face, – Associative conditions, such as sensory impairment, seizures, and learning disabilities that are not a resu ...
... gross and fine motor functions, balance, control, reflexes, posture. Oral motor dysfunction, such as swallowing and feeding difficulties, speech impairment, and poor muscle tone in the face, – Associative conditions, such as sensory impairment, seizures, and learning disabilities that are not a resu ...
PSY550 Research and Ingestion
... – The aqueous solution of formaldehyde gas; the most commonly used tissue fixative. • perfusion – The process by which an animal’s blood is replaced by fluid such as a saline solution or fixative in preparing the brain for histological examination. • microtome – An instrument that produces very thin ...
... – The aqueous solution of formaldehyde gas; the most commonly used tissue fixative. • perfusion – The process by which an animal’s blood is replaced by fluid such as a saline solution or fixative in preparing the brain for histological examination. • microtome – An instrument that produces very thin ...
History of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System
... Dandy-Walker Malformation -Enlarged posterior fossa -Cerebellar vermis is absent (associated w/ posture and locomotion) -Large midline cyst lined w/ ependymal and contiguous w/ leptomeninges represents the 4th ventricle and replaces the cerebellar vermis ...
... Dandy-Walker Malformation -Enlarged posterior fossa -Cerebellar vermis is absent (associated w/ posture and locomotion) -Large midline cyst lined w/ ependymal and contiguous w/ leptomeninges represents the 4th ventricle and replaces the cerebellar vermis ...
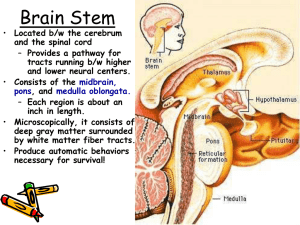
Brain - El Camino College
... General Motor area lies in front of central sulcus and control voluntary movements of skeletal ...
... General Motor area lies in front of central sulcus and control voluntary movements of skeletal ...
Slide 1
... 2 malformation (cerebellar vermis migrates into the spinal canal, blocking CSF flow out of ventricles. (Ventricles swell). ...
... 2 malformation (cerebellar vermis migrates into the spinal canal, blocking CSF flow out of ventricles. (Ventricles swell). ...
The Brain
... Surround blood vessels that penetrate brain tissue. *The skull is a mixed blessing. It protects the brain from outside mechanical damage, but the brain requires protection from hitting the hard cranial surface. (like a motorist in a car w/out a seat belt). ...
... Surround blood vessels that penetrate brain tissue. *The skull is a mixed blessing. It protects the brain from outside mechanical damage, but the brain requires protection from hitting the hard cranial surface. (like a motorist in a car w/out a seat belt). ...
Central Nervous System
... Functions of the Cerebral Cortex - Emotions • Experiencing and expressing emotions involves the function of the limbic system – Area of the brain that surrounds the corpus callosum – For proper expression the limbic system functions with the cerebral cortex ...
... Functions of the Cerebral Cortex - Emotions • Experiencing and expressing emotions involves the function of the limbic system – Area of the brain that surrounds the corpus callosum – For proper expression the limbic system functions with the cerebral cortex ...
Chapter 11
... of s.c. & CSF is withdrawn • Site is usually b/t L1-L2 or L3-L4 (a.k.a. spinal tap) • A manometer used to measure CSF pressure • CSF can be analyzed for viruses, bacteria, bleeding, tumors of the n.s., MS, & early-onset Alzheimers ...
... of s.c. & CSF is withdrawn • Site is usually b/t L1-L2 or L3-L4 (a.k.a. spinal tap) • A manometer used to measure CSF pressure • CSF can be analyzed for viruses, bacteria, bleeding, tumors of the n.s., MS, & early-onset Alzheimers ...
Topic 8
... waste from the central nervous system through the blood-brain barrier. This allows for homeostatic regulation and distribution of neuroendocrine factors. 4. Prevention of brain ischemia: made by decreasing the amount of CSF in the limited space inside the skull. This decreases total intracranial pre ...
... waste from the central nervous system through the blood-brain barrier. This allows for homeostatic regulation and distribution of neuroendocrine factors. 4. Prevention of brain ischemia: made by decreasing the amount of CSF in the limited space inside the skull. This decreases total intracranial pre ...
PATHOLOGY/HISTOLOGY TEST KIT 6C: MORE BRAIN (26 vials)
... miasm / inherited taint represented by the chronic disease, e.g. the tubercular and syphilitic miasms are well known among homeopaths; these do not indicate the presence of the disease, but indicate a chronic tendency to manifest particular symptoms: the person with a tubercular miasm is always ner ...
... miasm / inherited taint represented by the chronic disease, e.g. the tubercular and syphilitic miasms are well known among homeopaths; these do not indicate the presence of the disease, but indicate a chronic tendency to manifest particular symptoms: the person with a tubercular miasm is always ner ...
Bio_257_Unit_3_17
... into the ventricles. They also remove waste products from the CSF and adjust its composition over time. CSF differs markedly from blood in its [soluble protein] and cellular content. • About 500mL of CSF is produced per day. The total volume of CSF at any given moment is 150mL • CSF circulates from ...
... into the ventricles. They also remove waste products from the CSF and adjust its composition over time. CSF differs markedly from blood in its [soluble protein] and cellular content. • About 500mL of CSF is produced per day. The total volume of CSF at any given moment is 150mL • CSF circulates from ...
Nervous System Bookwork—KEY
... generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way conduction occurs at synapse because axons (not dendrites) release the neurotran ...
... generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way conduction occurs at synapse because axons (not dendrites) release the neurotran ...
THE_NERVOUS_SYSTEM_(Part_I)
... 1. Protection – acts to cushion a blow to the head and lesson impact 2. Buoyancy – because brain is in fluid its net weight is reduced and pressure at the base of the brain is reduced ...
... 1. Protection – acts to cushion a blow to the head and lesson impact 2. Buoyancy – because brain is in fluid its net weight is reduced and pressure at the base of the brain is reduced ...
Hydrocephalus

Hydrocephalus (from Greek hydro-, meaning ""water"", and kephalos, meaning ""head"") is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain. This causes increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and may cause progressive enlargement of the head if it occurs in childhood, potentially causing convulsion, tunnel vision, and mental disability. It was once informally called ""Water on the brain.""Hydrocephalus can be caused by congenital or acquired factors. Congenital causes include Spina Bifida, Arnold–Chiari malformation, craniosynostosis, Dandy–Walker syndrome, and Vein of Galen malformations. Acquired causes include hemorrhage, meningitis, head trauma, tumors, and cysts.Two types of hydrocephalus are commonly described non-communicating hydrocephalus and communicating hydrocephalus, although there is evidence that communicating forms can lead to obstruction of CSF flow in many instances.In non-communicating hydrocephalus, the CSF in the ventricles can not reach the subarachnoid space. This results from obstruction of interventricular foramina, cerebral aqueduct, or the outflow foramens of the fourth ventricle (median and lateral apertures). The most common obstruction is in the cerebral aqueduct. A block at any of these sites leads rapidly to dilatation of one or more ventricles. If the skull is still pliable, as it is in children younger than 2 years, the head may enlarge.In communicating hydrocephalus, the obstruction of CSF flow is in the subarachnoid space from prior bleeding or meningitis. This causes thickening of the arachnoid leading to blockage of the return-flow channels. In some patients, the spaces filled by CSF are uniformly enlarged without an increase in intercranial pressure. This special form of communicating hydrocephalus is called normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), which results specifically from impaired CSF reabsorption at the arachnoid granulations. NPH's clinical manifestations are gait abnormality, dementia, and involuntary urination. NPH usually occurs in elderly patients.