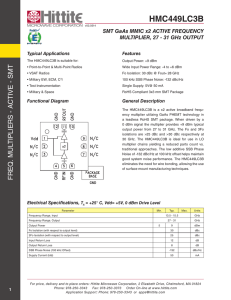
DESIGN OF GIGAHERTZ TUNING RANGE 5 GHz LC
... on them, there is need for multi-band multi-standart RF transceivers. One of the main requirement of such transceivers is relatively wide operating frequency range. This coincides with one of the challenges in high-speed integrated circuit design – wide range frequency synthesis. Usually phase locke ...
... on them, there is need for multi-band multi-standart RF transceivers. One of the main requirement of such transceivers is relatively wide operating frequency range. This coincides with one of the challenges in high-speed integrated circuit design – wide range frequency synthesis. Usually phase locke ...
PUNJAB TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
... components, Transistor as an Amplifier, Transistor characteristics in CB, CE and CC modes. Operating point, bias stability, various biasing circuits, stabilization against Ico, VBE and beta, Construction, Characteristics & applications of Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), UJT and MOSFET. Unit ...
... components, Transistor as an Amplifier, Transistor characteristics in CB, CE and CC modes. Operating point, bias stability, various biasing circuits, stabilization against Ico, VBE and beta, Construction, Characteristics & applications of Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), UJT and MOSFET. Unit ...
Circuit Techniques for On-Chip Clocking and Synchronization Behzad Mesgarzadeh
... computing at multi-gigahertz clock frequencies. The ever-increasing chip size and speed call for new methodologies in clock distribution network. Conventional global synchronization techniques exhibit many drawbacks in the advanced VLSI chips such as high-speed microprocessors. A significant percent ...
... computing at multi-gigahertz clock frequencies. The ever-increasing chip size and speed call for new methodologies in clock distribution network. Conventional global synchronization techniques exhibit many drawbacks in the advanced VLSI chips such as high-speed microprocessors. A significant percent ...
R4076E LFAA
... relays. If the protection does not have a separate ‘3PH trip’ output, input 6 to terminal B11 is not required. 7. TERMINAL B13: This input may be energised by a contact on an intertrip receive repeat relay if a direct intertripping scheme is in use. If this input is energised, the auto-reclose relay ...
... relays. If the protection does not have a separate ‘3PH trip’ output, input 6 to terminal B11 is not required. 7. TERMINAL B13: This input may be energised by a contact on an intertrip receive repeat relay if a direct intertripping scheme is in use. If this input is energised, the auto-reclose relay ...
... Each pulse shown in FIGURES 3B and 3C is dispersed petition rate, such as 25 kilocycles per second, to a suit into its component frequencies by delay lines 13 and 14, able bandpass ?lter 11, which transforms each pulse into respectively, so that the lowest frequency components are a short burst of c ...
Amplifi er Application Guide 1
... Another problem to avoid is the presence of large levels of radio frequencies or RF in the input signal. Although high RF levels may not pose a threat to the amplifier, they can burn out tweeters or other loads that are sensitive to high frequencies. Extremely high RF levels can also cause your ampl ...
... Another problem to avoid is the presence of large levels of radio frequencies or RF in the input signal. Although high RF levels may not pose a threat to the amplifier, they can burn out tweeters or other loads that are sensitive to high frequencies. Extremely high RF levels can also cause your ampl ...
Linear and Digital IC Applications - ECM
... 1. An ideal op-amp draws no current at both the input terminals I.e. I1 = I2 = 0. Thus its input impedance is infinite. Any source can drive it and there is no loading on the driver stage 2. The gain of an ideal op-amp is infinite, hence the differential input Vd = V1 – V2 is essentially zero for th ...
... 1. An ideal op-amp draws no current at both the input terminals I.e. I1 = I2 = 0. Thus its input impedance is infinite. Any source can drive it and there is no loading on the driver stage 2. The gain of an ideal op-amp is infinite, hence the differential input Vd = V1 – V2 is essentially zero for th ...
THE L6569: A NEW HIGH VOLTAGE IC DRIVER FOR
... The circuit consumption is defined by the MOSFETs gate charge, the I.C. consumption, the oscillator, and the shunt regulator. Several circuits are possible. In many applications a snubber is used to reduce the dissipation in the MOSFETs. When this snubber is used in conjunction with a start up resis ...
... The circuit consumption is defined by the MOSFETs gate charge, the I.C. consumption, the oscillator, and the shunt regulator. Several circuits are possible. In many applications a snubber is used to reduce the dissipation in the MOSFETs. When this snubber is used in conjunction with a start up resis ...
Electricity and Measurement Experiments
... We commence with some background information on electrical circuits, and a simple introductory experiment, Electric Circuits- A Review?, to enhance your understanding of the basics of electrical circuit operation. You may be familiar with the initial ideas of measurement in electric circuits - ammet ...
... We commence with some background information on electrical circuits, and a simple introductory experiment, Electric Circuits- A Review?, to enhance your understanding of the basics of electrical circuit operation. You may be familiar with the initial ideas of measurement in electric circuits - ammet ...
Regulated Cascode TIA
... such as capacitive peaking technique, inductive peaking technique, common-gate (CG) input configuration, and commondrain (CD) input configuration. The CG and CD input configurations relax the effect of large input parasitic capacitance from the bandwidth determination better than the conventional co ...
... such as capacitive peaking technique, inductive peaking technique, common-gate (CG) input configuration, and commondrain (CD) input configuration. The CG and CD input configurations relax the effect of large input parasitic capacitance from the bandwidth determination better than the conventional co ...
chapter 2: other linear circuits
... network, plus one (usually) gain set resistance, RG. Also unlike an op amp is the fact that the internal resistance network and RG are isolated from the signal input terminals. In amp gain can also be preset via an internal RG by pin selection, (again isolated from the signal inputs). Typical in amp ...
... network, plus one (usually) gain set resistance, RG. Also unlike an op amp is the fact that the internal resistance network and RG are isolated from the signal input terminals. In amp gain can also be preset via an internal RG by pin selection, (again isolated from the signal inputs). Typical in amp ...
Alexander
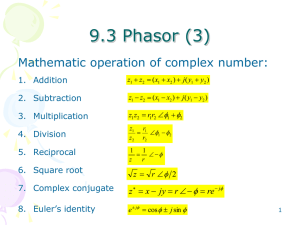
... • Amplitude and phase difference are two principal concerns in the study of voltage and current sinusoids. • Phasor will be defined from the cosine function in all our proceeding study. If a voltage or current expression is in the form of a sine, it will be changed to a cosine by subtracting from th ...
... • Amplitude and phase difference are two principal concerns in the study of voltage and current sinusoids. • Phasor will be defined from the cosine function in all our proceeding study. If a voltage or current expression is in the form of a sine, it will be changed to a cosine by subtracting from th ...
MAX9994 SiGe High-Linearity, 1700MHz to 2200MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer/Switch General Description
... SNR degradations in the mixer, including the LO noise as defined in Maxim Application Note 2021. ...
... SNR degradations in the mixer, including the LO noise as defined in Maxim Application Note 2021. ...
Electricity_tutorial
... When the voltage is lower on the positive leg than on the negative leg then the current does not flow (the resistance is very high). The negative leg of a diode is the one with the line closest to it. It is called the cathode. The postive end is called the anode. Usually when current is flowing thro ...
... When the voltage is lower on the positive leg than on the negative leg then the current does not flow (the resistance is very high). The negative leg of a diode is the one with the line closest to it. It is called the cathode. The postive end is called the anode. Usually when current is flowing thro ...
Alexander
... • Amplitude and phase difference are two principal concerns in the study of voltage and current sinusoids. • Phasor will be defined from the cosine function in all our proceeding study. If a voltage or current expression is in the form of a sine, it will be changed to a cosine by subtracting from th ...
... • Amplitude and phase difference are two principal concerns in the study of voltage and current sinusoids. • Phasor will be defined from the cosine function in all our proceeding study. If a voltage or current expression is in the form of a sine, it will be changed to a cosine by subtracting from th ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.