Document
... I can’t believe how quickly the dog chased the cat. Mrs. Jones rides horses. The cowboys rode cattle trails for days. The team celebrated by having pizzas. ...
... I can’t believe how quickly the dog chased the cat. Mrs. Jones rides horses. The cowboys rode cattle trails for days. The team celebrated by having pizzas. ...
CHAPTER 4 in depth
... each other, and (2) the nominative plural -‐-‐ and hence neuter plural because of rule (1) -‐-‐ is always a short "-‐a". ...
... each other, and (2) the nominative plural -‐-‐ and hence neuter plural because of rule (1) -‐-‐ is always a short "-‐a". ...
AR verb notes ANSWERS
... There are 3 different translations in English for a Spanish verb phrase. Any one of those translations can be accepted when asked to translate sentences to English. Use all PRESENT TENSE only. ...
... There are 3 different translations in English for a Spanish verb phrase. Any one of those translations can be accepted when asked to translate sentences to English. Use all PRESENT TENSE only. ...
Grammar & Mechanics
... Two-Part (Phrasal) Verbs (Idioms) “Many verbs in English are followed by an adverb or a preposition (also called a participle), and these two-part verbs, also called phrasal verbs, are different from verbs with helpers. The particle that follows the verb changes the meaning of the phrasal verb in i ...
... Two-Part (Phrasal) Verbs (Idioms) “Many verbs in English are followed by an adverb or a preposition (also called a participle), and these two-part verbs, also called phrasal verbs, are different from verbs with helpers. The particle that follows the verb changes the meaning of the phrasal verb in i ...
Guided Reading Sentence Improvement Red Group
... Grammar Homework - Sentence Improvement Red Group Use your neatest writing to copy out these sentences, improving them by adding adjectives, adverbs, powerful verbs, a wow opener and using one of these connectives to extend them. before ...
... Grammar Homework - Sentence Improvement Red Group Use your neatest writing to copy out these sentences, improving them by adding adjectives, adverbs, powerful verbs, a wow opener and using one of these connectives to extend them. before ...
Creole Lexicon - Groupe Européen de Recherches en Langues
... base word so that creole words, such as lari (‘road’), monpè (‘priest’), and divin (‘wine’) take a creole article when spoken to give, for example, on lari, monpè-la, and divin-la-sa. This process can be compared, in contemporary terms, to a prefixation and seems to be used, in Martinique at least, ...
... base word so that creole words, such as lari (‘road’), monpè (‘priest’), and divin (‘wine’) take a creole article when spoken to give, for example, on lari, monpè-la, and divin-la-sa. This process can be compared, in contemporary terms, to a prefixation and seems to be used, in Martinique at least, ...
Spelling Scheme Year 6 - St Mary`s Catholic Primary School
... assent: to agree/agreement (verb and noun) bridal: to do with a bride at a wedding bridle: reins etc. for controlling a horse cereal: made from grain (e.g. breakfast cereal) serial: adjective from the noun series – a succession of things one after the other compliment: to make nice remarks about som ...
... assent: to agree/agreement (verb and noun) bridal: to do with a bride at a wedding bridle: reins etc. for controlling a horse cereal: made from grain (e.g. breakfast cereal) serial: adjective from the noun series – a succession of things one after the other compliment: to make nice remarks about som ...
Participles - Stjohns
... participle is that form of the verb which is used like an adjective. l Since it is a verb, it has tense and voice. It can take a direct object, an indirect object, etc. l Since it is an adjective, it has case, number, and gender, and it will modify a noun. ...
... participle is that form of the verb which is used like an adjective. l Since it is a verb, it has tense and voice. It can take a direct object, an indirect object, etc. l Since it is an adjective, it has case, number, and gender, and it will modify a noun. ...
Finite and Non-Finite Verbs
... • A non-finite verb (sometimes called a verbal) is any of several verb forms that are not finite verbs; that is, they cannot serve as the root of an independent clause. ...
... • A non-finite verb (sometimes called a verbal) is any of several verb forms that are not finite verbs; that is, they cannot serve as the root of an independent clause. ...
TEACHING FRENCH USING MNENONIC - MN
... Mnemonic devices are basically memory aides. I have always found them useful as have those who take my classes. When trying to create one, teachers should never hesitate to give free reign to their imagination. They must play with the letters and, when necessary, look for other examples that fit the ...
... Mnemonic devices are basically memory aides. I have always found them useful as have those who take my classes. When trying to create one, teachers should never hesitate to give free reign to their imagination. They must play with the letters and, when necessary, look for other examples that fit the ...
Unit of Study Assessment Checklist
... occurring general academic and content-specific words and phrases in conversations and discussions. ELP.6-8.S10.L2- Student uses nouns, pronouns, verbs, prepositions, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositional phrases, and produces simple and compound sentences, with support (including vis ...
... occurring general academic and content-specific words and phrases in conversations and discussions. ELP.6-8.S10.L2- Student uses nouns, pronouns, verbs, prepositions, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositional phrases, and produces simple and compound sentences, with support (including vis ...
Parts of Speech
... Joe will meet us at the game, or he will see us later at Burger King. Ann is small, yet she is very strong. CORRELATIVE CONJUNCTIONS – pairs of conjunctions that join words or word groups that are used in the same way. EXAMPLES both…and not only…but also either…or neither…nor whether…or Both trees a ...
... Joe will meet us at the game, or he will see us later at Burger King. Ann is small, yet she is very strong. CORRELATIVE CONJUNCTIONS – pairs of conjunctions that join words or word groups that are used in the same way. EXAMPLES both…and not only…but also either…or neither…nor whether…or Both trees a ...
Writing Complete Sentences
... • John finished writing his story. (before noun) • The idea for it was mine. (alone) ...
... • John finished writing his story. (before noun) • The idea for it was mine. (alone) ...
ACT prep Spring 2012 - Parkway C-2
... getting boring. The sound of it drones. It’s like a stuck record. The ear demands some variety. Now listen. I vary the sentence length, and I create music. Music. The writing sings. It has a pleasant rhythm, a lilt, a harmony. I use short sentences. And I use sentences of medium length. And sometime ...
... getting boring. The sound of it drones. It’s like a stuck record. The ear demands some variety. Now listen. I vary the sentence length, and I create music. Music. The writing sings. It has a pleasant rhythm, a lilt, a harmony. I use short sentences. And I use sentences of medium length. And sometime ...
1 SPANISH 101. LECCIÓN PRELIMINAR VERBO SER (to describe
... Note that unos and unas are the equivalent of some in English. As a general rule, nouns of persons and animals that end in –o are masculine and those that end in –a are feminine: abuelo/abuela, perro/perra. With nouns of things and abstract concepts there is no specific ending, so you will have to s ...
... Note that unos and unas are the equivalent of some in English. As a general rule, nouns of persons and animals that end in –o are masculine and those that end in –a are feminine: abuelo/abuela, perro/perra. With nouns of things and abstract concepts there is no specific ending, so you will have to s ...
Spanish 2 Spring Midterm Review Vocabulary: 3B and 4A Grammar
... 9. dormir to sleep durmiendo 5. servir to serve sirviendo Group 2 – Verbs that end in –eer/-aer/-uir (change i-y) 10. leer leyendo 12. creer creyendo 11. traer trayendo 13. destruir destruyendo 6. When you use object pronouns (reflexive, direct, indirect) with the present progressive, you either put ...
... 9. dormir to sleep durmiendo 5. servir to serve sirviendo Group 2 – Verbs that end in –eer/-aer/-uir (change i-y) 10. leer leyendo 12. creer creyendo 11. traer trayendo 13. destruir destruyendo 6. When you use object pronouns (reflexive, direct, indirect) with the present progressive, you either put ...
I am writing a letter The passive voice is used
... be to, used to, will, would, be going to, would like to, would rather. ...
... be to, used to, will, would, be going to, would like to, would rather. ...
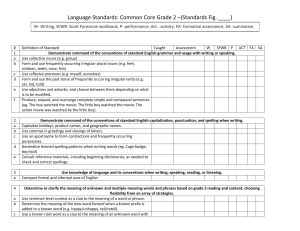
Language Standards: Common Core Grade 2 –(Standards Fig
... Definition of Standard Taught Assessment W SFWB P ACT FA SA Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage with writing or speaking. Use collective nouns (e.g. group) Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g. feet, children, teeth, mice, fish) Use r ...
... Definition of Standard Taught Assessment W SFWB P ACT FA SA Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage with writing or speaking. Use collective nouns (e.g. group) Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g. feet, children, teeth, mice, fish) Use r ...
Parts of Speech - University of Sussex
... hand, none of the words arrive, with, unlucky, this, because, delivered or very can fill the slot, and so these words cannot be nouns. (But see below for a class of nouns that cannot appear in this slot.) English nouns exhibit only one inflectional distinction: that between singular and plural. The ...
... hand, none of the words arrive, with, unlucky, this, because, delivered or very can fill the slot, and so these words cannot be nouns. (But see below for a class of nouns that cannot appear in this slot.) English nouns exhibit only one inflectional distinction: that between singular and plural. The ...
Daily Grammar Practice - NOTES
... Joins words, phrases, and clauses; types include: Coordinating – “FANBOYS” (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) Subordinating – start dependent clauses; followed by a subject and verb; (after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, as if, e ...
... Joins words, phrases, and clauses; types include: Coordinating – “FANBOYS” (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) Subordinating – start dependent clauses; followed by a subject and verb; (after, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, as if, e ...
Study Guide: National Latin Exam
... A Latin preposition can be followed by a noun in either of two cases: accusative or ablative. Memorize the prepositions that take the ablative case. Then, when you encounter any other preposition, you will know that it must be followed by the accusative case. The prepositions that take the ablative ...
... A Latin preposition can be followed by a noun in either of two cases: accusative or ablative. Memorize the prepositions that take the ablative case. Then, when you encounter any other preposition, you will know that it must be followed by the accusative case. The prepositions that take the ablative ...
Noun Functions
... Example: Using the previous sentence, one would say Tilly should give the pen to whom or what or for whom or what? Here, the indirect object would be Reanna. 7. If the verb is linking, see if you have a word on the other side of the verb that renames the subject. If you do, that word is the predicat ...
... Example: Using the previous sentence, one would say Tilly should give the pen to whom or what or for whom or what? Here, the indirect object would be Reanna. 7. If the verb is linking, see if you have a word on the other side of the verb that renames the subject. If you do, that word is the predicat ...
Study Guide: National Latin Exam
... A Latin preposition can be followed by a noun in either of two cases: accusative or ablative. Memorize the prepositions that take the ablative case. Then, when you encounter any other preposition, you will know that it must be followed by the accusative case. The prepositions that take the ablative ...
... A Latin preposition can be followed by a noun in either of two cases: accusative or ablative. Memorize the prepositions that take the ablative case. Then, when you encounter any other preposition, you will know that it must be followed by the accusative case. The prepositions that take the ablative ...