Module 4
... • Resistance: the opposition to the movement of electrons, measured in ohms (Ω) by an ohmmeter and represented by R in formulas. • Resistance is like friction and turns electrical energy into heat when current flows. • Conductors permit current flow (low resistance) and insulators block current flow ...
... • Resistance: the opposition to the movement of electrons, measured in ohms (Ω) by an ohmmeter and represented by R in formulas. • Resistance is like friction and turns electrical energy into heat when current flows. • Conductors permit current flow (low resistance) and insulators block current flow ...
Low-Frequency RFID in a Nutshell
... The RF voltage is the voltage that is generated by the magnetic field of the RFID base station at the transponder antenna. The RF voltage is limited by the internal RF limiter of the transponder. The RF voltage is used to charge the VCL capacitor (typically 220 nF); VCL is the operating voltage for ...
... The RF voltage is the voltage that is generated by the magnetic field of the RFID base station at the transponder antenna. The RF voltage is limited by the internal RF limiter of the transponder. The RF voltage is used to charge the VCL capacitor (typically 220 nF); VCL is the operating voltage for ...
Time transfer through optical fibers over a distance of 73 km with an
... constant trigger level and a 50 Ω input impedance was used. The delay CABR between the UTC(PTB) reference point and the input to the remote setup was measured by subsequently connecting UTC(PTB) and 1PPSREF to one input of the TIC while at the second input an auxiliary 1 PPS (phase coherent to UTC(P ...
... constant trigger level and a 50 Ω input impedance was used. The delay CABR between the UTC(PTB) reference point and the input to the remote setup was measured by subsequently connecting UTC(PTB) and 1PPSREF to one input of the TIC while at the second input an auxiliary 1 PPS (phase coherent to UTC(P ...
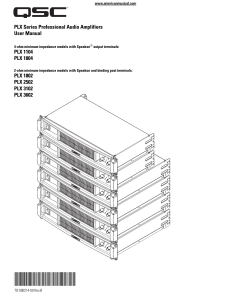
Manual - American Musical Supply
... than four 8-ohm speakers per channel, or if the speaker wiring is shorted. The red Clip LED will flash brightly, and the amplifier may sound distorted. If the amplifier is driven hard under these conditions, the current limit will be further reduced, causing an increase in distortion. If the amplifi ...
... than four 8-ohm speakers per channel, or if the speaker wiring is shorted. The red Clip LED will flash brightly, and the amplifier may sound distorted. If the amplifier is driven hard under these conditions, the current limit will be further reduced, causing an increase in distortion. If the amplifi ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... One technique for increasing the capacitive load drive capability of the amplifier operating in unity gain is to insert a small resistor, typically 10Ω to 20Ω, in series with the output; see Figure 6. This resistor significantly reduces the overshoot and ringing associated with large capacitive load ...
... One technique for increasing the capacitive load drive capability of the amplifier operating in unity gain is to insert a small resistor, typically 10Ω to 20Ω, in series with the output; see Figure 6. This resistor significantly reduces the overshoot and ringing associated with large capacitive load ...
Ohm`s Law 1 Object 2 Apparatus 3 Theory
... A resistor is a circuit element which dissipates electrical energy in the form of heat. All conductors (metals) have resistance, but the material used in most resistors is carbon-glass. Resistance manifests itself at the microscopic level as collisions between conduction electrons (those actually in ...
... A resistor is a circuit element which dissipates electrical energy in the form of heat. All conductors (metals) have resistance, but the material used in most resistors is carbon-glass. Resistance manifests itself at the microscopic level as collisions between conduction electrons (those actually in ...
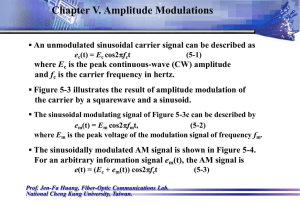
Chap05--Amplitude Mo..
... Indeed, many use a second down conversion and second IF amplifier system following the first IF. Such a superheterodyne receiver is called a double-conversion receiver. The LO frequency is almost always higher than the RF carrier frequency, a characteristic referred to as high-side injection to ...
... Indeed, many use a second down conversion and second IF amplifier system following the first IF. Such a superheterodyne receiver is called a double-conversion receiver. The LO frequency is almost always higher than the RF carrier frequency, a characteristic referred to as high-side injection to ...
Transistor Devices Inc.
... on the 0-5 A/V is 0.5 ohm, and minimum resistance on the 0-20 A/V is 0.05 ohm. For example, to test a 12V battery with a two ohm resistive load, the mode selector should be set to the 2 A/V position, and the coarse and fine load adjust controls adjusted to obtain the 6A load. ...
... on the 0-5 A/V is 0.5 ohm, and minimum resistance on the 0-20 A/V is 0.05 ohm. For example, to test a 12V battery with a two ohm resistive load, the mode selector should be set to the 2 A/V position, and the coarse and fine load adjust controls adjusted to obtain the 6A load. ...
500-mA DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE DRIVER THS6012 FEATURES
... Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating conditions" is not implied. Exposure to a ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating conditions" is not implied. Exposure to a ...
Output Capacitor-less Video Drivers High-performance Video Driver Series
... BH768xxFVM Series devices provide both a low-voltage video driver and a large dynamic range (approximately 5.2 Vpp). A resistance termination method (150 kΩ termination) is used instead of the clamp method, which only supports video signals, since it supports various signal types. The BH768xxFVM ser ...
... BH768xxFVM Series devices provide both a low-voltage video driver and a large dynamic range (approximately 5.2 Vpp). A resistance termination method (150 kΩ termination) is used instead of the clamp method, which only supports video signals, since it supports various signal types. The BH768xxFVM ser ...
Auto-titrating pH Meter
... or resistance to electrical current, stemming from the glass membrane which houses the electrodes. This special glass has tiny pores which cannot support much electrical current. This ultimately results in the impossibility of measuring voltage measurements strictly with a digital multimeter and our ...
... or resistance to electrical current, stemming from the glass membrane which houses the electrodes. This special glass has tiny pores which cannot support much electrical current. This ultimately results in the impossibility of measuring voltage measurements strictly with a digital multimeter and our ...
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits
... where we have substituted I = + dq / dt for the current. Since I must be the same in all parts of the series circuit, the current across the resistance R is equal to the rate of increase of charge on the capacitor plates. The current flow in the circuit will continue to decrease because the charge a ...
... where we have substituted I = + dq / dt for the current. Since I must be the same in all parts of the series circuit, the current across the resistance R is equal to the rate of increase of charge on the capacitor plates. The current flow in the circuit will continue to decrease because the charge a ...
Chapter06
... The total line current equals the sum of the branch currents for all parallel strings. The RT for the entire circuit equals the applied voltage divided by the total line current. For any resistance in a series string, the IR voltage drop across that resistance equals the string’s current multiplied ...
... The total line current equals the sum of the branch currents for all parallel strings. The RT for the entire circuit equals the applied voltage divided by the total line current. For any resistance in a series string, the IR voltage drop across that resistance equals the string’s current multiplied ...
uncorrected page proofs
... appliances were connected in series, they would all be on or off at the same time; and they would share the voltage between them, so no appliance would receive the full voltage. This would present problems when designing the devices, as it would not be known what voltage to allow for. Car lights, fr ...
... appliances were connected in series, they would all be on or off at the same time; and they would share the voltage between them, so no appliance would receive the full voltage. This would present problems when designing the devices, as it would not be known what voltage to allow for. Car lights, fr ...
Stochastic Switching Circuit Synthesis Daniel Wilhelm Jehoshua Bruck
... Let F i be the string associated with circuit Ci , where P r(Ci) = a/q i , for integers a and q. F i has length i and a non-zero least significant digit. Then, by opening or closing some pswitch x in Ci , one of the new circuits is at least i − 1 digits long. Why? Suppose that both of the new circui ...
... Let F i be the string associated with circuit Ci , where P r(Ci) = a/q i , for integers a and q. F i has length i and a non-zero least significant digit. Then, by opening or closing some pswitch x in Ci , one of the new circuits is at least i − 1 digits long. Why? Suppose that both of the new circui ...
Series-Parallel Circuits
... The total line current equals the sum of the branch currents for all parallel strings. The RT for the entire circuit equals the applied voltage divided by the total line current. For any resistance in a series string, the IR voltage drop across that resistance equals the string’s current multiplied ...
... The total line current equals the sum of the branch currents for all parallel strings. The RT for the entire circuit equals the applied voltage divided by the total line current. For any resistance in a series string, the IR voltage drop across that resistance equals the string’s current multiplied ...
Stochastic Switching Circuit Synthesis
... Let F i be the string associated with circuit C i , where P r(Ci) = a/q i , for integers a and q. F i has length i and a non-zero least significant digit. Then, by opening or closing some pswitch x in C i , one of the new circuits is at least i − 1 digits long. Why? Suppose that both of the new circ ...
... Let F i be the string associated with circuit C i , where P r(Ci) = a/q i , for integers a and q. F i has length i and a non-zero least significant digit. Then, by opening or closing some pswitch x in C i , one of the new circuits is at least i − 1 digits long. Why? Suppose that both of the new circ ...
R 12 - Courses
... Find the resistance seen at terminals A and B of the circuit shown. This is correct as far as it goes. The resistor R12 is indeed in parallel with R6. However, we will save some time if we recognize that R7 is also in parallel with each of these two other resistors. We can combine all three of them ...
... Find the resistance seen at terminals A and B of the circuit shown. This is correct as far as it goes. The resistor R12 is indeed in parallel with R6. However, we will save some time if we recognize that R7 is also in parallel with each of these two other resistors. We can combine all three of them ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.