Statistical Natural Language Procesing: linguistic
... VBD – verb third person singular (e.g. ‘likes’) ...
... VBD – verb third person singular (e.g. ‘likes’) ...
Parts of Speech
... Pronouns replace nouns to avoid unnecessary repetition. They usually replace nouns that directly ...
... Pronouns replace nouns to avoid unnecessary repetition. They usually replace nouns that directly ...
Verbs
... Intransitive verbs are verbs without an object. Ex: He travels with the other musicians. Travels who or what? No answer=no object ...
... Intransitive verbs are verbs without an object. Ex: He travels with the other musicians. Travels who or what? No answer=no object ...
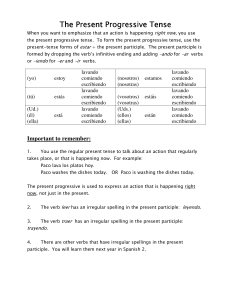
The Present Progressive Tense The Present
... When you want to emphasize that an action is happening right now, you use the present progressive tense. To form the present progressive tense, use the present-tense forms of estar + the present participle. The present participle is formed by dropping the verb’s infinitive ending and adding –ando fo ...
... When you want to emphasize that an action is happening right now, you use the present progressive tense. To form the present progressive tense, use the present-tense forms of estar + the present participle. The present participle is formed by dropping the verb’s infinitive ending and adding –ando fo ...
Superior Sentences
... ◦ Simple [will walk] ◦ Perfect [will have walked] ◦ Progressive [will be walking] ...
... ◦ Simple [will walk] ◦ Perfect [will have walked] ◦ Progressive [will be walking] ...
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... For present perfect tense, another action is assumed, for example, the sentence: “I have studied for two hours” implies that I will do more studying. • Progressive verbs, also known as continuous verbs, indicate something happening continuously over a certain period of time, for example: I will be ...
... For present perfect tense, another action is assumed, for example, the sentence: “I have studied for two hours” implies that I will do more studying. • Progressive verbs, also known as continuous verbs, indicate something happening continuously over a certain period of time, for example: I will be ...
GRAMMAR REVIEW: Parts of Speech
... Oh! I almost forgot – I had a Pampered Chef party to restart my business. That was fun, but a lot of work. I missed my Key Club kids, and yes, even some of my students. I’m glad to be back at school. Are you? ...
... Oh! I almost forgot – I had a Pampered Chef party to restart my business. That was fun, but a lot of work. I missed my Key Club kids, and yes, even some of my students. I’m glad to be back at school. Are you? ...
Action Verb: Tells what the subject does. • Jeremy likes to run
... courthouse steps. Predicate: tells what the subject is or what it does (always contains the verb). • An angry, thin man walked up the courthouse steps. ...
... courthouse steps. Predicate: tells what the subject is or what it does (always contains the verb). • An angry, thin man walked up the courthouse steps. ...
Nota Bene-- C:\NBWIN\EXAMS\HEBREW~1\PARSIN~1.NB Job 1
... Parsing involves breaking a word down into its component grammatical parts. In dealing with Hebrew this is very important since a single Hebrew word may contain a variety of elements that could correspond to a number of words in English. At the same time, the ability to strip away added elements wil ...
... Parsing involves breaking a word down into its component grammatical parts. In dealing with Hebrew this is very important since a single Hebrew word may contain a variety of elements that could correspond to a number of words in English. At the same time, the ability to strip away added elements wil ...
Parts of Speech
... But if your sentence does not have both a subject and verb after the conjunction, your sentence does not need a comma, for example: Mickey [subject] likes [verb] going to the beach and ...
... But if your sentence does not have both a subject and verb after the conjunction, your sentence does not need a comma, for example: Mickey [subject] likes [verb] going to the beach and ...
Revising - Mr. Riley's Class
... difference between boring and interesting. To make writing more effective, writers often use descriptive language. – descriptive language includes: • sensory details – words that appeal to the senses • colorful modifiers – adjectives and adverbs that give vivid details • action words – verbs that sh ...
... difference between boring and interesting. To make writing more effective, writers often use descriptive language. – descriptive language includes: • sensory details – words that appeal to the senses • colorful modifiers – adjectives and adverbs that give vivid details • action words – verbs that sh ...
PDF
... c) Before I could run the shiny red sports car stopped in front of me. 3. Write a sentence for each of these types of punctuation to show how they work. For example: exclamation mark – The boy shouted “WOLF!” a) full stop b) exclamation mark c) speech marks d)comma 4. Write a sentence saying what th ...
... c) Before I could run the shiny red sports car stopped in front of me. 3. Write a sentence for each of these types of punctuation to show how they work. For example: exclamation mark – The boy shouted “WOLF!” a) full stop b) exclamation mark c) speech marks d)comma 4. Write a sentence saying what th ...
Heading Glossary of grammatical terms
... I am leaving when I’ve finished. (two clauses – one sentence) ■ comparative (see adjective) ■ conjugation/conjugate A conjugation is the pattern of a verb’s forms. For example, the regular verb to talk is conjugated as follows: infinitive to talk, present tense I talk, he/she talks, past I talked, ...
... I am leaving when I’ve finished. (two clauses – one sentence) ■ comparative (see adjective) ■ conjugation/conjugate A conjugation is the pattern of a verb’s forms. For example, the regular verb to talk is conjugated as follows: infinitive to talk, present tense I talk, he/she talks, past I talked, ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Articles are actually adjectives. (This is mind-boggling, I know). “A” and “an” are called indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a general group--a sweater, a slice of pie, a ...
... Articles are actually adjectives. (This is mind-boggling, I know). “A” and “an” are called indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a general group--a sweater, a slice of pie, a ...
review exercise - East Penn School District
... Roy is always hungry. Always is an adverb modifying an adjective Roy is almost always hungry. Almost is an adverb modifying another adverb, modifying an adjective 6. Preposition: word that shows a relationship of a noun or pronoun to some other word in the sentence. Ex: aboard, about, above, across, ...
... Roy is always hungry. Always is an adverb modifying an adjective Roy is almost always hungry. Almost is an adverb modifying another adverb, modifying an adjective 6. Preposition: word that shows a relationship of a noun or pronoun to some other word in the sentence. Ex: aboard, about, above, across, ...
1. Translating Verbs 2. Personal Endings 3. Questions
... NEVER have EST in the sentence UNLESS IT IS THE MAIN VERB—She is a girl. NEVER have SUNT in the sentence UNLESS IT IS THE MAIN VERB—They are boys. ...
... NEVER have EST in the sentence UNLESS IT IS THE MAIN VERB—She is a girl. NEVER have SUNT in the sentence UNLESS IT IS THE MAIN VERB—They are boys. ...
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, SRINAGAR REVISION WORKSHEET
... Examples: Delhi, table, cat, Manoj etc. 2. Common Nouns are names of people, places, animals or things of same kind. Examples: Girl, car, pen etc. 3. Proper Noun are special names of people, places, animals or things. Proper nouns always ...
... Examples: Delhi, table, cat, Manoj etc. 2. Common Nouns are names of people, places, animals or things of same kind. Examples: Girl, car, pen etc. 3. Proper Noun are special names of people, places, animals or things. Proper nouns always ...