Parts of Speech: Nouns
... Parts of Speech: Pronouns • Pronouns are either singular or plural. • Singular pronouns replace singular nouns (which name one) • Plural pronouns replace plural nouns (which name more than one) Write the sentences below. Circle the pronoun that best completes the sentence. Then label it singular or ...
... Parts of Speech: Pronouns • Pronouns are either singular or plural. • Singular pronouns replace singular nouns (which name one) • Plural pronouns replace plural nouns (which name more than one) Write the sentences below. Circle the pronoun that best completes the sentence. Then label it singular or ...
Lecture slides
... Harriet to ask for help with one of the assignments which have to be finished for the next morphology class • Fulfill particular functions in the sentence • That: Subordinating conjunction • Which: Relative Pronoun • Function word, content word distinction: important for both language acquisition an ...
... Harriet to ask for help with one of the assignments which have to be finished for the next morphology class • Fulfill particular functions in the sentence • That: Subordinating conjunction • Which: Relative Pronoun • Function word, content word distinction: important for both language acquisition an ...
The Eight Parts of Speech Poem
... All names of persons, places, ideas, and things Are nouns, such as Caesar, home, love and rings. Pronouns are used in place of nouns: I think, she sings, they work, he frowns. When the kind you wish to state Use an adjective, such as “great!” Next we have the verbs which tell Of action, being, state ...
... All names of persons, places, ideas, and things Are nouns, such as Caesar, home, love and rings. Pronouns are used in place of nouns: I think, she sings, they work, he frowns. When the kind you wish to state Use an adjective, such as “great!” Next we have the verbs which tell Of action, being, state ...
parts of speech here
... The people who live there are on vacation. Interrogative – who, whom, which, what, whose Used to ask questions Ex/ Who borrowed my pen? Demonstrative – this, these, that, those Used to point out persons or things Ex/ This is my lucky day. Indefinite – all, few, none, another, any, anybody, anyone, b ...
... The people who live there are on vacation. Interrogative – who, whom, which, what, whose Used to ask questions Ex/ Who borrowed my pen? Demonstrative – this, these, that, those Used to point out persons or things Ex/ This is my lucky day. Indefinite – all, few, none, another, any, anybody, anyone, b ...
GRAMMAR SYLLABUS Verbs Regular and irregular forms Modal
... Wish/if only + past simple, past perfect, would Would rather, had better Gerunds and infinitives Used to/would (past habits) Get/be used to Verbs of the senses + adjective/like/as if Auxiliary verbs So do I – neither do I Reply questions For emphasis Reported Speech Structures with reporting verbs R ...
... Wish/if only + past simple, past perfect, would Would rather, had better Gerunds and infinitives Used to/would (past habits) Get/be used to Verbs of the senses + adjective/like/as if Auxiliary verbs So do I – neither do I Reply questions For emphasis Reported Speech Structures with reporting verbs R ...
Chapter Two
... Coordinating conjunctions and or but nor Cell phones and computers can change your life. Cell phones or computers can change your life. ...
... Coordinating conjunctions and or but nor Cell phones and computers can change your life. Cell phones or computers can change your life. ...
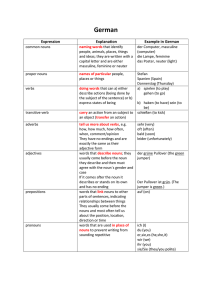
German - Crofton School
... words that link nouns to other parts of sentences, indicating relationships between things They usually come before the nouns and most often tell us about the position, location, direction or time words that are used in place of nouns to prevent writing from ...
... words that link nouns to other parts of sentences, indicating relationships between things They usually come before the nouns and most often tell us about the position, location, direction or time words that are used in place of nouns to prevent writing from ...
Making Subjects and Verbs Agree • A plural verb should be used
... o Sally and her friends are preparing for a group presentation. • Use a singular verb when two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by “or” or “nor”. o Neither excessive note card use nor memorization is conducive to an effective presentation. • The verb should agree with the part of the ...
... o Sally and her friends are preparing for a group presentation. • Use a singular verb when two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by “or” or “nor”. o Neither excessive note card use nor memorization is conducive to an effective presentation. • The verb should agree with the part of the ...
Present - Grade 4 Merlins
... Lesson 2: verbs in the present Verbs show action in a sentence. Verbs also tell when the action happens. A verb in the present tense tells about an action that is happening NOW. ...
... Lesson 2: verbs in the present Verbs show action in a sentence. Verbs also tell when the action happens. A verb in the present tense tells about an action that is happening NOW. ...
Year 5 Parents Curriculum Presentation
... -These come before nouns or noun phrases A, an, the, this, that, these, those Prepositions - Link nouns or pronouns in a sentence. They usually indicate when or where something happens - About, above, across, after, under, behind, upon, over, between. ...
... -These come before nouns or noun phrases A, an, the, this, that, these, those Prepositions - Link nouns or pronouns in a sentence. They usually indicate when or where something happens - About, above, across, after, under, behind, upon, over, between. ...
study guide grammar test
... You must be able to identify the subject of a sentence. Concrete and abstract nouns Count and non-count nouns. Know when to use “few” v. “less” and “some” v. “any” Nominative and objective case pronouns Indefinite pronouns: singular, plural, and those that can be both Possessive pronouns: my, ours, ...
... You must be able to identify the subject of a sentence. Concrete and abstract nouns Count and non-count nouns. Know when to use “few” v. “less” and “some” v. “any” Nominative and objective case pronouns Indefinite pronouns: singular, plural, and those that can be both Possessive pronouns: my, ours, ...
NOUNS-VERBS-ADJECTIVES
... Underline once the nouns, twice the verbs, and circle the adjectives. ...
... Underline once the nouns, twice the verbs, and circle the adjectives. ...
Unit 1 * the 8 Parts of Speech
... 2. They do all of the following: state that something exists, show time, and establish relationships. ...
... 2. They do all of the following: state that something exists, show time, and establish relationships. ...
practical assignment
... 6. Sa skalks ni swarith aithans. 7. Sa thiudans jah sa skalks itand thans fiskans. ...
... 6. Sa skalks ni swarith aithans. 7. Sa thiudans jah sa skalks itand thans fiskans. ...
Subject
... I am seven years old today! Missy and I are bestfriends. Those dogs were in my backyard. ...
... I am seven years old today! Missy and I are bestfriends. Those dogs were in my backyard. ...
Chapter 7. Frequently looked up verbs
... Sceorte hwīle is an example of the accusative being used in an expression of time. Note that, as man could mean either ‘man’ or ‘person’, and as hē agrees with man chiefly as a grammatical masculine, the ‘person’ and ‘he or she’ senses are fully possible. ...
... Sceorte hwīle is an example of the accusative being used in an expression of time. Note that, as man could mean either ‘man’ or ‘person’, and as hē agrees with man chiefly as a grammatical masculine, the ‘person’ and ‘he or she’ senses are fully possible. ...
Grammar Study Sheet
... A. English is a subject verb object language: it prefers a sequence of subject–verb–object in its simplest, unmarked declarative statements. B. Interrogative sentences invert word order. C. English also sees some use of the OSV (object-subject-verb) word order, especially when making comparisons usi ...
... A. English is a subject verb object language: it prefers a sequence of subject–verb–object in its simplest, unmarked declarative statements. B. Interrogative sentences invert word order. C. English also sees some use of the OSV (object-subject-verb) word order, especially when making comparisons usi ...
The Old English Alphabet
... Past tense was used to indicate all past actions and events. All the forms of the verb were synthetic, while the analytic forms started to appear. ...
... Past tense was used to indicate all past actions and events. All the forms of the verb were synthetic, while the analytic forms started to appear. ...
Parts of Speech
... Number: Singular or Plural Gender: Masculine, Feminine, or Neuter Nouns belong to declensions, or general patterns of endings. The genitive singular signals a noun’s declension: -ae ...
... Number: Singular or Plural Gender: Masculine, Feminine, or Neuter Nouns belong to declensions, or general patterns of endings. The genitive singular signals a noun’s declension: -ae ...
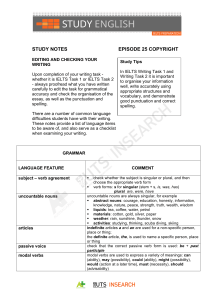
study notes epi - Australia Plus TV
... and, or or but, a comma is unnecessary provided both verbs have the same subject • after linking words such as: listing words (first of all, second, finally, subsequently), ideas which are similar or equal (also, furthermore, moreover, in addition), ideas ...
... and, or or but, a comma is unnecessary provided both verbs have the same subject • after linking words such as: listing words (first of all, second, finally, subsequently), ideas which are similar or equal (also, furthermore, moreover, in addition), ideas ...
subject-predicate-prepositional phrases
... • A, an, and the signal nouns • Is, am, was, were…are always verbs. • When you see –ed, it MIGHT mean it is a past tense verb. ...
... • A, an, and the signal nouns • Is, am, was, were…are always verbs. • When you see –ed, it MIGHT mean it is a past tense verb. ...
Nothing but Nouns
... Personal (I, you, he, she, it) Reflexive/Intensive (they end in -self) Demonstrative (this, that, these, those) Interrogative? (which, who, whom, whose) Relative (that, which, who, whose, whom) Indefinite (anyone, most, anybody…) ...
... Personal (I, you, he, she, it) Reflexive/Intensive (they end in -self) Demonstrative (this, that, these, those) Interrogative? (which, who, whom, whose) Relative (that, which, who, whose, whom) Indefinite (anyone, most, anybody…) ...