The Clause - Mohawk College
... Relative Pronoun (or Relative Adverb) + Subject + Verb = Incomplete Thought Relative Pronoun + Verb = Incomplete Thought Here are some examples: Whom Mrs. Peters hit in the head with a ruler Whom = relative pronoun | Mrs. Peters = subject | hit = verb When he chews and chews with great enthusiasm Wh ...
... Relative Pronoun (or Relative Adverb) + Subject + Verb = Incomplete Thought Relative Pronoun + Verb = Incomplete Thought Here are some examples: Whom Mrs. Peters hit in the head with a ruler Whom = relative pronoun | Mrs. Peters = subject | hit = verb When he chews and chews with great enthusiasm Wh ...
Grammar: Complements What are they? How do I find them?
... Better! We now know he was a leader—a complement (a predicate nominative) ...
... Better! We now know he was a leader—a complement (a predicate nominative) ...
Phrases - Boardworks
... Because it is not a complete thought. What is it missing? A subject (the main noun of a sentence) A verb (the main action of a sentence) Add a subject and a verb to the phrase ‘to the park’ to make it into a complete sentence.© Boardworks Ltd 2015 3 of 6 ...
... Because it is not a complete thought. What is it missing? A subject (the main noun of a sentence) A verb (the main action of a sentence) Add a subject and a verb to the phrase ‘to the park’ to make it into a complete sentence.© Boardworks Ltd 2015 3 of 6 ...
ppt
... sentence(VP) --> noun_phrase(Actor), verb_phrase(Actor,VP). noun_phrase(NP) --> proper_noun(NP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> intrans_verb(Actor,VP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> trans_verb(Actor,Y,VP), ...
... sentence(VP) --> noun_phrase(Actor), verb_phrase(Actor,VP). noun_phrase(NP) --> proper_noun(NP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> intrans_verb(Actor,VP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> trans_verb(Actor,Y,VP), ...
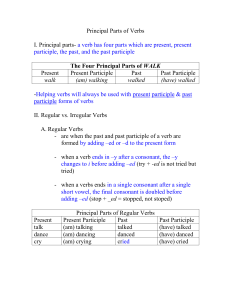
Principal Parts of Verbs2
... -Helping verbs will always be used with present participle & past participle forms of verbs II. Regular vs. Irregular Verbs A. Regular Verbs - are when the past and past participle of a verb are formed by adding –ed or –d to the present form - when a verb ends in –y after a consonant, the –y changes ...
... -Helping verbs will always be used with present participle & past participle forms of verbs II. Regular vs. Irregular Verbs A. Regular Verbs - are when the past and past participle of a verb are formed by adding –ed or –d to the present form - when a verb ends in –y after a consonant, the –y changes ...
Parsing and Semantics in DCGs
... sentence(VP) --> noun_phrase(Actor), verb_phrase(Actor,VP). noun_phrase(NP) --> proper_noun(NP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> intrans_verb(Actor,VP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> trans_verb(Actor,Y,VP), ...
... sentence(VP) --> noun_phrase(Actor), verb_phrase(Actor,VP). noun_phrase(NP) --> proper_noun(NP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> intrans_verb(Actor,VP). verb_phrase(Actor,VP) --> trans_verb(Actor,Y,VP), ...
Reflexive Verbs with Commands
... In Spanish, we use reflexive verbs when we want to say someone does something to, at, or for oneself. The reflexive verbs in Spanish require a reflexive pronoun that will refer to the person doing the action. The idea of reflexives in English: I do to, at, for ...
... In Spanish, we use reflexive verbs when we want to say someone does something to, at, or for oneself. The reflexive verbs in Spanish require a reflexive pronoun that will refer to the person doing the action. The idea of reflexives in English: I do to, at, for ...
Direct and Indirect Object Pronouns
... there is an infinitive or a present participle (gerund). In these cases, the object pronoun may follow and be attached to the infinitive or the present participle, or it may also go immediately before the conjugated verb. Note that when you add a DO pronoun to a present participle, you must write an ...
... there is an infinitive or a present participle (gerund). In these cases, the object pronoun may follow and be attached to the infinitive or the present participle, or it may also go immediately before the conjugated verb. Note that when you add a DO pronoun to a present participle, you must write an ...
Parts of Speech - Open School BC
... Forming Abstract Nouns Many abstract nouns are formed by adding suffixes (-ness, -ity, -tion) to adjectives or verbs to make a noun form. Examples are happiness, formality, and gradation. Some nouns take one suffix and not another. ...
... Forming Abstract Nouns Many abstract nouns are formed by adding suffixes (-ness, -ity, -tion) to adjectives or verbs to make a noun form. Examples are happiness, formality, and gradation. Some nouns take one suffix and not another. ...
Grammar Reteaching
... For plural nouns ending in -s, just add an apostrophe. To form the possessive of plural nouns that do not end in -s, add -’s. players’ caps ...
... For plural nouns ending in -s, just add an apostrophe. To form the possessive of plural nouns that do not end in -s, add -’s. players’ caps ...
Atlas: A book of maps or a book of tables, charts, pictures on one
... Preposition: think of a mouse; can that mouse maneuver that word. A relation or function word that connects a noun or pronoun to another part of a sentence ( "in", "by", "for", to", etc.). In the sentence "Steven hit the ball and ran for first base," the word "for" is a preposition that joins "firs ...
... Preposition: think of a mouse; can that mouse maneuver that word. A relation or function word that connects a noun or pronoun to another part of a sentence ( "in", "by", "for", to", etc.). In the sentence "Steven hit the ball and ran for first base," the word "for" is a preposition that joins "firs ...
FJCL State Latin Forum 2006
... Reason: The most likely Latin for the English “The soldier did not pity the enemy” would use miseret, which leads to the expectation of a genitive of the object of pity. Analysis: Some expressions of feeling or emotion use an impersonal verb, putting the one affected in the accusative and the source ...
... Reason: The most likely Latin for the English “The soldier did not pity the enemy” would use miseret, which leads to the expectation of a genitive of the object of pity. Analysis: Some expressions of feeling or emotion use an impersonal verb, putting the one affected in the accusative and the source ...
File
... Underline the subordinate clause in this sentence. 3. Whoever leaves last, please turn out the lights. Circle the subject of this sentence. 4. Go and see if there are any ice pops in the freezer. Circle the coordinating conjunctions in this sentence. 5. We went to the store and got milk so we wouldn ...
... Underline the subordinate clause in this sentence. 3. Whoever leaves last, please turn out the lights. Circle the subject of this sentence. 4. Go and see if there are any ice pops in the freezer. Circle the coordinating conjunctions in this sentence. 5. We went to the store and got milk so we wouldn ...
parts of speech
... adv’s can modify- bc it is a verb form (verbal) gerund phrases- (can function as APPOSITIVES/APP PHRASES) 1 find verbal 2 ask: verbal + who/what? =DO of gerund (DOG) 3 ask: verbal + DO + to/for what/whom? = IOG 4 ask adv Q’s (to see which adv’s modify the gerund- these are included in the phrase) ve ...
... adv’s can modify- bc it is a verb form (verbal) gerund phrases- (can function as APPOSITIVES/APP PHRASES) 1 find verbal 2 ask: verbal + who/what? =DO of gerund (DOG) 3 ask: verbal + DO + to/for what/whom? = IOG 4 ask adv Q’s (to see which adv’s modify the gerund- these are included in the phrase) ve ...
The Phrase
... by the preposition of. Likewise, one of the noblest pieces of Latin prose is Cicero's "De Senectute," which might be translated "Of Old Age." These expressions introduced by a preposition are not sentences, but phrases. A phrase is a group of related words not containing a subject and predicate. A p ...
... by the preposition of. Likewise, one of the noblest pieces of Latin prose is Cicero's "De Senectute," which might be translated "Of Old Age." These expressions introduced by a preposition are not sentences, but phrases. A phrase is a group of related words not containing a subject and predicate. A p ...
Verb: a word used to express an action, a condition, or a state of being.
... – It smells flowery • linking -- smell links the subject, I, to the predicate adjective, flowery ...
... – It smells flowery • linking -- smell links the subject, I, to the predicate adjective, flowery ...
Shawn Madden - Veracity O`Madden
... NOTE: The preferred version of this is the one listed above-it contains the entire Word of God, not part of it-one ought not walk around with less than the whole counsel of Holy Writ. It used to sell for about $135.00 but it can be found HERE for much less. If strapped for cash, you can find a BHS i ...
... NOTE: The preferred version of this is the one listed above-it contains the entire Word of God, not part of it-one ought not walk around with less than the whole counsel of Holy Writ. It used to sell for about $135.00 but it can be found HERE for much less. If strapped for cash, you can find a BHS i ...
Chapter 2. Style
... Belt, the Midwest, the South, the West). Do not capitalize the adjectival form (e.g., midwestern practices, southern states, western Texas). Note the following distinction: the southeastern United States, but the US Southeast. • The first letter of genus and all higher taxa (e.g., family and order ...
... Belt, the Midwest, the South, the West). Do not capitalize the adjectival form (e.g., midwestern practices, southern states, western Texas). Note the following distinction: the southeastern United States, but the US Southeast. • The first letter of genus and all higher taxa (e.g., family and order ...
12 Editing for Grammar Conventions
... 1. ‘Many people would find this question familiar..’ 2. ‘We assume we would land ourselves the perfect job’ ‘Would’ used in place of ‘will’ or ‘is’ or in some cases, used in sentences where modal verbs or verbs are not required at all. ...
... 1. ‘Many people would find this question familiar..’ 2. ‘We assume we would land ourselves the perfect job’ ‘Would’ used in place of ‘will’ or ‘is’ or in some cases, used in sentences where modal verbs or verbs are not required at all. ...
Using Subject-Verb Agreement
... For each of the following sentences, choose the verb that agrees with the compound subject. 1. Ants and spiders (has, have) invaded the backyard. 2. Mandy and her friends (is, are) going to the movies. 3. A statue or a fountain (looks, look) good in a park setting. ...
... For each of the following sentences, choose the verb that agrees with the compound subject. 1. Ants and spiders (has, have) invaded the backyard. 2. Mandy and her friends (is, are) going to the movies. 3. A statue or a fountain (looks, look) good in a park setting. ...
Using Subject-Verb Agreement
... For each of the following sentences, choose the verb that agrees with the compound subject. 1. Ants and spiders (has, have) invaded the backyard. 2. Mandy and her friends (is, are) going to the movies. 3. A statue or a fountain (looks, look) good in a park setting. ...
... For each of the following sentences, choose the verb that agrees with the compound subject. 1. Ants and spiders (has, have) invaded the backyard. 2. Mandy and her friends (is, are) going to the movies. 3. A statue or a fountain (looks, look) good in a park setting. ...
Sentence Types - Net Start Class
... A complex sentence has an independent clause joined by one or more dependent clauses. A complex sentence always has a subordinator such as because, since, after, although, or when or a relative pronoun such as that, who, or which. • Subordinator- linking words that are used to join clauses • Relativ ...
... A complex sentence has an independent clause joined by one or more dependent clauses. A complex sentence always has a subordinator such as because, since, after, although, or when or a relative pronoun such as that, who, or which. • Subordinator- linking words that are used to join clauses • Relativ ...
PRESENTATION NAME
... clause answers these questions about a verb, an adjective, or another adverb: – how? – when? – where? ...
... clause answers these questions about a verb, an adjective, or another adverb: – how? – when? – where? ...
Using Subject-Verb Agreement
... For each of the following sentences, choose the verb that agrees with the compound subject. 1. Ants and spiders (has, have) invaded the backyard. 2. Mandy and her friends (is, are) going to the movies. 3. A statue or a fountain (looks, look) good in a park setting. ...
... For each of the following sentences, choose the verb that agrees with the compound subject. 1. Ants and spiders (has, have) invaded the backyard. 2. Mandy and her friends (is, are) going to the movies. 3. A statue or a fountain (looks, look) good in a park setting. ...