Small Signal * Low Frequency Transistor amplifier Circuits
... Consider a general amplifier as shown below. In this amplifier, the resistance R is common to the input and output circuits do not have a common resistance. The purpose of the following analysis is to remove the inter dependence of input and output circuits. So that either input circuits or outpu ...
... Consider a general amplifier as shown below. In this amplifier, the resistance R is common to the input and output circuits do not have a common resistance. The purpose of the following analysis is to remove the inter dependence of input and output circuits. So that either input circuits or outpu ...
Nov 2000 Low Distortion Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers Drive ADCs and Cables
... stage incorporates proprietary local feedback to reduce its output impedance (about 20Ω at 100MHz) and this helps attenuate the glitch as well. However, a remnant glitch persists and works its way through R2 and R1, being attenuated by a factor of 2 in the process, and arrives at the ...
... stage incorporates proprietary local feedback to reduce its output impedance (about 20Ω at 100MHz) and this helps attenuate the glitch as well. However, a remnant glitch persists and works its way through R2 and R1, being attenuated by a factor of 2 in the process, and arrives at the ...
A Wide Locking Range Differential Colpitts Injection Locked
... frequency divider (ILFD) • Divide-by-two ILFD can provide wide locking range, supply voltage of 2.4 V, the tuning range of the free running ILFD is from 4.46 to 5.6 GHz,about 1.14 GHz, and the locking range of the ILFD is from 8.03 to 11.63 GHz, about 3.6 GHz ...
... frequency divider (ILFD) • Divide-by-two ILFD can provide wide locking range, supply voltage of 2.4 V, the tuning range of the free running ILFD is from 4.46 to 5.6 GHz,about 1.14 GHz, and the locking range of the ILFD is from 8.03 to 11.63 GHz, about 3.6 GHz ...
UWB - Rutgers WINLAB
... V(t) is the pulse shape defined as the difference between two pulses shifted by the modulation parameter δ. It will then be correlated with the received signal for a statistical test ...
... V(t) is the pulse shape defined as the difference between two pulses shifted by the modulation parameter δ. It will then be correlated with the received signal for a statistical test ...
Basic Circuitry and X‐ray Production
... • If voltage is increased, and resistance is constant, what would happen to amperage? • If voltage is constant, and the resistance is increased, what would happen to amperage? • If voltage is constant, and the amperage is increased, what would happen to resistance? ...
... • If voltage is increased, and resistance is constant, what would happen to amperage? • If voltage is constant, and the resistance is increased, what would happen to amperage? • If voltage is constant, and the amperage is increased, what would happen to resistance? ...
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 01
... A mixer amplifier mixes several input signals and amplifies them at various levels ...
... A mixer amplifier mixes several input signals and amplifies them at various levels ...
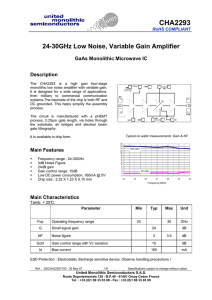
CHA2293
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However United Monolithic Semiconductors S.A.S. assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is g ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However United Monolithic Semiconductors S.A.S. assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is g ...
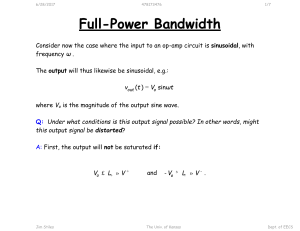
Full Power Bandwidth..
... It is true that the output will not saturate if magnitude of the sinewave is smaller than the saturation limits. However, this is not the only way that the signal can be distorted! Q: I almost forgot! A signal can also be distorted by slew-rate limiting. Could this problem possibly affect a sine wav ...
... It is true that the output will not saturate if magnitude of the sinewave is smaller than the saturation limits. However, this is not the only way that the signal can be distorted! Q: I almost forgot! A signal can also be distorted by slew-rate limiting. Could this problem possibly affect a sine wav ...
Thesis report Final
... 1.5V. When the RF transmitter is active, the RSSI output level will increase. The potentiometer connects to CMVin-, and is used to set the IDLE threshold voltage. Apply power to the receiver circuit, with no active transmitters in range, and adjust the potentiometer until the GREEN LED on COUT turns ...
... 1.5V. When the RF transmitter is active, the RSSI output level will increase. The potentiometer connects to CMVin-, and is used to set the IDLE threshold voltage. Apply power to the receiver circuit, with no active transmitters in range, and adjust the potentiometer until the GREEN LED on COUT turns ...
Electricity Web Quest - Atlanta Public Schools
... Open the DC only circuit simulator Directions: Choose the RUN NOW option Tools to build circuit are in the white box on the right side of the screen To remove parts or change voltage, resistance, etc…..right click on the part for more options!! 12. Find a way to make a single light bulb light up wit ...
... Open the DC only circuit simulator Directions: Choose the RUN NOW option Tools to build circuit are in the white box on the right side of the screen To remove parts or change voltage, resistance, etc…..right click on the part for more options!! 12. Find a way to make a single light bulb light up wit ...
Pre-Lab Work and Quiz - facstaff.bucknell.edu
... cables used to carry signals from one location to another pick up undesired signals and noise radiated by other devices. For example, the output from a medical sensor might be transmitted to a monitor via a cable, but that same cable might also pick up 60-Hz common-mode energy from the clinic’s AC w ...
... cables used to carry signals from one location to another pick up undesired signals and noise radiated by other devices. For example, the output from a medical sensor might be transmitted to a monitor via a cable, but that same cable might also pick up 60-Hz common-mode energy from the clinic’s AC w ...
compressor - Analogue Haven
... players love. We’ve also included a mix knob to blend in the dry signal for an even more transparent sound and a gain reduction meter so you know what the compressor is doing at all times. To help you get the most out of this product, we’ve put some brief instructional videos on our website: www.emp ...
... players love. We’ve also included a mix knob to blend in the dry signal for an even more transparent sound and a gain reduction meter so you know what the compressor is doing at all times. To help you get the most out of this product, we’ve put some brief instructional videos on our website: www.emp ...
vintage audio - Antique Radio Classified
... RCA’s Magic Eye, many radio manufacturers quickly purchased RCA’s license agreement for the electron-ray tube and circuit designs. The difference in cost at the retail level of this extra feature was typically five to seven dollars. Arvin, Fairbanks-Morse, Lafayette, and Westinghouse, in particular, ...
... RCA’s Magic Eye, many radio manufacturers quickly purchased RCA’s license agreement for the electron-ray tube and circuit designs. The difference in cost at the retail level of this extra feature was typically five to seven dollars. Arvin, Fairbanks-Morse, Lafayette, and Westinghouse, in particular, ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.