AC Measurements using Oscilloscope
... Your adjustments basically depends on two buttons, they are ”VOLTS/DIV” and ”TIME/DIV”. Notice that the ”VOLTS/DIV.” button changes your scale vertically and the ”TIME/DIV” changes your scale horizontally. 5) Adjust the frequency of the AC power supply from the heathkit trainer using the button on t ...
... Your adjustments basically depends on two buttons, they are ”VOLTS/DIV” and ”TIME/DIV”. Notice that the ”VOLTS/DIV.” button changes your scale vertically and the ”TIME/DIV” changes your scale horizontally. 5) Adjust the frequency of the AC power supply from the heathkit trainer using the button on t ...
Bears and Electric Fencing
... There are a number of different post types available for electric fencing, the most common being wooden, metal T-posts, fiberglass and plastic. Wooden and metal posts are typically more expensive and require the added expense of insulators, however they are more durable than plastic and fiberglass p ...
... There are a number of different post types available for electric fencing, the most common being wooden, metal T-posts, fiberglass and plastic. Wooden and metal posts are typically more expensive and require the added expense of insulators, however they are more durable than plastic and fiberglass p ...
LTS15-NP, LEM, current sensor 15Arms, Vout, +5V supply.pdf
... Please see the operation principle on the other side Only due to TCR IM. ...
... Please see the operation principle on the other side Only due to TCR IM. ...
IEEE Paper Template in A4 (V1) - Academic Science,International
... by following type of faults: Electrically related faults (33%): The faults come under this classification are over/under voltage, over load, phase reversing, unbalanced voltage, single phasing and earth fault. Mechanically related faults (32%): The rotor winding failure, stator winding failure and b ...
... by following type of faults: Electrically related faults (33%): The faults come under this classification are over/under voltage, over load, phase reversing, unbalanced voltage, single phasing and earth fault. Mechanically related faults (32%): The rotor winding failure, stator winding failure and b ...
TAINY GMOD-S3
... separating ability between the device and the battery. Take note of the technical data in the user manual as well as the installation and use regulations of the respective manufacturer of the power supply, battery or accumulator. ...
... separating ability between the device and the battery. Take note of the technical data in the user manual as well as the installation and use regulations of the respective manufacturer of the power supply, battery or accumulator. ...
Guide to Ohm Readings-fax
... Why? We do a quick and simple Ohms test to make sure no breaks or shorts have occurred that could affect the system’s performance. When? We advise that Ohm readings be taken before, during and after installation and that these are recorded for future reference. ...
... Why? We do a quick and simple Ohms test to make sure no breaks or shorts have occurred that could affect the system’s performance. When? We advise that Ohm readings be taken before, during and after installation and that these are recorded for future reference. ...
Digital OLTC Voltage Controller TAPCON® 250
... To avoid shock hazard, the chassis must be connected to an electrical ground. When servicing the TAPCON® 250 in a test area, the protective earth terminal must be attached to a seperate ground securely by use of a tool since it is not grounded by external connectors. ...
... To avoid shock hazard, the chassis must be connected to an electrical ground. When servicing the TAPCON® 250 in a test area, the protective earth terminal must be attached to a seperate ground securely by use of a tool since it is not grounded by external connectors. ...
Designing Wide Range Power Supplies for Three Phase Industrial
... across Q1 and U1 (due to leakage inductance) during the flyback interval. The circuit on the secondary of transformer T1 provides output rectification, filtering and feedback. Diode D10 rectifies the output. Capacitor C2 filters the rectified output. Inductor L2 and capacitor C3 form a second-stage ...
... across Q1 and U1 (due to leakage inductance) during the flyback interval. The circuit on the secondary of transformer T1 provides output rectification, filtering and feedback. Diode D10 rectifies the output. Capacitor C2 filters the rectified output. Inductor L2 and capacitor C3 form a second-stage ...
designs
... gate biasing configurations (Figure 3). In circuit “a”, which is used in the amplifier described here, D1 serves a purpose of preventing positive voltage from getting fed back to the bias source in case of a draingate short in a FET. This protects the other three devices from gate overvoltage. C1 – ...
... gate biasing configurations (Figure 3). In circuit “a”, which is used in the amplifier described here, D1 serves a purpose of preventing positive voltage from getting fed back to the bias source in case of a draingate short in a FET. This protects the other three devices from gate overvoltage. C1 – ...
Power Integrations
... run right through the capacitor lead pads and that no additional PC traces have been placed in series with C3. Note also that PC traces in series with L1 and the PC trace connecting C2 and C3 can be narrower and longer because current flow is essentially DC. 13) Heat sinks should be either connected ...
... run right through the capacitor lead pads and that no additional PC traces have been placed in series with C3. Note also that PC traces in series with L1 and the PC trace connecting C2 and C3 can be narrower and longer because current flow is essentially DC. 13) Heat sinks should be either connected ...
600 Watt SMB Transient Voltage Suppressor, 12 V, Bidirectional
... protected. In this situation, there is a time delay associated with the capacitance of the device and an overshoot condition associated with the inductance of the device and the inductance of the connection method. The capacitive effect is of minor importance in the parallel protection scheme becaus ...
... protected. In this situation, there is a time delay associated with the capacitance of the device and an overshoot condition associated with the inductance of the device and the inductance of the connection method. The capacitive effect is of minor importance in the parallel protection scheme becaus ...
Relay coupler
... The IM73-12-R/24VUC 1-channel relay coupler is particularly suitable for use as a coupling module for the safe galvanic isolation of binary signals. 2 synchronous controlled relays, each with 1 changeover contact are provided at the output. ...
... The IM73-12-R/24VUC 1-channel relay coupler is particularly suitable for use as a coupling module for the safe galvanic isolation of binary signals. 2 synchronous controlled relays, each with 1 changeover contact are provided at the output. ...
Optically Isolated - Dionics-USA
... The DIG-1185 Photovoltaic is a State-of- the-Art, optically coupled floating power source used primarily to control MOSFET/IGBT’s when electrical isolation between input and output is required. It is particularly well suited for Medical implant applications. In addition to the infrared LED and photo ...
... The DIG-1185 Photovoltaic is a State-of- the-Art, optically coupled floating power source used primarily to control MOSFET/IGBT’s when electrical isolation between input and output is required. It is particularly well suited for Medical implant applications. In addition to the infrared LED and photo ...
25471_energy_conversion_5
... • As seen in last Example, solving cct. containing transformers requires tedious operation to refer all voltages to a common level • In another approach, the need mentioned above is eliminated& impedance transformation is avoided • That method is known as per-unit system of measurement ...
... • As seen in last Example, solving cct. containing transformers requires tedious operation to refer all voltages to a common level • In another approach, the need mentioned above is eliminated& impedance transformation is avoided • That method is known as per-unit system of measurement ...
Description Features Ordering Information Outline Dimensions unit
... Supply Voltage of output driver and control circuits. ...
... Supply Voltage of output driver and control circuits. ...
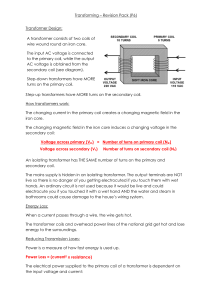
Transforming – Revision Pack (P6) Transformer Design: Step
... secondary coil. The mains supply is hidden in an isolating transformer. The output terminals are NOT live so there is no danger of you getting electrocuted if you touch them with wet hands. An ordinary circuit is not used because it would be live and could electrocute you if you touched it with a we ...
... secondary coil. The mains supply is hidden in an isolating transformer. The output terminals are NOT live so there is no danger of you getting electrocuted if you touch them with wet hands. An ordinary circuit is not used because it would be live and could electrocute you if you touched it with a we ...
Electrical Safety
... metals, with little resistance to electricity that allow electricity to flow • Insulators -- substances with high resistance to electricity like glass, porcelain, plastic, and dry wood that prevent electricity from getting to unwanted areas • Voltage—measure of electrical force OSHA Office of Traini ...
... metals, with little resistance to electricity that allow electricity to flow • Insulators -- substances with high resistance to electricity like glass, porcelain, plastic, and dry wood that prevent electricity from getting to unwanted areas • Voltage—measure of electrical force OSHA Office of Traini ...
18.4 - 18.5
... (b) Bulb dims to 1/4 its former brightness (1/2 current) (c) Bulb goes out (d) None of the above The wire “shunt” has almost no resistance and it is in parallel with a bulb having resistance. Therefore voltage across shunt (and bulb ) is ~ 0. Thus almost all the current follows the zero (or ex ...
... (b) Bulb dims to 1/4 its former brightness (1/2 current) (c) Bulb goes out (d) None of the above The wire “shunt” has almost no resistance and it is in parallel with a bulb having resistance. Therefore voltage across shunt (and bulb ) is ~ 0. Thus almost all the current follows the zero (or ex ...
You Thought You Knew Analog-----------------------------------
... and more familiar, it should be noted that standard generalpurpose types are not necessarily better simply because they are superior in terms of design and ease-of-use. A variety of other factors must be taken into account, and explains the wide variety of opamps available on the market. For example ...
... and more familiar, it should be noted that standard generalpurpose types are not necessarily better simply because they are superior in terms of design and ease-of-use. A variety of other factors must be taken into account, and explains the wide variety of opamps available on the market. For example ...
14PE7 Control of Reduced-Rating Dynamic Voltage Restorer With a
... Voltage sags in an electrical grid are not always possible to avoid because of the finite clearing time of the faults that cause the voltage sags and the propagation of sags from the Transmission and distribution systems to the low-voltage loads. Voltage sags are the common reasons for interruption ...
... Voltage sags in an electrical grid are not always possible to avoid because of the finite clearing time of the faults that cause the voltage sags and the propagation of sags from the Transmission and distribution systems to the low-voltage loads. Voltage sags are the common reasons for interruption ...
Producing Potato Power
... 2. Chemical reactions in the potato cell produce an electric current, a flow of charges through the potato. How is the potato cell like a flashlight battery? Students should identify that both contain electrolytes that conduct a current 3. Cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electric ...
... 2. Chemical reactions in the potato cell produce an electric current, a flow of charges through the potato. How is the potato cell like a flashlight battery? Students should identify that both contain electrolytes that conduct a current 3. Cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electric ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.