Following the path of light: recovering and
... To clarify what we mean by following the path of light, let us first discuss a simple experiment we use to introduce the problem of vision to students. Let us consider the object in Fig. 1(a), which is a small plastic box containing transparent gel deco beads and water. Refractive index of beads is v ...
... To clarify what we mean by following the path of light, let us first discuss a simple experiment we use to introduce the problem of vision to students. Let us consider the object in Fig. 1(a), which is a small plastic box containing transparent gel deco beads and water. Refractive index of beads is v ...
Reflections On Golden Scarabs
... with over one hundred species known (Hawks 2001) and new species still being discovered (Fig. 3). Although they are sometimes thought of as rare beetles, they are more properly regarded as restricted in distribution. Essentially, all of the montane forests from Arizona to Ecuador have one or more s ...
... with over one hundred species known (Hawks 2001) and new species still being discovered (Fig. 3). Although they are sometimes thought of as rare beetles, they are more properly regarded as restricted in distribution. Essentially, all of the montane forests from Arizona to Ecuador have one or more s ...
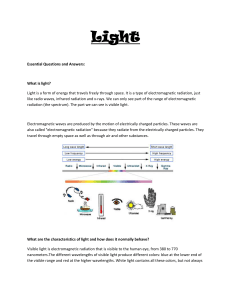
Essential Questions and Answers: What is light? Light is a form of
... as convex (magnifying) lenses. But they’re still used in a lot of different things. For example, eyeglasses have one convex surface and one concave surface. Between the two, the glasses can bend the light just the right amount before it gets to your eyes. One very useful thing about concave lenses i ...
... as convex (magnifying) lenses. But they’re still used in a lot of different things. For example, eyeglasses have one convex surface and one concave surface. Between the two, the glasses can bend the light just the right amount before it gets to your eyes. One very useful thing about concave lenses i ...
absorbance, a - srmbiotech25
... – The absorbing medium must not scatter the radiation - no turbidity; – The incident radiation must consist of parallel rays, each traversing the same length in the absorbing medium; – The incident radiation should preferably be monochromatic, or have at least a width that is narrower than that of t ...
... – The absorbing medium must not scatter the radiation - no turbidity; – The incident radiation must consist of parallel rays, each traversing the same length in the absorbing medium; – The incident radiation should preferably be monochromatic, or have at least a width that is narrower than that of t ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... Coating to Make Glass Invisible’. Clocks dial faces and showcase glasses and window panes cease to be visible. Light is not reflected from any angle. This can be used in eyeglasses to keep wearers to be bothered by light reflection or stray beams from side or behind. Camera lens with 8% less reflect ...
... Coating to Make Glass Invisible’. Clocks dial faces and showcase glasses and window panes cease to be visible. Light is not reflected from any angle. This can be used in eyeglasses to keep wearers to be bothered by light reflection or stray beams from side or behind. Camera lens with 8% less reflect ...
Chapter 4
... 2. Find the image of an object placed 40 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. What are the characteristics (location, size, direction, and nature) of the image? Location: 40 cm to left of mirror Size: Same as the object (M=1) ...
... 2. Find the image of an object placed 40 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. What are the characteristics (location, size, direction, and nature) of the image? Location: 40 cm to left of mirror Size: Same as the object (M=1) ...
Light and Optics Unit Test
... d. a solid 2. Which of the following is NOT a primary color? a. red b. blue c. yellow d. green 3. When most light passes through a surface but some rays are reflected the surface is called: a. transparent b. translucent c. opaque d. clear 4. If the angle of reflection off a smooth surface is 46o you ...
... d. a solid 2. Which of the following is NOT a primary color? a. red b. blue c. yellow d. green 3. When most light passes through a surface but some rays are reflected the surface is called: a. transparent b. translucent c. opaque d. clear 4. If the angle of reflection off a smooth surface is 46o you ...
Glencoe Physics Chapter 16
... 3. the same size - no enlargement or reduction 4. located the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror - image gets smaller as you move away 5. virtual - not real, appears to be behind the mirror Page 463; 6,9,10 ...
... 3. the same size - no enlargement or reduction 4. located the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror - image gets smaller as you move away 5. virtual - not real, appears to be behind the mirror Page 463; 6,9,10 ...
Chapter 20-Light The Nature of Light Visible Light Is a Form of
... e. Lenses are used in many kinds of instruments i. Camera=parts of a camera are lightproof box, opening in front of the camera, shutter over the opening, convex lens behind the opening, film at the back of the camera, device to hold and turn the film ii. Light microscope= two convex lenses one at ea ...
... e. Lenses are used in many kinds of instruments i. Camera=parts of a camera are lightproof box, opening in front of the camera, shutter over the opening, convex lens behind the opening, film at the back of the camera, device to hold and turn the film ii. Light microscope= two convex lenses one at ea ...
Document
... data that Grinnell students in the Modern Physics course take as part of an experiment in which they determine the age of the universe almost entirely from their own observations. The image is a raw CCD frame of the galaxy spectrum to which a plot of the spectrum and various explanatory notes have b ...
... data that Grinnell students in the Modern Physics course take as part of an experiment in which they determine the age of the universe almost entirely from their own observations. The image is a raw CCD frame of the galaxy spectrum to which a plot of the spectrum and various explanatory notes have b ...
EM Waves and Color
... None. They all travel at the same speed, the speed of light! Which EM wave has the most energy? Gamma rays. They have the highest frequency because they have the most energy. This is the type of energy usually released during an atomic bomb. ...
... None. They all travel at the same speed, the speed of light! Which EM wave has the most energy? Gamma rays. They have the highest frequency because they have the most energy. This is the type of energy usually released during an atomic bomb. ...
Prisms Lab - Mr. Ahearn`s Science
... • Prisms are typically made out of glass, but can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelength for which they are designed. • A prism can be used to break light up into its spectral colors (ROY G BIV). Prisms can also be used to reflect light, or to split light into components. ...
... • Prisms are typically made out of glass, but can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelength for which they are designed. • A prism can be used to break light up into its spectral colors (ROY G BIV). Prisms can also be used to reflect light, or to split light into components. ...
Light
... When light hits metal it knocks electrons off the surface. They found that red light cannot knock electrons off metal no matter how bright it is. If light were a wave then the brighter light should have more energy. Photons are light particles that contain certain amounts of energy based on their fr ...
... When light hits metal it knocks electrons off the surface. They found that red light cannot knock electrons off metal no matter how bright it is. If light were a wave then the brighter light should have more energy. Photons are light particles that contain certain amounts of energy based on their fr ...
Eyewear Lens Selection Guide
... Filter Shades: Protects against ultra-violet and infrared radiation generated when working with molten metal, and in welding, cutting, soldering and brazing. ...
... Filter Shades: Protects against ultra-violet and infrared radiation generated when working with molten metal, and in welding, cutting, soldering and brazing. ...
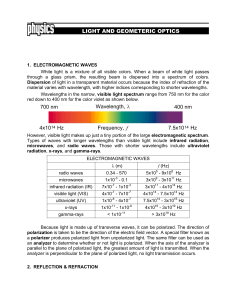
700 nm 400 nm Wavelength, λ Frequency, f 4x1014 Hz
... In Young’s double-slit experiment, light emerging from the two slits is used as two coherent sources. When the light is projected onto a screen, an interference pattern appears that consists of a series of alternating bright and dark fringes around a central maximum. Because the bright fringes indic ...
... In Young’s double-slit experiment, light emerging from the two slits is used as two coherent sources. When the light is projected onto a screen, an interference pattern appears that consists of a series of alternating bright and dark fringes around a central maximum. Because the bright fringes indic ...
Daedalon EO-85 Computerized Spectrophotometer
... appears to be a single color. The goal of this part is to measure the spectrum and determine the width of the wavelength band that is emitted in each case. 2. Measure the emission spectrum of the green, red and blue light emitting diodes in that order. The graphs will then be the same color as the L ...
... appears to be a single color. The goal of this part is to measure the spectrum and determine the width of the wavelength band that is emitted in each case. 2. Measure the emission spectrum of the green, red and blue light emitting diodes in that order. The graphs will then be the same color as the L ...
Wave Light Test
... Another ray is travelling through the glass towards the air. What angle of incidence at the top surface would cause the emerging ray to travel along the glass face? ...
... Another ray is travelling through the glass towards the air. What angle of incidence at the top surface would cause the emerging ray to travel along the glass face? ...
Lesson-2 Light Microscopy
... Microscopes are instruments designed to produce magnified visual or photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: produce a magnified image of the specimen, separate the details in the image, and render the details visible to the ...
... Microscopes are instruments designed to produce magnified visual or photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: produce a magnified image of the specimen, separate the details in the image, and render the details visible to the ...
LAB, A2 Color, Polarized Light
... 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the green and blue LEDs. 4. Remove the color filter from one of the flashlights. Examine the light produced by the white light and record your observations in the table. ...
... 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the green and blue LEDs. 4. Remove the color filter from one of the flashlights. Examine the light produced by the white light and record your observations in the table. ...
A crash course in optics
... box with a little hole on one side. It creates a real, reversed image on the opposite side of the box. Image is less bright than with a lens, but depth of field is almost infinite – the smaller the hole, the more so. Needs long exposure, but free of ...
... box with a little hole on one side. It creates a real, reversed image on the opposite side of the box. Image is less bright than with a lens, but depth of field is almost infinite – the smaller the hole, the more so. Needs long exposure, but free of ...
Real-Time Image Processing Requirements
... sky is also polarized, but this can be modeled and subtracted). To do this the light passing around the occulting disk is sent through polarization optics. These optics separate the light into two beams and each beam is refocused onto a camera. The polarizing elements are electrooptical and the ligh ...
... sky is also polarized, but this can be modeled and subtracted). To do this the light passing around the occulting disk is sent through polarization optics. These optics separate the light into two beams and each beam is refocused onto a camera. The polarizing elements are electrooptical and the ligh ...
Light - Effingham County Schools
... Transparent materials transmit almost all the light striking them, so you can see objects clearly through them. Only a small amount of light is absorbed and reflected. ...
... Transparent materials transmit almost all the light striking them, so you can see objects clearly through them. Only a small amount of light is absorbed and reflected. ...
Photographic film

This article is mainly concerned with still photography film. For motion picture film, please see film stock.Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent plastic film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film.The emulsion will gradually darken if left exposed to light, but the process is too slow and incomplete to be of any practical use. Instead, a very short exposure to the image formed by a camera lens is used to produce only a very slight chemical change, proportional to the amount of light absorbed by each crystal. This creates an invisible latent image in the emulsion, which can be chemically developed into a visible photograph. In addition to visible light, all films are sensitive to ultraviolet, X-rays and high-energy particles. Unmodified silver halide crystals are sensitive only to the blue part of the visible spectrum, producing unnatural-looking renditions of some colored subjects. This problem was overcome with the discovery that certain dyes, called sensitizing dyes, when adsorbed onto the silver halide crystals made them respond to other colors as well. First orthochromatic (sensitive to blue and green) and finally panchromatic (sensitive to all visible colors) films were developed. Panchromatic film renders all colors in shades of gray approximately matching their subjective brightness. By similar techniques special-purpose films can made sensitive into the infrared (IR) region of the spectrum.In black-and-white photographic film there is usually one layer of silver salts. When the exposed grains are developed, the silver salts are converted to metallic silver, which blocks light and appears as the black part of the film negative. Color film has at least three sensitive layers, incorporating different combinations of sensitizing dyes. Typically the blue-sensitive layer is on top, followed by a yellow filter layer to stop any remaining blue light from affecting the layers below. Next come a green-and-blue sensitive layer, and a red-and-blue sensitive layer, which record the green and red images respectively. During development, the exposed silver salts are converted to metallic silver, just as with black-and-white film. But in a color film, the by-products of the development reaction simultaneously combine with chemicals known as color couplers that are included either in the film itself or in the developer solution to form colored dyes. Because the by-products are created in direct proportion to the amount of exposure and development, the dye clouds formed are also in proportion to the exposure and development. Following development, the silver is converted back to silver salts in the bleach step. It is removed from the film during the process of fixing the image on the film with a dilute acidic solution such as acetic acid. Fixing leaves behind only the formed color dyes, which combine to make up the colored visible image. Later color films, like Kodacolor II, have as many as 12 emulsion layers, with upwards of 20 different chemicals in each layer.