We`re more than just cables and cord sets. Terminology Term and
... Direct Current. Current which moves in a single direction in a steady flow. Normal household electricity is alternating current (AC) which repeatedly reverses its direction. However, many electronics devices require DC, and therefore must convert the current into DC before using it. Ferrite Ferrimag ...
... Direct Current. Current which moves in a single direction in a steady flow. Normal household electricity is alternating current (AC) which repeatedly reverses its direction. However, many electronics devices require DC, and therefore must convert the current into DC before using it. Ferrite Ferrimag ...
Combinations of Capacitors
... Such a circuit could be used to switch to back-up power. Unfortunately there may be a time delay in such a circuit, so something more sophisticated is needed. ...
... Such a circuit could be used to switch to back-up power. Unfortunately there may be a time delay in such a circuit, so something more sophisticated is needed. ...
170M____
... is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information that will help the end user with design applications. Bussmann reserves the right, without notice, to change design or construction of any products and to discontinue or limit distribution of any products. Bu ...
... is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information that will help the end user with design applications. Bussmann reserves the right, without notice, to change design or construction of any products and to discontinue or limit distribution of any products. Bu ...
section 260573 - electrical systems analysis
... A preliminary power flow study and a complete protective device coordination study. Submit no later than ___ days after approval of the preliminary short circuit study. Distribution equipment shop drawings clearly indicating that the ratings of proposed equipment meet or exceed the ratings recommend ...
... A preliminary power flow study and a complete protective device coordination study. Submit no later than ___ days after approval of the preliminary short circuit study. Distribution equipment shop drawings clearly indicating that the ratings of proposed equipment meet or exceed the ratings recommend ...
Period 14 Activity Sheet: Electrical Safety and Transmission
... part of the circuit during normal operation of an appliance? ...
... part of the circuit during normal operation of an appliance? ...
Application Note Protecting Low Current Loads in Harsh
... resistor. A TVS with lower power rating is able to handle the resulting current. In this case a 500 W suppressor, such as the SA28A TVS, replaces the 5 kW device, saving board space and cost. An SA28A was chosen in this example since its current rating for a 10/1000 µs pulse is 11 A, easily withstan ...
... resistor. A TVS with lower power rating is able to handle the resulting current. In this case a 500 W suppressor, such as the SA28A TVS, replaces the 5 kW device, saving board space and cost. An SA28A was chosen in this example since its current rating for a 10/1000 µs pulse is 11 A, easily withstan ...
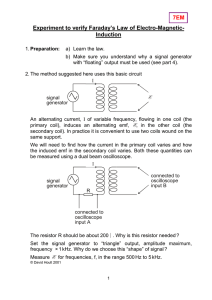
Experiment to verify Faraday’s Law of Electro-Magnetic- Induction 7EM
... maintain a constant peak voltage - why resistor R is needed - how your results verify Faraday’s law (assuming that they do !) Your report should also include a diagram showing what you saw on the oscilloscope screen. 4. The experiment will be done using a coil like the one shown below. In this case ...
... maintain a constant peak voltage - why resistor R is needed - how your results verify Faraday’s law (assuming that they do !) Your report should also include a diagram showing what you saw on the oscilloscope screen. 4. The experiment will be done using a coil like the one shown below. In this case ...
08-15 NewsLetters
... to unplug devices from the wall if you suspect a surge might be coming. Power strips do NOT provide surge protection. Be sure you are relying on the appropriate device for protection. Power strips and surge suppressors don't provide more power to a location, only more access to the same limited capa ...
... to unplug devices from the wall if you suspect a surge might be coming. Power strips do NOT provide surge protection. Be sure you are relying on the appropriate device for protection. Power strips and surge suppressors don't provide more power to a location, only more access to the same limited capa ...
Line to Ground Voltage Monitoring on Ungrounded
... worst conditions. The worst case burden is placed on the transformer during a line to ground fault. During a line to ground fault the voltage across the transformer will be equal to the system line to line voltage, providing maximum current flow. The value of “R” is selected such that transformer’s ...
... worst conditions. The worst case burden is placed on the transformer during a line to ground fault. During a line to ground fault the voltage across the transformer will be equal to the system line to line voltage, providing maximum current flow. The value of “R” is selected such that transformer’s ...
Data sheet PCT2000
... ten times higher overload capability, only. If the cables or jacks are not sufficient they could be interrupted in case of overload! For the same reason it is not allowed to use fuses in this current measurement wires. Before using jacks, test if they have a low impedance current path to prevent high ...
... ten times higher overload capability, only. If the cables or jacks are not sufficient they could be interrupted in case of overload! For the same reason it is not allowed to use fuses in this current measurement wires. Before using jacks, test if they have a low impedance current path to prevent high ...
Aim: The goal of this project is to study a Linear variable differential
... The goal of this project is to study a Linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) , typical characteristic of measuring devices and possible applications. Apparatus: LVDT, micrometer, analog transducer amplifier Theory Operating principle: Electromagnetic Induction Whenever the flux linkage thro ...
... The goal of this project is to study a Linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) , typical characteristic of measuring devices and possible applications. Apparatus: LVDT, micrometer, analog transducer amplifier Theory Operating principle: Electromagnetic Induction Whenever the flux linkage thro ...
Harmonics and Flicker Analysis in a Three phase
... mainly related to the non-linear voltage-current characteristic of the arc while the voltage fluctuations are due to the arc length changes that occur during the melting of the scrap. The current and voltage harmonic distortion leads to several problems in electrical power systems, namely incorrect ...
... mainly related to the non-linear voltage-current characteristic of the arc while the voltage fluctuations are due to the arc length changes that occur during the melting of the scrap. The current and voltage harmonic distortion leads to several problems in electrical power systems, namely incorrect ...
Kelvin Coaxial Probes
... A Kelvin probe is a coaxial contact probe with two electrically insulated measuring circuits. The typical 4-wire-methode is based on a constant current, flowing through the test resistance and the measurement of the resulting drop in voltage, which is directly proportional to the resistance value. A ...
... A Kelvin probe is a coaxial contact probe with two electrically insulated measuring circuits. The typical 4-wire-methode is based on a constant current, flowing through the test resistance and the measurement of the resulting drop in voltage, which is directly proportional to the resistance value. A ...
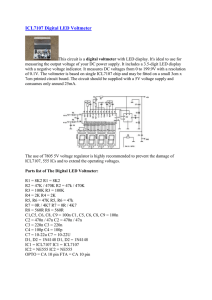
ICL7107 Digital LED Voltmeter
... of 0.1V. The voltmeter is based on single ICL7107 chip and may be fitted on a small 3cm x 7cm printed circuit board. The circuit should be supplied with a 5V voltage supply and consumes only around 25mA. ...
... of 0.1V. The voltmeter is based on single ICL7107 chip and may be fitted on a small 3cm x 7cm printed circuit board. The circuit should be supplied with a 5V voltage supply and consumes only around 25mA. ...
Chapter 20 Chapter 20 - Electricity Electricity
... • Answer: – A closed path that allows an electrical current to flow from a power source (i.e., batteries). Electricity flows from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. – If there are any “breaks” in the loop, electricity will not flow! – There are two types of circuits we will build: 1. Se ...
... • Answer: – A closed path that allows an electrical current to flow from a power source (i.e., batteries). Electricity flows from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. – If there are any “breaks” in the loop, electricity will not flow! – There are two types of circuits we will build: 1. Se ...
Type BR (1-inch) dual purpose arc fault/ground fault circuit
... connections in appliances or fixtures, or in contacts within equipment. Resolution: Identify the equipment causing the tripping, and repair or replace. Parallel arc Description: A high current arc has been detected between two conductors. High current arcs are typically parallel arcs, and are usuall ...
... connections in appliances or fixtures, or in contacts within equipment. Resolution: Identify the equipment causing the tripping, and repair or replace. Parallel arc Description: A high current arc has been detected between two conductors. High current arcs are typically parallel arcs, and are usuall ...
Transient Overvoltage Protection
... resistive, inductive and capacitive effects can cause transients as discharge currents attempt to flow through conductors/circuits and other electrical equipment. Electrical switching interrupts established magnetic fields, releasing stored energy from those fields, causing transient overvoltages as ...
... resistive, inductive and capacitive effects can cause transients as discharge currents attempt to flow through conductors/circuits and other electrical equipment. Electrical switching interrupts established magnetic fields, releasing stored energy from those fields, causing transient overvoltages as ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.