the parts of speech
... Interrogative sentence asks a questions and ends in a question mark. (?) Imperative sentence gives a command and ends in a period. (.) Exclamatory sentence expresses strong feelings and ends in an exclamation point. (!) ...
... Interrogative sentence asks a questions and ends in a question mark. (?) Imperative sentence gives a command and ends in a period. (.) Exclamatory sentence expresses strong feelings and ends in an exclamation point. (!) ...
Station 1: ACTIVE VS. PASSIVE VOICE Copy the following
... Gerund: The –ing form of a verb that acts as a noun—functions as either the subject, direct object, or predicate nominative of a sentence. Ex: Walking is healthy. (“walking” comes from a verb but is acting as a noun—in this case the subject of the sentence.) Ex: I love walking. (“walking” is the ger ...
... Gerund: The –ing form of a verb that acts as a noun—functions as either the subject, direct object, or predicate nominative of a sentence. Ex: Walking is healthy. (“walking” comes from a verb but is acting as a noun—in this case the subject of the sentence.) Ex: I love walking. (“walking” is the ger ...
Reported Speech-12º
... Reporting someone’s actual words (statements and questions) by using verbs say, reply, ask…) Reporting their emotions, tones by using specific reporting verbs like: (add, admit, advise, agree, announce, answer, ask, beg, claim, demand, explain, insist, order,persuade,promise, remind, reply,…) ...
... Reporting someone’s actual words (statements and questions) by using verbs say, reply, ask…) Reporting their emotions, tones by using specific reporting verbs like: (add, admit, advise, agree, announce, answer, ask, beg, claim, demand, explain, insist, order,persuade,promise, remind, reply,…) ...
Unit 3 - Ms. De masi Teaching website
... 1. Each of the tales in told by a different character. 2. Many writers have been influenced by Chaucer’s bawdy humour and insightful characterizations. ...
... 1. Each of the tales in told by a different character. 2. Many writers have been influenced by Chaucer’s bawdy humour and insightful characterizations. ...
Verbs that can be followed by both an infinitive and a gerund
... happensbefore or at the same time as the action of the main verb. ...
... happensbefore or at the same time as the action of the main verb. ...
Class_26
... Each form has an ending added to the work stem to indicate the nouns’s use in the sentence and its number (singular or plural) ...
... Each form has an ending added to the work stem to indicate the nouns’s use in the sentence and its number (singular or plural) ...
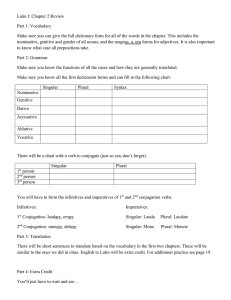
Chapter 2 Review - OCPS TeacherPress
... Make sure you can give the full dictionary form for all of the words in the chapter. This includes the nominative, genitive and gender of all nouns; and the magnus, a, um forms for adjectives. It is also important to know what case all prepositions take. Part 2: Grammar Make sure you know the functi ...
... Make sure you can give the full dictionary form for all of the words in the chapter. This includes the nominative, genitive and gender of all nouns; and the magnus, a, um forms for adjectives. It is also important to know what case all prepositions take. Part 2: Grammar Make sure you know the functi ...
PARTICIPLES: A W HEELOCK-FREE INTRODUCTION Participle
... FUTURE ACTIVE PARTICIPLES are formed from the fourth principal part by inserting -ūr- between the stem of the participle and the inflectional ending. So for cantāre (“to sing”) the fourth principal part is cantātus; strike off -us and you have the stem (cantāt-); add -ūr- (cantātūr-) and then re-att ...
... FUTURE ACTIVE PARTICIPLES are formed from the fourth principal part by inserting -ūr- between the stem of the participle and the inflectional ending. So for cantāre (“to sing”) the fourth principal part is cantātus; strike off -us and you have the stem (cantāt-); add -ūr- (cantātūr-) and then re-att ...
Spelling Scheme Year 6 - St Mary`s Catholic Primary School
... affect: usually a verb (e.g. The weather may affect our plans) effect: usually a noun (e.g. It may have an effect on our plans). If a verb, it means ‘bring about’ (e.g. He will effect changes in the running of the business.). altar: a table-like piece of furniture in a church alter: to change ascent ...
... affect: usually a verb (e.g. The weather may affect our plans) effect: usually a noun (e.g. It may have an effect on our plans). If a verb, it means ‘bring about’ (e.g. He will effect changes in the running of the business.). altar: a table-like piece of furniture in a church alter: to change ascent ...
Conjugating Verbs
... Conjugating Verbs In English, we can often use a verb without making any changes to it. The verb "walk" is used in the same form in all of these sentences. I walk. You walk. They walk. My neighbors walk. Their dogs walk. But sometimes we have to add -s or -es to the end of a verb. We do that when th ...
... Conjugating Verbs In English, we can often use a verb without making any changes to it. The verb "walk" is used in the same form in all of these sentences. I walk. You walk. They walk. My neighbors walk. Their dogs walk. But sometimes we have to add -s or -es to the end of a verb. We do that when th ...
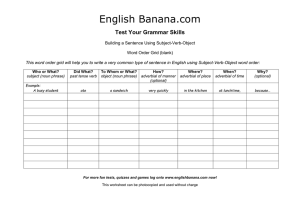
doc - English Banana
... Building a Sentence Using Subject-Verb-Object Word Order Grid (blank) This word order grid will help you to write a very common type of sentence in English using Subject-Verb-Object word order: Who or What? subject (noun phrase) Example: A busy student ...
... Building a Sentence Using Subject-Verb-Object Word Order Grid (blank) This word order grid will help you to write a very common type of sentence in English using Subject-Verb-Object word order: Who or What? subject (noun phrase) Example: A busy student ...
NOUN
... Jack - he, him girl - she, her tree - it My favorite tree is in our front yard; it provides shade for many. ...
... Jack - he, him girl - she, her tree - it My favorite tree is in our front yard; it provides shade for many. ...
File
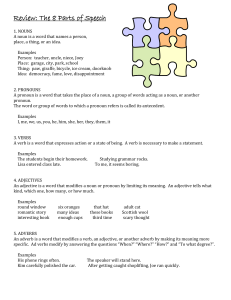
... meaning more specific. Ad verbs modify by answering the questions “When?” “Where?” “How?” and “To what degree?”. Examples His phone rings often. Kim carefully polished the car. ...
... meaning more specific. Ad verbs modify by answering the questions “When?” “Where?” “How?” and “To what degree?”. Examples His phone rings often. Kim carefully polished the car. ...
Fragments Handout
... Participial phrase A participial phrase is a participle plus its nouns and modifiers. A participle is often a present form of a verb ending in -ing or a past form of a verb ending in -ed. A participial phrase functions as an adjective in a sentence. Example 1: Eating her breakfast, the child watched ...
... Participial phrase A participial phrase is a participle plus its nouns and modifiers. A participle is often a present form of a verb ending in -ing or a past form of a verb ending in -ed. A participial phrase functions as an adjective in a sentence. Example 1: Eating her breakfast, the child watched ...
Parts of Speech - Bardstown City Schools
... specific. Ad verbs modify by answering the questions “When?” “Where?” “How?” and “To what degree?”. Examples His phone rings often. Kim carefully polished the car. ...
... specific. Ad verbs modify by answering the questions “When?” “Where?” “How?” and “To what degree?”. Examples His phone rings often. Kim carefully polished the car. ...
Year 5 - Crossley Fields
... they are used to name the subject or object of the verb. For example, in the phrase ‘Max ate chips’, ‘ate’ is the verb, ‘Max’ is the subject and ‘chips’ is the object. Adjective: Adjectives tell you more about a noun (for example: ‘the red dress’). Verb: A verb is the word that indicates what is hap ...
... they are used to name the subject or object of the verb. For example, in the phrase ‘Max ate chips’, ‘ate’ is the verb, ‘Max’ is the subject and ‘chips’ is the object. Adjective: Adjectives tell you more about a noun (for example: ‘the red dress’). Verb: A verb is the word that indicates what is hap ...
A brief revision on basics of Grammar
... because it describes a continuous action. Then I ask myself, Who is doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
... because it describes a continuous action. Then I ask myself, Who is doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
A brief revision on basics of Grammar
... because it describes a continuous action. Then I ask myself, Who is doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
... because it describes a continuous action. Then I ask myself, Who is doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
Preposition Use - Mohawk College
... Words that take the place of nouns. (Examples: She, he, it, we, I you, they, his, their, her, your) Substitute for nouns referring to people (Examples: I, me, my, mine, you, your, he, she, it, him, her, they, them, our, etc.) Pronouns that show ownership. (Examples: my, mine, our, his, her) Pronouns ...
... Words that take the place of nouns. (Examples: She, he, it, we, I you, they, his, their, her, your) Substitute for nouns referring to people (Examples: I, me, my, mine, you, your, he, she, it, him, her, they, them, our, etc.) Pronouns that show ownership. (Examples: my, mine, our, his, her) Pronouns ...
Direct and Indirect Objects
... An indirect object tells to what or to whom or for what or for whom an action is done. An indirect object often follows the verbs buy, bring, do, give, hand, offer, lend, teach, tell, play, write, send, make, and show. Determine the indirect object by rephrasing the sentence as a questions ending ...
... An indirect object tells to what or to whom or for what or for whom an action is done. An indirect object often follows the verbs buy, bring, do, give, hand, offer, lend, teach, tell, play, write, send, make, and show. Determine the indirect object by rephrasing the sentence as a questions ending ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Find a partner! Turn in your books to Exercise 3 on page 494. You will be identifying the adjectives and the words they modify in the following sentences. ...
... Find a partner! Turn in your books to Exercise 3 on page 494. You will be identifying the adjectives and the words they modify in the following sentences. ...
Phrases - Wando High School
... Sentence Parts and Phrases Phrase – a group of words that modify another • Preposition Phrase – a preposition followed by a noun or pronoun: gives position, relationship or direction – The key is under the rug Adjectivial - phrase functions like an adjective, describing a noun or pronoun Over Ed's ...
... Sentence Parts and Phrases Phrase – a group of words that modify another • Preposition Phrase – a preposition followed by a noun or pronoun: gives position, relationship or direction – The key is under the rug Adjectivial - phrase functions like an adjective, describing a noun or pronoun Over Ed's ...
Grammar Quiz 1: Study Guide Answers
... Walking from the CalTech gym at six in the morning with her backpack and fencing bag, the teacher noticed the quiet of the city and appreciated the calm before a hectic day. ...
... Walking from the CalTech gym at six in the morning with her backpack and fencing bag, the teacher noticed the quiet of the city and appreciated the calm before a hectic day. ...