HIERARCHIES AND COMPETING GENERALIZATIONS IN SERBO
... therefore to be neuter plural. As for the semantic features, they are assumed to be needed in W&Z for explaining the facts of pronominal coreference: a personal pronoun in the nominative form referring back to braća can be either ona or oni (see ex. (7a)), since a pronoun agrees with its antecedent ...
... therefore to be neuter plural. As for the semantic features, they are assumed to be needed in W&Z for explaining the facts of pronominal coreference: a personal pronoun in the nominative form referring back to braća can be either ona or oni (see ex. (7a)), since a pronoun agrees with its antecedent ...
paper - Ohlone - University of California, Santa Cruz
... we have gone farther in investigating semantic properties of the autonomous argument. The idea, in brief, will be that the referential properties of this element will not always support the kinds of part-whole relations which the logic of reciprocity demands (see McCloskey () and references cite ...
... we have gone farther in investigating semantic properties of the autonomous argument. The idea, in brief, will be that the referential properties of this element will not always support the kinds of part-whole relations which the logic of reciprocity demands (see McCloskey () and references cite ...
Functions of the Czech reflexive marker
... The “wedge” above the letter e in mě and tě indicates palatalization of the preceding consonant, not a change in vowel quality. ...
... The “wedge” above the letter e in mě and tě indicates palatalization of the preceding consonant, not a change in vowel quality. ...
Grammar Enrichment
... Study the underlined nouns in the following sentences. If a noun should be possessive, write it correctly, and label it possessive in the space provided. If a noun is plural but does not show possession, copy it, and label it plural. 1. Chris neighbors took part in Circleville annual health fair. ...
... Study the underlined nouns in the following sentences. If a noun should be possessive, write it correctly, and label it possessive in the space provided. If a noun is plural but does not show possession, copy it, and label it plural. 1. Chris neighbors took part in Circleville annual health fair. ...
primary argument case-marking in baltic and finnic
... employ the genitive (Baltic, Greek) or dative (Celtic, Germanic) to express the ablative function. The East-Baltic languages and Slavic (i)o-stem genitive singular ending has a remnant from the ablative *-ā (lith. vilko, la vilka, ocs vlъka). The original fundamental meaning of the ablative case was ...
... employ the genitive (Baltic, Greek) or dative (Celtic, Germanic) to express the ablative function. The East-Baltic languages and Slavic (i)o-stem genitive singular ending has a remnant from the ablative *-ā (lith. vilko, la vilka, ocs vlъka). The original fundamental meaning of the ablative case was ...
湖南省第一师范学院外语系备课用纸
... the position of the appositive each: if the appositive occurs before the verb, the following pronoun and corresponding determiner take the plural form; if, on the other hand, the appositive appears after the verb, the pronoun and corresponding determiner take the singular form, eg: They each had the ...
... the position of the appositive each: if the appositive occurs before the verb, the following pronoun and corresponding determiner take the plural form; if, on the other hand, the appositive appears after the verb, the pronoun and corresponding determiner take the singular form, eg: They each had the ...
Transformation Of sentences
... possibly, he didn't have anything else to do, for or because "Maria went shopping." How can the use of other coordinators change the relationship between the two clauses? What implications would the use of "yet" or "but" have on the meaning of the sentence? COMPLEX SENTENCE A complex sentence has an ...
... possibly, he didn't have anything else to do, for or because "Maria went shopping." How can the use of other coordinators change the relationship between the two clauses? What implications would the use of "yet" or "but" have on the meaning of the sentence? COMPLEX SENTENCE A complex sentence has an ...
Indo-Aryan: From the Vedas to Modern Times
... eyes , but has typo graphical advantages and is less m isleading than the tilde, when used to represent a class nasal. As for the vernaculars, it is customary to use a broad phonetic transcription not very different from the strict transliteration of the traditional script, but having the disadvanta ...
... eyes , but has typo graphical advantages and is less m isleading than the tilde, when used to represent a class nasal. As for the vernaculars, it is customary to use a broad phonetic transcription not very different from the strict transliteration of the traditional script, but having the disadvanta ...
E X E R C I S E S - Bedfordstmartins
... Exercises for EasyWriter is a resource for teachers and students. Its exercises consist of sentences and paragraphs in need of revision; most are designed so that students can edit directly on the pages of this book. The exercise sets are numbered to correspond to chapters in EasyWriter. Students ca ...
... Exercises for EasyWriter is a resource for teachers and students. Its exercises consist of sentences and paragraphs in need of revision; most are designed so that students can edit directly on the pages of this book. The exercise sets are numbered to correspond to chapters in EasyWriter. Students ca ...
PERT Review Guide - Valencia College
... In the sentences that follow, choose the correct form of the verb. 1. Every evening, a mother raccoon along with her three cubs (tips, tip) over the garbage cans and (strews, strew) trash all over the backyard. 2. During a typical Florida summer, both the blazing sun and the heavy traffic (makes, ma ...
... In the sentences that follow, choose the correct form of the verb. 1. Every evening, a mother raccoon along with her three cubs (tips, tip) over the garbage cans and (strews, strew) trash all over the backyard. 2. During a typical Florida summer, both the blazing sun and the heavy traffic (makes, ma ...
course reader
... what has generally been accepted, still, Jackendoff (1977) carries the seeds of what later is to develop into two separate nominal projections, the Noun Phrase and a Determiner Phrase. It is assumed that instead of an N’’ (=NP) and an N’ (=N-bar) there are three levels inside the nominal constructio ...
... what has generally been accepted, still, Jackendoff (1977) carries the seeds of what later is to develop into two separate nominal projections, the Noun Phrase and a Determiner Phrase. It is assumed that instead of an N’’ (=NP) and an N’ (=N-bar) there are three levels inside the nominal constructio ...
Arabic Loanwords in Tatar and Swahili: Morphological Assimilation
... 3.1 The Analyses of Arabic Loanwords in Tatar and Swahili The formation of both Tatar and Swahili was influenced by Arabic, which had profoundly influenced them in religious, scientific, cultural and economic aspects. Both languages used the Arabic script. The change from Arabic script to the Russia ...
... 3.1 The Analyses of Arabic Loanwords in Tatar and Swahili The formation of both Tatar and Swahili was influenced by Arabic, which had profoundly influenced them in religious, scientific, cultural and economic aspects. Both languages used the Arabic script. The change from Arabic script to the Russia ...
- SOAS Research Online
... with l, r, y or w in second position are permitted (in addition to some unusual clusters with initial m + stop). In the syllable rhyme, a final glottal stop may occur after a vowel or vowel + glide (w or y) combination; otherwise, syllables may end in a final nasal consonant (m, n or ŋ) or stop (p, ...
... with l, r, y or w in second position are permitted (in addition to some unusual clusters with initial m + stop). In the syllable rhyme, a final glottal stop may occur after a vowel or vowel + glide (w or y) combination; otherwise, syllables may end in a final nasal consonant (m, n or ŋ) or stop (p, ...
On expletive subject pronoun drop in Colloquial French
... ‘[m]orphologization is complete with 3Sg. verbs that disallow a referential subject, as in weather verbs [. . .] and impersonal verbs’. Even if one were to grant this circumvention, the proposed analysis is still conceptually problematic. For why should of all verbs (certain) impersonals be the prec ...
... ‘[m]orphologization is complete with 3Sg. verbs that disallow a referential subject, as in weather verbs [. . .] and impersonal verbs’. Even if one were to grant this circumvention, the proposed analysis is still conceptually problematic. For why should of all verbs (certain) impersonals be the prec ...
t-lemma - Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics
... • prototypically corresponds to the morphological gender ...
... • prototypically corresponds to the morphological gender ...
Tying Ideas Together with Conjunctions and Relative Pronouns
... conjunction. If you see such a clause alone without a main clause — for example, weil er seine Stimme verloren hat (because he lost his voice) — you’re left waiting to find out more information. • Relative clause (dependent clause): This type of clause can’t stand on its own even though it has a sen ...
... conjunction. If you see such a clause alone without a main clause — for example, weil er seine Stimme verloren hat (because he lost his voice) — you’re left waiting to find out more information. • Relative clause (dependent clause): This type of clause can’t stand on its own even though it has a sen ...
Contents: MyGrammarLab Advanced C1–C2
... Comment clause: We waited for ages, which was really annoying. It’s the man whose car was towed away. The person to whom this letter is addressed … It was the day when the heatwave started. The goods, half of which were damaged, arrived today. You can invite whoever you like. Turning the corner, we ...
... Comment clause: We waited for ages, which was really annoying. It’s the man whose car was towed away. The person to whom this letter is addressed … It was the day when the heatwave started. The goods, half of which were damaged, arrived today. You can invite whoever you like. Turning the corner, we ...
PDF file - University of Cambridge
... As such, they represent a case of boundary reanalysis ((ii) above), and, in fact, Janda (2001: 303) refers to this type of case as ‘upgrading via reanalysis’. Examples include the English possessive clitic ’s from an earlier genitive case ending,3 the Irish firstperson-plural pronoun muid from an ea ...
... As such, they represent a case of boundary reanalysis ((ii) above), and, in fact, Janda (2001: 303) refers to this type of case as ‘upgrading via reanalysis’. Examples include the English possessive clitic ’s from an earlier genitive case ending,3 the Irish firstperson-plural pronoun muid from an ea ...
the english tongue. - Cunningham Memorial Library
... familiar with every dialect of Greek, and every variety of classical style, there should be so few who have really made themselves acquainted with the origin, the nlstory, and the gradual developmeut into Its present form of that mother wugue which 18 already spoken over half the world, and which em ...
... familiar with every dialect of Greek, and every variety of classical style, there should be so few who have really made themselves acquainted with the origin, the nlstory, and the gradual developmeut into Its present form of that mother wugue which 18 already spoken over half the world, and which em ...
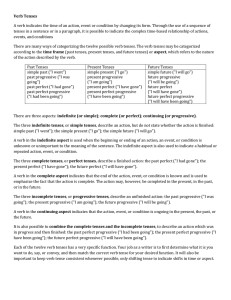
VerbTenseInProgress
... unknown or unimportant to the meaning of the sentence. The indefinite aspect is also used to indicate a habitual or repeated action, event, or condition. The three complete tenses, or perfect tenses, describe a finished action: the past perfect ("I had gone"); the present perfect ("I have gone"); th ...
... unknown or unimportant to the meaning of the sentence. The indefinite aspect is also used to indicate a habitual or repeated action, event, or condition. The three complete tenses, or perfect tenses, describe a finished action: the past perfect ("I had gone"); the present perfect ("I have gone"); th ...
the feeling of great pleasure
... ‘Delighted’ is an adjective having an identical form with, but different features from, the past participle of the verb ‘delight’, having the syntactic functions as head of adjectival phrases, pre-modifier of noun phrases and complement. Morphologically, it has two morphemes: the root delight and su ...
... ‘Delighted’ is an adjective having an identical form with, but different features from, the past participle of the verb ‘delight’, having the syntactic functions as head of adjectival phrases, pre-modifier of noun phrases and complement. Morphologically, it has two morphemes: the root delight and su ...
NLP - Words
... Saxon genitive It is obtained with the suffix –’s for singular nouns and plurals not ending in s (f.i. children’s) and with the suffix –’ for regular plurals and some nouns ending in s or z) ...
... Saxon genitive It is obtained with the suffix –’s for singular nouns and plurals not ending in s (f.i. children’s) and with the suffix –’ for regular plurals and some nouns ending in s or z) ...
FNLP Lecture 8 Part-of-speech tagging and HMMs What is part of
... • Because, like spell correction etc, HMM can also be viewed as a noisy channel model. – Someone wants to send us a sequence of tags: P (T ) – During encoding, “noise” converts each tag to a word: P (S|T ) – We try to decode the observed words back to the original tags. ...
... • Because, like spell correction etc, HMM can also be viewed as a noisy channel model. – Someone wants to send us a sequence of tags: P (T ) – During encoding, “noise” converts each tag to a word: P (S|T ) – We try to decode the observed words back to the original tags. ...
ra - Stichting Papua Erfgoed
... they lived in gardens which were made by clearing part of the forest. If one garden was exhausted, they abandoned it and made a new garden. In addition to gardening, they hunted and gathered food in the forest to supplement their diet. People lived together in clans, and made their gardens on their ...
... they lived in gardens which were made by clearing part of the forest. If one garden was exhausted, they abandoned it and made a new garden. In addition to gardening, they hunted and gathered food in the forest to supplement their diet. People lived together in clans, and made their gardens on their ...
slips of speech - WATA - World Association of Arab Translators
... words; and to determine, in every case, what good usage dictates, is not an easy matter. Authors, like words, must be tested by time before their forms of expression may become a law for others. Pope, in his Essay on Criticism, laid down a rule which, for point and brevity, has never been excelled: ...
... words; and to determine, in every case, what good usage dictates, is not an easy matter. Authors, like words, must be tested by time before their forms of expression may become a law for others. Pope, in his Essay on Criticism, laid down a rule which, for point and brevity, has never been excelled: ...