Digital Color Reproduction
... At E’, only by a common scale factor across the entire image, the two scenes will look quite similar. In that case, the scenes will look rather like one another because it is as if we are looking at the original through dark glasses. If the original and reproduction differ by an additive offset, how ...
... At E’, only by a common scale factor across the entire image, the two scenes will look quite similar. In that case, the scenes will look rather like one another because it is as if we are looking at the original through dark glasses. If the original and reproduction differ by an additive offset, how ...
Physically-Based Glare Effects for Digital Images
... and the real experience of looking at a small incandescent bulb. The real bulb differs from the digital image in two important ways. The first difference is a qualitative “brightness” that the bulb possesses. The second difference is the hazy glow that can be seen around the bulb. This glow not only ...
... and the real experience of looking at a small incandescent bulb. The real bulb differs from the digital image in two important ways. The first difference is a qualitative “brightness” that the bulb possesses. The second difference is the hazy glow that can be seen around the bulb. This glow not only ...
Subpixel Scatter in Digital Micromirror Devices
... Figure 5. A sketch of the scatter measurement instrument (upper left). The fold mirror periscope design was built and modeled in FRED (an exploded view upper right). The bottom two photographs were taken to show the physical setup. ...
... Figure 5. A sketch of the scatter measurement instrument (upper left). The fold mirror periscope design was built and modeled in FRED (an exploded view upper right). The bottom two photographs were taken to show the physical setup. ...
Nikonorov_Fresnel_Le.. - The Computer Vision Foundation
... Let lC be the left border, and rC be the right border of this area. In the transition area, an abrupt change of values in red or blue or both color channels occurs. The algorithm transforms signals in red and blue channels to match the signal in the green channel in the transition area N C ( xc ) as ...
... Let lC be the left border, and rC be the right border of this area. In the transition area, an abrupt change of values in red or blue or both color channels occurs. The algorithm transforms signals in red and blue channels to match the signal in the green channel in the transition area N C ( xc ) as ...
Diffractive optical elements stored on photopolymers
... Young’s fringes based two beams interferometer. This interferometer has been successfully applied in the phase-shift characterization of liquid crystal displays (LCDs)[7]. It shows a good precision, and due to its quasi-common path architecture is a robust setup, less sensible to changing environmen ...
... Young’s fringes based two beams interferometer. This interferometer has been successfully applied in the phase-shift characterization of liquid crystal displays (LCDs)[7]. It shows a good precision, and due to its quasi-common path architecture is a robust setup, less sensible to changing environmen ...
A Simple Classroom Demonstration of Natural Convection
... using an overhead projector. The demonstration is based on the principle of schlieren imaging, commonly used to visualize variations in density for gas flows. The demonstration requires a few hours of preparation time, but very little in materials cost, assuming an overhead projector is already avai ...
... using an overhead projector. The demonstration is based on the principle of schlieren imaging, commonly used to visualize variations in density for gas flows. The demonstration requires a few hours of preparation time, but very little in materials cost, assuming an overhead projector is already avai ...
Intraframe Scene Capturing and Speed Measurement Based on
... the other hand, there are methods in the literature aiming at producing reliable speed estimates, based on optical information only [2–5]. Scientific studies in this field can be divided into two major research directions: optical flow (interframe) and motion-blur (intraframe) based displacement cal ...
... the other hand, there are methods in the literature aiming at producing reliable speed estimates, based on optical information only [2–5]. Scientific studies in this field can be divided into two major research directions: optical flow (interframe) and motion-blur (intraframe) based displacement cal ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... The wooden step wedge was placed on a 24 x 30cm cassette, a control exposure was made by keeping the mAs constant at 16mAs and varying the kVp, thus 45, 50, 55, 60, 65 and 70kVp respectively at constant film to focus distance (FFD) of 100cm, a total of six exposure were made. The same procedure ...
... The wooden step wedge was placed on a 24 x 30cm cassette, a control exposure was made by keeping the mAs constant at 16mAs and varying the kVp, thus 45, 50, 55, 60, 65 and 70kVp respectively at constant film to focus distance (FFD) of 100cm, a total of six exposure were made. The same procedure ...
... PMMA and the photoresist have only negligible effects on the imaging quality. Although the illumination is normal to the plane of the object, the subwavelength object scatters the incident radiation in different directions. Two types of polarization for the scattered waves in reference to the plane ...
Femto-Photography: Capturing and Visualizing the
... 3 (right)). Alternatively, if we want to observe pulse propagation itself, rather than the interactions with large objects, we direct the laser beam across the field of view of the camera through a scattering medium (see the bottle scene in Figure 1). Because all the pulses are statistically identic ...
... 3 (right)). Alternatively, if we want to observe pulse propagation itself, rather than the interactions with large objects, we direct the laser beam across the field of view of the camera through a scattering medium (see the bottle scene in Figure 1). Because all the pulses are statistically identic ...
Proceedings Template
... and 3-5 element relay optics. On the other hand, a conventional scrolling-color system will require 3 color splitting dichroics, mirrors for positioning the 3 beams, optics for focusing each color onto the modulator, and optics for manipulation of the beams to cause the scrolling action. Each focusi ...
... and 3-5 element relay optics. On the other hand, a conventional scrolling-color system will require 3 color splitting dichroics, mirrors for positioning the 3 beams, optics for focusing each color onto the modulator, and optics for manipulation of the beams to cause the scrolling action. Each focusi ...
Examples of convex lens
... silver chloride in each interval of the visible spectrum he got from a glass prism. He first found that blue light cause silver chloride to turn black more than red light did. Then he placed the silver chloride in to the region beyond violet, where no light could be seen by naked eye, but silver chl ...
... silver chloride in each interval of the visible spectrum he got from a glass prism. He first found that blue light cause silver chloride to turn black more than red light did. Then he placed the silver chloride in to the region beyond violet, where no light could be seen by naked eye, but silver chl ...
Lecture 7 Optical Lithography
... • However, higher NA lenses also decrease the depth of focus. (See next slide for derivation.) ...
... • However, higher NA lenses also decrease the depth of focus. (See next slide for derivation.) ...
measuring wavelength discrimination threshold along the entire
... same time to the interference filter too. The other digital linear scale detects this displacement. Hence with moving the interference filter the wavelength changes in both channels, but when moving the input slot of the measuring light only its own wavelength is changing relative to the wavelength ...
... same time to the interference filter too. The other digital linear scale detects this displacement. Hence with moving the interference filter the wavelength changes in both channels, but when moving the input slot of the measuring light only its own wavelength is changing relative to the wavelength ...
Light Magic – Optics and Vision - New England Board of Higher
... 3. To block out other nearby light sources, use a short cardboard tube. 4. To separate the colors so they don’t overlap, use a slit. ...
... 3. To block out other nearby light sources, use a short cardboard tube. 4. To separate the colors so they don’t overlap, use a slit. ...
7.1 textbook answers - aiss-science-9
... b Optical fibres work by passing light along the fibre through totally internal reflection. This requires that the surface of the fibre be very smooth. Scratches on the surface of the optical fibre would prevent the light from being reflected. Instead, the light might be scattered or escape from the ...
... b Optical fibres work by passing light along the fibre through totally internal reflection. This requires that the surface of the fibre be very smooth. Scratches on the surface of the optical fibre would prevent the light from being reflected. Instead, the light might be scattered or escape from the ...
Schlieren Visualization
... Undeflected light rays are affected uniformly by the knife edge and the intensity of the image is reduced with increased cutoff. As light passes through a density field with a non-constant first derivative, the light rays are deflected as shown in Figure 2. If light rays are deflected towards the kn ...
... Undeflected light rays are affected uniformly by the knife edge and the intensity of the image is reduced with increased cutoff. As light passes through a density field with a non-constant first derivative, the light rays are deflected as shown in Figure 2. If light rays are deflected towards the kn ...
Get
... enhancing films. Considering materials cost of LCDs, a polarizer is one of the most expensive optical components [18–20]. In general, the polarizer is made of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with stretching and dying process so that protection films are required at one side of the PVA film. The conventional ...
... enhancing films. Considering materials cost of LCDs, a polarizer is one of the most expensive optical components [18–20]. In general, the polarizer is made of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with stretching and dying process so that protection films are required at one side of the PVA film. The conventional ...
Role of Color Interference on the Insect`s Cuticle Coloration
... attribute that depends on illumination, the spectral reflectance of an object and its surroundings, as well as the spectral receptor types and further neural processing in the animal in question. Thus the same object might appear differently colored to different viewing organisms. Insects are master ...
... attribute that depends on illumination, the spectral reflectance of an object and its surroundings, as well as the spectral receptor types and further neural processing in the animal in question. Thus the same object might appear differently colored to different viewing organisms. Insects are master ...
Three models of light
... the image is called real. • If a screen is put at the real image, the rays will scatter in all directions and an image can be seen on the screen, just as if it were a real object. ...
... the image is called real. • If a screen is put at the real image, the rays will scatter in all directions and an image can be seen on the screen, just as if it were a real object. ...
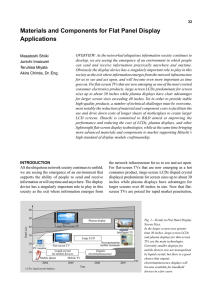
Materials and Components for Flat Panel Display
... several microns to several hundred microns in diameter, and are used in CCD (charge-coupled device) image sensors, 3D display elements, optical communications, and a host of other optical devices. Indeed, the MLA occupies a central place in Hitachi Maxell, Ltd.’s strategy to create more advanced opt ...
... several microns to several hundred microns in diameter, and are used in CCD (charge-coupled device) image sensors, 3D display elements, optical communications, and a host of other optical devices. Indeed, the MLA occupies a central place in Hitachi Maxell, Ltd.’s strategy to create more advanced opt ...
31.3. Rear Projection - Contrast and Gain
... displays. As an example, shadow mask CRTs and LCDs that utilize spatial color synthesis techniques to create full color image are less efficient than monochrome displays. In a color CRT only about one-fifth of the electrons pass through the shadow mask and become available for visible light creation ...
... displays. As an example, shadow mask CRTs and LCDs that utilize spatial color synthesis techniques to create full color image are less efficient than monochrome displays. In a color CRT only about one-fifth of the electrons pass through the shadow mask and become available for visible light creation ...
Chapter 12: Light
... • The colors of the visible spectrum differ from one another in terms of wavelength • Each combination of wavelengths has its own special sense of color • When white light strikes most objects certain colors are absorbed and certain colors are reflected, the reflected light is the color you see • Th ...
... • The colors of the visible spectrum differ from one another in terms of wavelength • Each combination of wavelengths has its own special sense of color • When white light strikes most objects certain colors are absorbed and certain colors are reflected, the reflected light is the color you see • Th ...
lecture8 - Tamara L Berg
... When you turn the lens of a camera to focus it -- you're moving it closer or farther away from the film surface. As you move the lens, you can line up the focused real image of an object so it falls directly on the film surface. ...
... When you turn the lens of a camera to focus it -- you're moving it closer or farther away from the film surface. As you move the lens, you can line up the focused real image of an object so it falls directly on the film surface. ...
Photographic film

This article is mainly concerned with still photography film. For motion picture film, please see film stock.Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent plastic film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film.The emulsion will gradually darken if left exposed to light, but the process is too slow and incomplete to be of any practical use. Instead, a very short exposure to the image formed by a camera lens is used to produce only a very slight chemical change, proportional to the amount of light absorbed by each crystal. This creates an invisible latent image in the emulsion, which can be chemically developed into a visible photograph. In addition to visible light, all films are sensitive to ultraviolet, X-rays and high-energy particles. Unmodified silver halide crystals are sensitive only to the blue part of the visible spectrum, producing unnatural-looking renditions of some colored subjects. This problem was overcome with the discovery that certain dyes, called sensitizing dyes, when adsorbed onto the silver halide crystals made them respond to other colors as well. First orthochromatic (sensitive to blue and green) and finally panchromatic (sensitive to all visible colors) films were developed. Panchromatic film renders all colors in shades of gray approximately matching their subjective brightness. By similar techniques special-purpose films can made sensitive into the infrared (IR) region of the spectrum.In black-and-white photographic film there is usually one layer of silver salts. When the exposed grains are developed, the silver salts are converted to metallic silver, which blocks light and appears as the black part of the film negative. Color film has at least three sensitive layers, incorporating different combinations of sensitizing dyes. Typically the blue-sensitive layer is on top, followed by a yellow filter layer to stop any remaining blue light from affecting the layers below. Next come a green-and-blue sensitive layer, and a red-and-blue sensitive layer, which record the green and red images respectively. During development, the exposed silver salts are converted to metallic silver, just as with black-and-white film. But in a color film, the by-products of the development reaction simultaneously combine with chemicals known as color couplers that are included either in the film itself or in the developer solution to form colored dyes. Because the by-products are created in direct proportion to the amount of exposure and development, the dye clouds formed are also in proportion to the exposure and development. Following development, the silver is converted back to silver salts in the bleach step. It is removed from the film during the process of fixing the image on the film with a dilute acidic solution such as acetic acid. Fixing leaves behind only the formed color dyes, which combine to make up the colored visible image. Later color films, like Kodacolor II, have as many as 12 emulsion layers, with upwards of 20 different chemicals in each layer.