Sentence Basics - Tech Coach Corner
... How do I teach a mini-lesson? 1. Explain clearly your understanding of the topic and then give an example 2. Guide your classmates through a practice activity and/or more examples 3. Provide a creative way to “test” your classmates understanding and ability to apply the new material Teaching Tip: B ...
... How do I teach a mini-lesson? 1. Explain clearly your understanding of the topic and then give an example 2. Guide your classmates through a practice activity and/or more examples 3. Provide a creative way to “test” your classmates understanding and ability to apply the new material Teaching Tip: B ...
s-v_agreement
... How do I teach a mini-lesson? 1. Explain clearly your understanding of the topic and then give an example 2. Guide your classmates through a practice activity and/or more examples 3. Provide a creative way to “test” your classmates understanding and ability to apply the new material Teaching Tip: B ...
... How do I teach a mini-lesson? 1. Explain clearly your understanding of the topic and then give an example 2. Guide your classmates through a practice activity and/or more examples 3. Provide a creative way to “test” your classmates understanding and ability to apply the new material Teaching Tip: B ...
AteneodeZamboanga University “Mothers”
... (The joys of a mother are the following: Father loves her, her daughter imitates her, the woman next door confides in her.) c. What are her pains? (The pains of a mother are the following: when her son ignores her, motorists hurry around, teachers phone her.) d. How do you describe your own mother? ...
... (The joys of a mother are the following: Father loves her, her daughter imitates her, the woman next door confides in her.) c. What are her pains? (The pains of a mother are the following: when her son ignores her, motorists hurry around, teachers phone her.) d. How do you describe your own mother? ...
4th Grade Language Curriculum
... preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun (usually something you can see). It may end with an abstract noun (with much happiness), but usually ends with a concrete noun (with my dad). A phrase doesn t express a complete thought; it will not serve as a subject or verb in a sentence. It s possible t ...
... preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun (usually something you can see). It may end with an abstract noun (with much happiness), but usually ends with a concrete noun (with my dad). A phrase doesn t express a complete thought; it will not serve as a subject or verb in a sentence. It s possible t ...
ing is a gerund - ELT Concourse home
... a) The fittings she had in the living room didn’t match the carpet at all. Clearly a noun here; it’s even made plural and countable. b) Her fitting of the carpet was pretty amateurish. Modified by a possessive, her, so arguably a noun but it’s not referring to a thing; it’s referring to an action an ...
... a) The fittings she had in the living room didn’t match the carpet at all. Clearly a noun here; it’s even made plural and countable. b) Her fitting of the carpet was pretty amateurish. Modified by a possessive, her, so arguably a noun but it’s not referring to a thing; it’s referring to an action an ...
Ser and Estar: Part IV
... something is from, use ser. To describe location, or where something is located right now, use estar. To tell where an event is taking place, use ser. ...
... something is from, use ser. To describe location, or where something is located right now, use estar. To tell where an event is taking place, use ser. ...
WH Chapter 4 Complements Teacher Version
... An Indirect object tells to what or whom or for what or whom an action is done. Verbs that often take indirect objects include: bring, give, hand, lend, make, send, show, teach, tell and write. ...
... An Indirect object tells to what or whom or for what or whom an action is done. Verbs that often take indirect objects include: bring, give, hand, lend, make, send, show, teach, tell and write. ...
Parts of a Sentence
... Example 1: I wanted to eat a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. We didn’t have any jelly. This example has no conjunction. Here is how to connect it with a conjunction. Example 2: I wanted to eat a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, but we didn’t have any jelly. “But,” the conjunction in this sentence ...
... Example 1: I wanted to eat a peanut butter and jelly sandwich. We didn’t have any jelly. This example has no conjunction. Here is how to connect it with a conjunction. Example 2: I wanted to eat a peanut butter and jelly sandwich, but we didn’t have any jelly. “But,” the conjunction in this sentence ...
Lesson 33
... Ex. moratur – he delays, conati erant – they had tried PAP, FAP, future active infinitive are active forms Locative Case With names of cities, towns, small islands, domus and rus no preposition used to express place Use a case called locativeLike genitive in singular in nouns of 1st& 2nd dec, otherw ...
... Ex. moratur – he delays, conati erant – they had tried PAP, FAP, future active infinitive are active forms Locative Case With names of cities, towns, small islands, domus and rus no preposition used to express place Use a case called locativeLike genitive in singular in nouns of 1st& 2nd dec, otherw ...
1B Use of adjectives
... Adjectives can be used in either an attributive sense or a predicative sense. An attributive adjective presents an attribute of the noun that, from a grammatical point of view, is simply assumed to be true. For example: if I say, “The purple cow ate the grass,” I merely specify which cow did the eat ...
... Adjectives can be used in either an attributive sense or a predicative sense. An attributive adjective presents an attribute of the noun that, from a grammatical point of view, is simply assumed to be true. For example: if I say, “The purple cow ate the grass,” I merely specify which cow did the eat ...
Kinds of Sentences Study Guide
... The actors are here. There is some soup in the pot. Some soup is in the pot. [Sometimes there must be dropped for the sentence to make sense.] Understood Subjects o The subject you is not stated in a command or request. You is called an understood subject. Ex: (you) Wait for me in the library. Compo ...
... The actors are here. There is some soup in the pot. Some soup is in the pot. [Sometimes there must be dropped for the sentence to make sense.] Understood Subjects o The subject you is not stated in a command or request. You is called an understood subject. Ex: (you) Wait for me in the library. Compo ...
Grade Eight ~ California State
... 63. Parallel structures use similar grammatical construction. They are also called parallelisms. 64. Participial phrases contain verbs acting as adjectives. For instance, “Looking at the displays, I lost track of time.” 65. Past participles are verb forms in the past tense form that act as adjective ...
... 63. Parallel structures use similar grammatical construction. They are also called parallelisms. 64. Participial phrases contain verbs acting as adjectives. For instance, “Looking at the displays, I lost track of time.” 65. Past participles are verb forms in the past tense form that act as adjective ...
Phrases, Clauses, and Appositives
... A sentence requires a subject, predicate and a complete thought. Phrases, subordinate clauses, and appositives are missing the complete thought, and sometimes a subject and predicate. Let’s take a look at each one. 1. A phrase is a group of words that don’t have both a subject and a predicate. Phras ...
... A sentence requires a subject, predicate and a complete thought. Phrases, subordinate clauses, and appositives are missing the complete thought, and sometimes a subject and predicate. Let’s take a look at each one. 1. A phrase is a group of words that don’t have both a subject and a predicate. Phras ...
Grammar Punctuation Spelling years 5 and 6
... The r is doubled if the –fer is still stressed when the ending is added. ...
... The r is doubled if the –fer is still stressed when the ending is added. ...
chapter 3 – the morphology of english
... 6. {care} + {-less} + {-ly} {care} is a noun meaning “attentiveness.” {-less} creates adjectives meaning “without” (hopeless). {-ly} makes adverbs from adjectives (sadly). 7. {boy} + {-ish} + {-ness} {boy} is a noun meaning “male child.” {-ish} creates adjectives meaning “having the quality of ” (fo ...
... 6. {care} + {-less} + {-ly} {care} is a noun meaning “attentiveness.” {-less} creates adjectives meaning “without” (hopeless). {-ly} makes adverbs from adjectives (sadly). 7. {boy} + {-ish} + {-ness} {boy} is a noun meaning “male child.” {-ish} creates adjectives meaning “having the quality of ” (fo ...
sentence-structure
... Misplaced Participles When completely dissected, the assistant pulls up the seminal vesicles with a grasper and the rest of the dissection is carried out in the same way. Contingent on grant funding, the researcher also plans an add-on study, in which the effectiveness of a manualized behavioral th ...
... Misplaced Participles When completely dissected, the assistant pulls up the seminal vesicles with a grasper and the rest of the dissection is carried out in the same way. Contingent on grant funding, the researcher also plans an add-on study, in which the effectiveness of a manualized behavioral th ...
This Power Point is about… the word class: VERBS
... I went for a walk yesterday. I will go for a walk tomorrow. I was going for a walk when I saw the crash. I am going for a walk. ...
... I went for a walk yesterday. I will go for a walk tomorrow. I was going for a walk when I saw the crash. I am going for a walk. ...
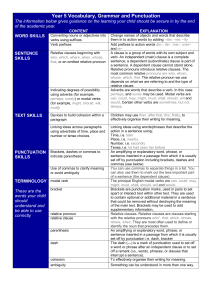
Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
complete subject
... Declarative – Makes a statement; always ends with a period. Interrogative – Asks a question; always ends with a question mark Imperative – Tells or asks someone to do something. Usually ends in a period, but may end with an exclamation point. Exclamatory – Shows strong feelings; always ends with an ...
... Declarative – Makes a statement; always ends with a period. Interrogative – Asks a question; always ends with a question mark Imperative – Tells or asks someone to do something. Usually ends in a period, but may end with an exclamation point. Exclamatory – Shows strong feelings; always ends with an ...
parts of speech - dr
... To be learnt on the separate lesson relative pronouns (who, which, what, that) used in complex sentences To be learnt on the separate lesson demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these, those) indefinite pronouns (some, all, both, each, etc.) ...
... To be learnt on the separate lesson relative pronouns (who, which, what, that) used in complex sentences To be learnt on the separate lesson demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these, those) indefinite pronouns (some, all, both, each, etc.) ...
Phrases - Mrs. Maldonado`s English Class
... • The peasants decided to rebel. (noun) • The soldier’s only hope was to surrender. (noun) • I have no goal except to finish school. (noun) • You have only one choice, to stay. (noun) • The children showed a willingness to cooperate. (adjective) • Some people were unable to fight. (adverb) ...
... • The peasants decided to rebel. (noun) • The soldier’s only hope was to surrender. (noun) • I have no goal except to finish school. (noun) • You have only one choice, to stay. (noun) • The children showed a willingness to cooperate. (adjective) • Some people were unable to fight. (adverb) ...
Verbals Gerunds A gerund ends in -ing and can be used as a noun
... ______9. Then, the great shows will be running again! A. verb ...
... ______9. Then, the great shows will be running again! A. verb ...
Build the correct OE VP for the sentence She shoves the man. (man
... p. 65). Since weorpan is a Class 3 strong verb that has the infinitive stem vowel -eo-, the preterite singular vowel should be -ea- (see p. 75). Then we remove the infinitive ending -an, and do not add anything, as there is no ending in the 1st person singular past indicative of strong verbs (see p. ...
... p. 65). Since weorpan is a Class 3 strong verb that has the infinitive stem vowel -eo-, the preterite singular vowel should be -ea- (see p. 75). Then we remove the infinitive ending -an, and do not add anything, as there is no ending in the 1st person singular past indicative of strong verbs (see p. ...
Parts of Speech Reference Sheet
... Linking verb (State of being) – instead of showing what the subject is doing, this verb shows the subject in a state of being. It links the subject to some other word in the sentence that describes, identifies, or gives more information about it. Ex: John was sick for two days. John is hungry. o CHA ...
... Linking verb (State of being) – instead of showing what the subject is doing, this verb shows the subject in a state of being. It links the subject to some other word in the sentence that describes, identifies, or gives more information about it. Ex: John was sick for two days. John is hungry. o CHA ...