Internal and external forces again: changes in word order in Old
... typical rhythmic pattern of ‘strong’+‘weak’, so that the ultimate justification for it may be prosodic. But as Vennemann points out (personal communication) the essential question is why an inherited Indo-European phenomenom like Wackernagel’s Law seems only to have affected some languages. As there i ...
... typical rhythmic pattern of ‘strong’+‘weak’, so that the ultimate justification for it may be prosodic. But as Vennemann points out (personal communication) the essential question is why an inherited Indo-European phenomenom like Wackernagel’s Law seems only to have affected some languages. As there i ...
Verbals: Infinitives Verbals: Infinitive Phrases
... Verbals: Infinitives Verbals are formed from verbs and are used as adjectives, nouns, or adverbs. One kind of verbal is the infinitive. An infinitive is a verb form that that can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Most infinitives begin with to. ...
... Verbals: Infinitives Verbals are formed from verbs and are used as adjectives, nouns, or adverbs. One kind of verbal is the infinitive. An infinitive is a verb form that that can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Most infinitives begin with to. ...
MODES OF LINGUISTIC COMMUNICATION
... Functional or grammatical morphemes are free morphemes which have little or no meaning on their own, but which have a grammatical function. For example, the articles the and an indicate whether a noun is definite or indefinite -the boy or a boy. In a language, these morphemes are represented by pron ...
... Functional or grammatical morphemes are free morphemes which have little or no meaning on their own, but which have a grammatical function. For example, the articles the and an indicate whether a noun is definite or indefinite -the boy or a boy. In a language, these morphemes are represented by pron ...
Test ReviewPronounsSentenceTypesAPRIL2
... 3. How many independent clauses are contained in a compound sentence? 4. Are the “FANBOYS” a hip-hop musical group? 5. List the “FANBOYS.” ...
... 3. How many independent clauses are contained in a compound sentence? 4. Are the “FANBOYS” a hip-hop musical group? 5. List the “FANBOYS.” ...
Grammar At A Glance Document
... o The verb—the verb tells us what is happening or identifies the action taking place in the sentence. It represents the process. o Participant as subject of the verb—the subject is the participant in the sentence doing the action. (the ‘doer’ of the verb) o Participant as object of the verb—the obje ...
... o The verb—the verb tells us what is happening or identifies the action taking place in the sentence. It represents the process. o Participant as subject of the verb—the subject is the participant in the sentence doing the action. (the ‘doer’ of the verb) o Participant as object of the verb—the obje ...
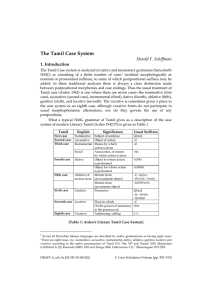
The Tamil Case System
... overall semantic analysis for each case morpheme/postposition. There is a need here not only to determine what semantic distinctions are involved, but also what the surfacestructure categories are, since there is not even agreement in this area. Since the Tamil case/postpositional system seems to in ...
... overall semantic analysis for each case morpheme/postposition. There is a need here not only to determine what semantic distinctions are involved, but also what the surfacestructure categories are, since there is not even agreement in this area. Since the Tamil case/postpositional system seems to in ...
Spanish Courses 2
... FUNCTIONAL CONTENT: - To distinguish between continuously ongoing actions and habitual actions. - To express feelings. - To describe friendly or sentimental relations. GRAMMATICAL CONTENT: - Irregular reflexive verbs in the present indicative. LEXICAL CONTENT: - Objects and verbs concerning the pers ...
... FUNCTIONAL CONTENT: - To distinguish between continuously ongoing actions and habitual actions. - To express feelings. - To describe friendly or sentimental relations. GRAMMATICAL CONTENT: - Irregular reflexive verbs in the present indicative. LEXICAL CONTENT: - Objects and verbs concerning the pers ...
PVBMT: A Principal Verb based Approach for English to Bangla
... in [8]. It is based on SMT which needs millions of parallel bilingual text corpora. For better translation, it emphasizes to generate rules for preposition binding. The preposition handle module of this approach is divided into two parts: (1) pre-process sub-module and (2) post-process sub-module. T ...
... in [8]. It is based on SMT which needs millions of parallel bilingual text corpora. For better translation, it emphasizes to generate rules for preposition binding. The preposition handle module of this approach is divided into two parts: (1) pre-process sub-module and (2) post-process sub-module. T ...
Developing a Computational Tool for Learning and Testing the
... In Sri Lanka and India, English is taught as a second language and it is very important especially for the students of ESL at the secondary level in schools and for the students in the higher educational institutes. For this approach or study, the students at CAS in linguistics at Annamalai Universi ...
... In Sri Lanka and India, English is taught as a second language and it is very important especially for the students of ESL at the secondary level in schools and for the students in the higher educational institutes. For this approach or study, the students at CAS in linguistics at Annamalai Universi ...
An Overview of Lexical Semantics
... shatter, and snap; like touch are: pat, stroke, and tickle; like hit are: bash, kick, pound, tap, and whack. We have isolated these four classes of verbs by their syntactic behavior. In the rest of this Section, I present some of the semantic evidence linguists use to identify these same verb classe ...
... shatter, and snap; like touch are: pat, stroke, and tickle; like hit are: bash, kick, pound, tap, and whack. We have isolated these four classes of verbs by their syntactic behavior. In the rest of this Section, I present some of the semantic evidence linguists use to identify these same verb classe ...
Gra MM ar - EEC
... dollar, IBM, and tangerine. Abstract nouns name generalized ideas such as qualities or concepts that are not easily pictured. Emotion, power, and tension are typical examples of abstract nouns. Business writing is most effective when concrete words predominate. It is clearer to write We need 16-poun ...
... dollar, IBM, and tangerine. Abstract nouns name generalized ideas such as qualities or concepts that are not easily pictured. Emotion, power, and tension are typical examples of abstract nouns. Business writing is most effective when concrete words predominate. It is clearer to write We need 16-poun ...
Document
... identify what verb tense is used. “As you can see, all of the verbs are in present simple tense, which is the tense we are reviewing today.” o Present Simple Use - We use Present Simple when speaking about actions or things that are habitual or always true. (I go to school every day.) Key Words ...
... identify what verb tense is used. “As you can see, all of the verbs are in present simple tense, which is the tense we are reviewing today.” o Present Simple Use - We use Present Simple when speaking about actions or things that are habitual or always true. (I go to school every day.) Key Words ...
3015 FRENCH MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper
... NB Reward identical noun and adjective combination each time, subject to justification by sense and use of minus symbols. (g) Adjectives based on the past participle of an –er verb should not be credited if the final acute accent is missing. (h) Comparison: While plus TC will now score (See Adverbs, ...
... NB Reward identical noun and adjective combination each time, subject to justification by sense and use of minus symbols. (g) Adjectives based on the past participle of an –er verb should not be credited if the final acute accent is missing. (h) Comparison: While plus TC will now score (See Adverbs, ...
ECE Guidebook - Services - University of Northwestern St. Paul
... This story is about Sam Houston. A man who once lived wildly but reformed later. It began to rain. Although the sun was shining brightly. Because of the intense wind, the trees were bent sideways. We should all exercise. For example, playing hockey. Since the marathon runner fainted after ten miles. ...
... This story is about Sam Houston. A man who once lived wildly but reformed later. It began to rain. Although the sun was shining brightly. Because of the intense wind, the trees were bent sideways. We should all exercise. For example, playing hockey. Since the marathon runner fainted after ten miles. ...
Subject−Verb Inversion in Russian
... two arguments of the verb (due to the syncretism of nominative and accusative forms in some nouns) (2) mat’ uvidela doch’ mother saw daughter ’Mother saw daughter’ ≠ ’Daughter saw mother’ However, Russian allows for the subject of both transitive and intransitive (unaccusative and unergative) verbs ...
... two arguments of the verb (due to the syncretism of nominative and accusative forms in some nouns) (2) mat’ uvidela doch’ mother saw daughter ’Mother saw daughter’ ≠ ’Daughter saw mother’ However, Russian allows for the subject of both transitive and intransitive (unaccusative and unergative) verbs ...
Studies in African Linguistics Volume 10, Number 2, July 1979 A
... phonetic/phonological transcription and in the descriptive grammatical terms used. ...
... phonetic/phonological transcription and in the descriptive grammatical terms used. ...
On the processing of regular and irregular forms of verbs and nouns
... But there are exceptions. English provides illustrative cases of such exceptions: a few plural nouns are not produced by adding the suffix -s (teeth, women, fish) and a good number of verbs take a past tense form that does not contain the suffix -ed (ran, sat, went). The occurrence of these irregula ...
... But there are exceptions. English provides illustrative cases of such exceptions: a few plural nouns are not produced by adding the suffix -s (teeth, women, fish) and a good number of verbs take a past tense form that does not contain the suffix -ed (ran, sat, went). The occurrence of these irregula ...
61 tomo santraukos - Lietuvių kalbos institutas
... predicative verbʼs need foe complementation results not from its lexical meaning but from the lack of such a meaning, its syntactic frame (or argument structure) cannot be predicted from verbal semantics. In other words, a semantically deficient verb cannot betreated as a semantic functor. The depen ...
... predicative verbʼs need foe complementation results not from its lexical meaning but from the lack of such a meaning, its syntactic frame (or argument structure) cannot be predicted from verbal semantics. In other words, a semantically deficient verb cannot betreated as a semantic functor. The depen ...
e-Version
... This second group includes verbs that are not regular. They are called irregular verbs. All verbs in the English language can be divided into two groups: regular verbs and irregular verbs. Most English verbs are regular. Irregular verbs have verb forms that require memorization before you can use th ...
... This second group includes verbs that are not regular. They are called irregular verbs. All verbs in the English language can be divided into two groups: regular verbs and irregular verbs. Most English verbs are regular. Irregular verbs have verb forms that require memorization before you can use th ...
Conjunctions - Gordon State College
... subject. It is doing an action. The second word is that action. So all of the sentences above consist of a subject & a verb. A clause, very simply, is a group of words containing a subject & a verb. A sentence is therefore a clause, because a sentence always has at least one subject & one verb, but ...
... subject. It is doing an action. The second word is that action. So all of the sentences above consist of a subject & a verb. A clause, very simply, is a group of words containing a subject & a verb. A sentence is therefore a clause, because a sentence always has at least one subject & one verb, but ...
The Infinitive and the Infinitive Phrase
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
The Infinitive and the Infinitive Phrase
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
The Infinitive and the Infinitive Phrase
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
The Infinitive and the Infinitive Phrase
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
Refining your draft
... you might consider numbering sub-paragraphs. This paragraph would benefit from the use of subparagraphs to make the meaning clearer Farmers store seeds in a variety of ways. For almost all of the seeds, adequate sun-drying precedes storage. This destroys any eggs laid on the seed by pests. Pulses li ...
... you might consider numbering sub-paragraphs. This paragraph would benefit from the use of subparagraphs to make the meaning clearer Farmers store seeds in a variety of ways. For almost all of the seeds, adequate sun-drying precedes storage. This destroys any eggs laid on the seed by pests. Pulses li ...