Español 7
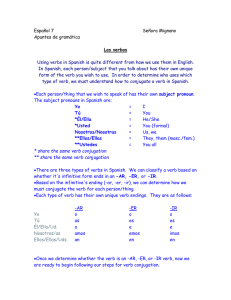
... form of the verb you wish to use. In order to determine who uses which type of verb, we must understand how to conjugate a verb in Spanish. Each person/thing that we wish to speak of has their own subject pronoun. The subject pronouns in Spanish are: Yo ...
... form of the verb you wish to use. In order to determine who uses which type of verb, we must understand how to conjugate a verb in Spanish. Each person/thing that we wish to speak of has their own subject pronoun. The subject pronouns in Spanish are: Yo ...
Regular "er" Verbs
... Many Spanish verbs are completely regular, meaning that they follow a specific pattern of conjugation. In this lesson you will learn to conjugate regular ar, er, and ir verbs (in the present tense). Before you can do that, you must memorize the following subject pronouns. yo (I) tú (you informa ...
... Many Spanish verbs are completely regular, meaning that they follow a specific pattern of conjugation. In this lesson you will learn to conjugate regular ar, er, and ir verbs (in the present tense). Before you can do that, you must memorize the following subject pronouns. yo (I) tú (you informa ...
Spanish - University of Otago
... supported my Honours exchange in 2013, when I spent the first semester living and studying Spanish literature in Madrid, before coming back to write my dissertation (in Spanish!). The experience was amazing and unforgettable; the personal growth that comes from exchanges and travel is invaluable, as ...
... supported my Honours exchange in 2013, when I spent the first semester living and studying Spanish literature in Madrid, before coming back to write my dissertation (in Spanish!). The experience was amazing and unforgettable; the personal growth that comes from exchanges and travel is invaluable, as ...
Direct Object Pronouns
... First of all you must remember that a direct object in a sentence is the person, event or thing affected by the verb. The main difference between the use of the direct object pronouns in Spanish and English is their placement. While in English they substitute the direct object (and its article) and ...
... First of all you must remember that a direct object in a sentence is the person, event or thing affected by the verb. The main difference between the use of the direct object pronouns in Spanish and English is their placement. While in English they substitute the direct object (and its article) and ...
Subjects of Verbs - Light Bulb Languages
... use to replace these nouns ? e.g. Paul likes swimming. He Paul swims every day. We Ana and I speak Spanish. ...
... use to replace these nouns ? e.g. Paul likes swimming. He Paul swims every day. We Ana and I speak Spanish. ...
Linguistic Development in L2 Spanish: Creation and analysis of a
... another central discussion in language learning theory. Spanish word order is variable, with subjects both preceding and following verbs, in varying circumstances. The different possibilities are controlled by two interacting factors: a) the grammar associated with particular types of verb, and b) t ...
... another central discussion in language learning theory. Spanish word order is variable, with subjects both preceding and following verbs, in varying circumstances. The different possibilities are controlled by two interacting factors: a) the grammar associated with particular types of verb, and b) t ...
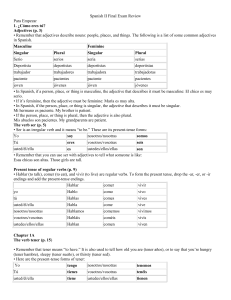
Spanish II Final Exam Review
... • In Spanish, if the person, place, or thing is singular, the adjective that describes it must be singular. Mi hermano es paciente. My brother is patient. • If the person, place, or thing is plural, then the adjective is also plural. Mis abuelos son pacientes. My grandparents are patient. The verb s ...
... • In Spanish, if the person, place, or thing is singular, the adjective that describes it must be singular. Mi hermano es paciente. My brother is patient. • If the person, place, or thing is plural, then the adjective is also plural. Mis abuelos son pacientes. My grandparents are patient. The verb s ...
hablar....................... hablando
... I am studying. I am studying with María. In English, present progressive can be used to describe what is happening now, or what will happen in the future. I am studying now. I am studying with María tonight. In Spanish, the present progressive is only used to describe an action that is in the proces ...
... I am studying. I am studying with María. In English, present progressive can be used to describe what is happening now, or what will happen in the future. I am studying now. I am studying with María tonight. In Spanish, the present progressive is only used to describe an action that is in the proces ...
Spanish Pronouns - FunSpanishlearning
... Vosotros and vosotras both have a parenthesis around them. This is because in the western hemisphere, they are usually not used. They both mean “you” and are used for informal situations. Also, you should have seen “Ud.” This also means you and is an abbreviation of usted. Use Ud. when you are addre ...
... Vosotros and vosotras both have a parenthesis around them. This is because in the western hemisphere, they are usually not used. They both mean “you” and are used for informal situations. Also, you should have seen “Ud.” This also means you and is an abbreviation of usted. Use Ud. when you are addre ...
Using the BDI with Children from Spanish-Speaking
... EC 27 In English this tests two plural forms ending with /s/ and two ending with /z/. In Spanish this difference would be /s/ and /es/. The examples given test three /s/ and one /es/. In English the number of syllables in the word remains the same, while in Spanish the number of syllables increases ...
... EC 27 In English this tests two plural forms ending with /s/ and two ending with /z/. In Spanish this difference would be /s/ and /es/. The examples given test three /s/ and one /es/. In English the number of syllables in the word remains the same, while in Spanish the number of syllables increases ...
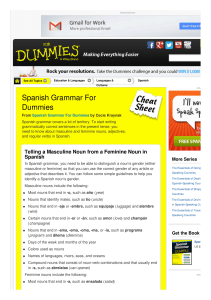
Spanish Grammar For Dummies Cheat Sheet
... In Spanish grammar, adjectives have to agree with the nouns they modify in both gender and number, no matter what: Gender: If a noun is feminine, like la muchacha (the girl), the adjective must be feminine, too. For example, to talk about a tall girl, you’d say la muchacha alta (the tall girl). If t ...
... In Spanish grammar, adjectives have to agree with the nouns they modify in both gender and number, no matter what: Gender: If a noun is feminine, like la muchacha (the girl), the adjective must be feminine, too. For example, to talk about a tall girl, you’d say la muchacha alta (the tall girl). If t ...
Subject Pronouns
... • In this presentation we’re going to look at the form and use of subject pronouns in Spanish. ...
... • In this presentation we’re going to look at the form and use of subject pronouns in Spanish. ...
Spanish Discovery
... • A further advantage that Cortes had was his ability to rally other natives to his side. Some of the Aztecs’ neighbors were unhappy with the tribute the Aztecs demanded of them, and they welcomed the opportunity to ally themselves with the Europeans to help defeat the Aztec Empire. • In 1535, Cort ...
... • A further advantage that Cortes had was his ability to rally other natives to his side. Some of the Aztecs’ neighbors were unhappy with the tribute the Aztecs demanded of them, and they welcomed the opportunity to ally themselves with the Europeans to help defeat the Aztec Empire. • In 1535, Cort ...
2016 Summer Toledo Courses
... This internship course offer students the unique opportunity to experience the Spanish work environment and further immerse themselves into life in Toledo. The internships are designed to introduce students to the rich culture for which Toledo is known. This experiential learning will be coupled wit ...
... This internship course offer students the unique opportunity to experience the Spanish work environment and further immerse themselves into life in Toledo. The internships are designed to introduce students to the rich culture for which Toledo is known. This experiential learning will be coupled wit ...
Impersonal “se” (passive voice)
... These are "impersonal expressions". In other words, we don't really have anyone specific in mind when we say "They say..." or "One" or " You". We mean people in general. This is what we mean by "impersonal". Spanish has a slightly different format for expressing this Impersonal voice. Spanish adds t ...
... These are "impersonal expressions". In other words, we don't really have anyone specific in mind when we say "They say..." or "One" or " You". We mean people in general. This is what we mean by "impersonal". Spanish has a slightly different format for expressing this Impersonal voice. Spanish adds t ...
Flowers
... •In the first sentence, we name the person who is Mexican. •In the second sentence, we replace the person’s name with the word ‘él’. ...
... •In the first sentence, we name the person who is Mexican. •In the second sentence, we replace the person’s name with the word ‘él’. ...
Present Tense Verbs
... Tutorials Spanish Cool! Provides students with a bilingual tutorial on the present indicative. There is also information on dialect differences in the Spanish-speaking world. A mailing list is available for those interested in improving their Spanish. (Juan Ramón, Madrid, Spain) Present Progressive ...
... Tutorials Spanish Cool! Provides students with a bilingual tutorial on the present indicative. There is also information on dialect differences in the Spanish-speaking world. A mailing list is available for those interested in improving their Spanish. (Juan Ramón, Madrid, Spain) Present Progressive ...
To be, or not to be?
... The Spanish verb ser is also irregular. ser = to be yo soy = I am tú eres = you are él es = he is ella es = she is usted es = you are nosotros somos = we are ellos son = they are ustedes son = you (all) are ...
... The Spanish verb ser is also irregular. ser = to be yo soy = I am tú eres = you are él es = he is ella es = she is usted es = you are nosotros somos = we are ellos son = they are ustedes son = you (all) are ...
conjugation. In this lesson
... Many Spanish verbs are completely regular, meaning that they follow a specific pattern of conjugation. In this lesson you will learn to conjugate regular -ar, -er, and -ir verbs (in the present tense). Before you can do that, you must memorize the following subject pronouns. yo (I) tú (you - inform ...
... Many Spanish verbs are completely regular, meaning that they follow a specific pattern of conjugation. In this lesson you will learn to conjugate regular -ar, -er, and -ir verbs (in the present tense). Before you can do that, you must memorize the following subject pronouns. yo (I) tú (you - inform ...
Spanish 3 Mid-term Exam Outline
... with your password. Go to the online edition and click on the book pages tab. Re-read all of the information presented, and then do the more practice activities which change every 2-3 pages of the text. ...
... with your password. Go to the online edition and click on the book pages tab. Re-read all of the information presented, and then do the more practice activities which change every 2-3 pages of the text. ...
In English, you`ll hear statements like "You shouldn`t smoke in a
... These are "impersonal expressions". In other words, we don't really have anyone specific in mind when we say "They say..." or "One" or " You". We mean people in general. This is what we mean by "impersonal". Spanish has a slightly different format for expressing this Impersonal voice. Spanish adds t ...
... These are "impersonal expressions". In other words, we don't really have anyone specific in mind when we say "They say..." or "One" or " You". We mean people in general. This is what we mean by "impersonal". Spanish has a slightly different format for expressing this Impersonal voice. Spanish adds t ...
Conjugating regular present tense verbs
... All Spanish verbs end with either –ar, -er or –ir in their infinitive forms. The infinitive form is the verb without a subject or tense. In English it translates as “to + verb”. EXAMPLE: “hablar” means “to talk/speak” You conjugate an infinitive verb to make it match the subject. To conjugate ...
... All Spanish verbs end with either –ar, -er or –ir in their infinitive forms. The infinitive form is the verb without a subject or tense. In English it translates as “to + verb”. EXAMPLE: “hablar” means “to talk/speak” You conjugate an infinitive verb to make it match the subject. To conjugate ...
To be, or not to be? - Plain Local Schools
... The Spanish verb ser is also irregular. ser = to be yo soy = I am tú eres = you are él es = he is ella es = she is usted es = you are nosotros somos = we are ellos son = they are ustedes son = you (all) are ...
... The Spanish verb ser is also irregular. ser = to be yo soy = I am tú eres = you are él es = he is ella es = she is usted es = you are nosotros somos = we are ellos son = they are ustedes son = you (all) are ...
To be, or not to be? - Edgewater Public Schools
... The Spanish verb ser is also irregular. ser = to be yo soy = I am tú eres = you are él es = he is ella es = she is usted es = you are nosotros somos = we are ellos son = they are ustedes son = you (all) are ...
... The Spanish verb ser is also irregular. ser = to be yo soy = I am tú eres = you are él es = he is ella es = she is usted es = you are nosotros somos = we are ellos son = they are ustedes son = you (all) are ...
Spanish dialects and varieties

Some of the regional varieties of the Spanish language are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar.While all Spanish dialects use the same written standard, all spoken varieties differ from the written variety, in different degrees. There are differences between European Spanish (also called Peninsular Spanish) and the Spanish of the Americas, as well as many different dialect areas both within Spain and within Hispanic America.Prominent differences of pronunciation among dialects of Spanish include: the maintenance vs. loss of distinction between the phonemes /θ/ and /s/ (distinción vs. seseo); the maintenance or loss of distinction between phonemes represented orthographically by ll and y (yeísmo); the maintenance of syllable-final [s] vs. its weakening to [h] (called aspiration, or the more precise term debuccalization), or its loss; and the tendency, in areas of central Mexico and of the Andean highlands, to reduction (especially devoicing), or loss, of unstressed vowels, mainly when they are in contact with voiceless consonants.Among grammatical features, the most prominent variation among dialects is in the use of the second-person pronouns. In most of Spain, the informal second-person plural pronoun is vosotros, while in Hispanic America the only second-person plural pronoun, for both formal and informal registers, is ustedes. And for the second-person singular familiar pronoun, some dialects use tú (and its associated verb forms), while others use either vos (see voseo) or both tú and vos (which, together with usted, can make for a possible three-tiered distinction of formalities).There are significant differences in vocabulary among regional varieties of Spanish, particularly in the domains of food products, everyday objects, and clothes; and many Hispanic American varieties show considerable lexical influence from Native American languages.