Grammatical Features of English
... It was getting darker and darker Can be used with the simple past to describe an interruption of some kind. It was getting darker and darker, when he heard the sound of a fire alarm. Used in descriptions and for casual speech He was eating his breakfast, listening to the radio and feeling more than ...
... It was getting darker and darker Can be used with the simple past to describe an interruption of some kind. It was getting darker and darker, when he heard the sound of a fire alarm. Used in descriptions and for casual speech He was eating his breakfast, listening to the radio and feeling more than ...
Context Clues
... • Step Two: Insert another word that means the same thing (synonym) in place of the suffix, prefix, or root. • Step Three: Insert a word that means the opposite (antonym) in place of the suffix, prefix, or root. – Ex. Antinationalistic ...
... • Step Two: Insert another word that means the same thing (synonym) in place of the suffix, prefix, or root. • Step Three: Insert a word that means the opposite (antonym) in place of the suffix, prefix, or root. – Ex. Antinationalistic ...
The Simple Sentence
... An infinitive phrase consists of to followed by a verb (to fish). This infinitive is a noun, the subject of the sentence. ...
... An infinitive phrase consists of to followed by a verb (to fish). This infinitive is a noun, the subject of the sentence. ...
Grammar Terms Revision!
... Active Voice, Passive Voice, Subject, Object, • The dog saw the cat. • The cat was seen by the dog. ...
... Active Voice, Passive Voice, Subject, Object, • The dog saw the cat. • The cat was seen by the dog. ...
Grammar Notes: Subject / Verb Agreement
... Collective nouns usually take singular verbs. A collective noun has a singular form even though it refers to a group of individuals or things. Examples include army, audience, crowd, group, team, committee, class, and family. These nouns take a singular verb when the group acts as one unit. The floc ...
... Collective nouns usually take singular verbs. A collective noun has a singular form even though it refers to a group of individuals or things. Examples include army, audience, crowd, group, team, committee, class, and family. These nouns take a singular verb when the group acts as one unit. The floc ...
Parts of Speech
... Action Verbs – express observable action: He runs. She sneezed. They dance very well. Nonaction verbs – express your mental state, possession, appearance, and the 5 senses. These verbs are not usually used in progressive form. I think it’s cold. She has 2 sons. I hear the music. Linking Verbs (also ...
... Action Verbs – express observable action: He runs. She sneezed. They dance very well. Nonaction verbs – express your mental state, possession, appearance, and the 5 senses. These verbs are not usually used in progressive form. I think it’s cold. She has 2 sons. I hear the music. Linking Verbs (also ...
Gerunds Infinitives and Participles Fill in Blank Notes
... Infinitives in the subject position are often used for general or habitual actions. Here are some examples: To live a happy life is everyone’s deepest desire. ...
... Infinitives in the subject position are often used for general or habitual actions. Here are some examples: To live a happy life is everyone’s deepest desire. ...
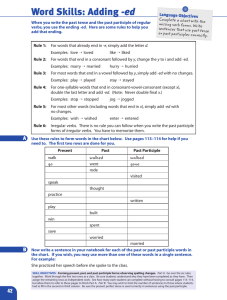
Word Skills: Adding -ed
... For example: She practiced her speech before she spoke to the class. SKILL OBJECTIVES: Forming present, past, and past participle forms; observing spelling changes. Part A: Go over the six rules together. Work through the first two rows as a class. Be sure students understand why they have been comp ...
... For example: She practiced her speech before she spoke to the class. SKILL OBJECTIVES: Forming present, past, and past participle forms; observing spelling changes. Part A: Go over the six rules together. Work through the first two rows as a class. Be sure students understand why they have been comp ...
Grammar Glossary for Parents Please find below a glossary of the
... Parenthesis is the addition of extra information to an already formed sentence. A parenthesis can be separated from the sentence with dashes, commas or brackets, and these are known as parentheses. When the parenthesis is removed from the sentence, it should still be grammatically correct. So, to ma ...
... Parenthesis is the addition of extra information to an already formed sentence. A parenthesis can be separated from the sentence with dashes, commas or brackets, and these are known as parentheses. When the parenthesis is removed from the sentence, it should still be grammatically correct. So, to ma ...
V. Pitfalls in Grammar and Rhetoric – Part II Adverbs: Adverbs are
... V. Pitfalls in Grammar and Rhetoric – Part II ...
... V. Pitfalls in Grammar and Rhetoric – Part II ...
12 The Autobiography of Admiral Ahmose Part III
... The sDm.in.f verb form applied to the verb xar “rage” expresses subsequent action, but what the pharaoh was reacting to is hidden in the lacuna. One may only guess that his rage was triggered by having learned some action of the Nubians. In the next sentence the narrative infinitive of the verb wdi ...
... The sDm.in.f verb form applied to the verb xar “rage” expresses subsequent action, but what the pharaoh was reacting to is hidden in the lacuna. One may only guess that his rage was triggered by having learned some action of the Nubians. In the next sentence the narrative infinitive of the verb wdi ...
Chapter 21: The Present Passive System
... The next word is finis, finis, f., meaning “end, limit, boundary, purpose.” It's a third-declension feminine i-stem noun. In the plural, like many Latin words, it has a special meaning. “Ends” implied to the Romans “boundaries,” and from that the sense of the “boundaries of a country,” thus its “te ...
... The next word is finis, finis, f., meaning “end, limit, boundary, purpose.” It's a third-declension feminine i-stem noun. In the plural, like many Latin words, it has a special meaning. “Ends” implied to the Romans “boundaries,” and from that the sense of the “boundaries of a country,” thus its “te ...
Grammar: Local Achievement Exam Prep. Week 2 Notes Parts of a
... Indirect Object: The person/thing that something is given to/ done for. An indirect object: Answers the question “to whom?” or “for whom?” Will always be a noun or pronoun You can’t have an indirect object without a direct object! Examples of Indirect Object: We will make him an offer. The attendant ...
... Indirect Object: The person/thing that something is given to/ done for. An indirect object: Answers the question “to whom?” or “for whom?” Will always be a noun or pronoun You can’t have an indirect object without a direct object! Examples of Indirect Object: We will make him an offer. The attendant ...
Takakjy 311 Summer 2014 Study Guide for final exam (9
... Your final will have 3 seen passages, 1 sight passage, vocabulary identification, parsing, and grammar questions. It will be cumulative (look on weebly for passages that are fair game) Parsing guidelines: Parse: Please provide the appropriate grammatical information for each underlined word (see cha ...
... Your final will have 3 seen passages, 1 sight passage, vocabulary identification, parsing, and grammar questions. It will be cumulative (look on weebly for passages that are fair game) Parsing guidelines: Parse: Please provide the appropriate grammatical information for each underlined word (see cha ...
Language Usage - Eastern Florida State College
... How we speak and write creates an impression of who we are. When there are errors in our writing or speaking, we project a negative image. Proper usage (grammar) in our writing and speaking is critical to creating a positive image, especially in the workplace. The purpose of this presentation-works ...
... How we speak and write creates an impression of who we are. When there are errors in our writing or speaking, we project a negative image. Proper usage (grammar) in our writing and speaking is critical to creating a positive image, especially in the workplace. The purpose of this presentation-works ...
b - Angos
... SVS - wey.-on.do (see below) “riverside” SVC - was.no “weight” CV - is.ka “hit” CVC - pan.ho “wing” CVS - kay.so “seaweed” CSV - mwe “with” CSVC - syen “hundred” CSVS - (no example) ...
... SVS - wey.-on.do (see below) “riverside” SVC - was.no “weight” CV - is.ka “hit” CVC - pan.ho “wing” CVS - kay.so “seaweed” CSV - mwe “with” CSVC - syen “hundred” CSVS - (no example) ...
Daily Grammar Practice
... demonstrative (dem pron): (demonstrate which one) this, that, these, those indefinite (ind pron): (don't refer to a definite person or thing) each, either, neither, few, some, all, most, several, few, many, none, one, someone, no one, everyone, anyone, somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, more, ...
... demonstrative (dem pron): (demonstrate which one) this, that, these, those indefinite (ind pron): (don't refer to a definite person or thing) each, either, neither, few, some, all, most, several, few, many, none, one, someone, no one, everyone, anyone, somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, more, ...
Verbs: Lie-Lay Verbs: Lie-Lay, Sit-Set, Rise
... never has a direct object. (Intransitive verb) Example: He lies on the couch. (Reclines) Lay (lay, laid, laid, laying) means to put; it always takes a direct object. (Transitive verb) Example: He lays the book on the desk. (Puts) Note: It you are not sure which form of the verb to use, apply put as ...
... never has a direct object. (Intransitive verb) Example: He lies on the couch. (Reclines) Lay (lay, laid, laid, laying) means to put; it always takes a direct object. (Transitive verb) Example: He lays the book on the desk. (Puts) Note: It you are not sure which form of the verb to use, apply put as ...
grammar - rdonnell
... Auxiliary verbs are: may, might, shall, will, should, can, could, would, have, had, has… ...
... Auxiliary verbs are: may, might, shall, will, should, can, could, would, have, had, has… ...
Sentence Parts and Phrases
... • Intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (ex: Please sit down.) • All linking verbs (lv) are intransitive ...
... • Intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (ex: Please sit down.) • All linking verbs (lv) are intransitive ...
Sentence Parts and Phrases
... • Intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (ex: Please sit down.) • All linking verbs (lv) are intransitive ...
... • Intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (ex: Please sit down.) • All linking verbs (lv) are intransitive ...
Sentence Parts and Phrases
... • Intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (ex: Please sit down.) • All linking verbs (lv) are intransitive ...
... • Intransitive verb (vi): does not take a direct object (ex: Please sit down.) • All linking verbs (lv) are intransitive ...