New CMOS Realization of Voltage Differencing Buffered Amplifier
... The main DC and AC characteristics of VDBA, such as plots of IZ against VP, plots of VZ against VW, frequency responses of IZ/VP and VW/VZ are obtained from LTSPICE simulations and given in Figs. 5-8. The DC transfer characteristic of IZ against VP for VDBA is shown in Fig. 5 that is obtained when o ...
... The main DC and AC characteristics of VDBA, such as plots of IZ against VP, plots of VZ against VW, frequency responses of IZ/VP and VW/VZ are obtained from LTSPICE simulations and given in Figs. 5-8. The DC transfer characteristic of IZ against VP for VDBA is shown in Fig. 5 that is obtained when o ...
View File - UET Taxila
... THEVENIN’S THEOREM It often occurs in practice that a particular element in a circuit is variable while other elements are fixed. For example, a household outlet terminal may be connected to different appliances constituting a variable load. Each time the variable element is changed, the entire cir ...
... THEVENIN’S THEOREM It often occurs in practice that a particular element in a circuit is variable while other elements are fixed. For example, a household outlet terminal may be connected to different appliances constituting a variable load. Each time the variable element is changed, the entire cir ...
pdf
... Abstract: This presentation propose a method for noise‐aware unsupervised speech activity detection (SAD). Combo‐SAD (Sadjadi and Hansen, 2013) is a method for unsupervised SAD based on features that quantifies temporal as well as spectral signatures of voiced speech‐segments. This method was teste ...
... Abstract: This presentation propose a method for noise‐aware unsupervised speech activity detection (SAD). Combo‐SAD (Sadjadi and Hansen, 2013) is a method for unsupervised SAD based on features that quantifies temporal as well as spectral signatures of voiced speech‐segments. This method was teste ...
manley neo-classic se/pp 300b
... IMPORTANT Never operate this amp without a speaker or load connected. Never drive this amp into a short circuit. Most solid state amps can be operated without a load or speaker and some can drive a short circuit because of protection circuitry. These are different - Like most tube amps the output po ...
... IMPORTANT Never operate this amp without a speaker or load connected. Never drive this amp into a short circuit. Most solid state amps can be operated without a load or speaker and some can drive a short circuit because of protection circuitry. These are different - Like most tube amps the output po ...
nihms
... Thus the combination of the HPF and LPF helps to remove unwanted DC signal and high frequency noise including 60 Hz (50 Hz in some countries) mains interference, while amplifying the low amplitude pulse signal (AC component) 101 times. The output from the first signal conditioning stage goes to a si ...
... Thus the combination of the HPF and LPF helps to remove unwanted DC signal and high frequency noise including 60 Hz (50 Hz in some countries) mains interference, while amplifying the low amplitude pulse signal (AC component) 101 times. The output from the first signal conditioning stage goes to a si ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... The potential of CMOS frequency divider for high speed applications has been conventional in numbers of circuits, low voltage operations and low power consumption in CMOS based dividers makes them suitable for compact integration of communication system [1]. Basic gates and flip-flops can be used to ...
... The potential of CMOS frequency divider for high speed applications has been conventional in numbers of circuits, low voltage operations and low power consumption in CMOS based dividers makes them suitable for compact integration of communication system [1]. Basic gates and flip-flops can be used to ...
Using the Optical Port of the 71M6511/71M6513
... output signal from low to high is usually very fast. In the opposite direction, the resistor R1 has to remove the charges from the saturated transistor and overcome charges in parasitic capacitors. This usually causes the transition from high to low to be much slower. When R1 is connected to the col ...
... output signal from low to high is usually very fast. In the opposite direction, the resistor R1 has to remove the charges from the saturated transistor and overcome charges in parasitic capacitors. This usually causes the transition from high to low to be much slower. When R1 is connected to the col ...
SCAN92LV090 9 Channel Bus LVDS Transceiver w/ Boundary SCAN General Description
... differential line drivers and nine receivers. To minimize bus loading, the driver outputs and receiver inputs are internally connected. The separate I/O of the logic side allows for loop back support. The device also features a flow through pin out which allows easy PCB routing for short stubs betwe ...
... differential line drivers and nine receivers. To minimize bus loading, the driver outputs and receiver inputs are internally connected. The separate I/O of the logic side allows for loop back support. The device also features a flow through pin out which allows easy PCB routing for short stubs betwe ...
SWITCHED CAPACITOR CIRCUITS
... Some important non-idealities to consider include: 1. DC Gain: sets the accuracy of the charge transfer, how ‘grounded’ the virtual ground is 2. Unity-gain freq, Phase Margin & Slew Rate: determines maximum clock frequency 3. DC Offsets: circuit techniques to combat this and ...
... Some important non-idealities to consider include: 1. DC Gain: sets the accuracy of the charge transfer, how ‘grounded’ the virtual ground is 2. Unity-gain freq, Phase Margin & Slew Rate: determines maximum clock frequency 3. DC Offsets: circuit techniques to combat this and ...
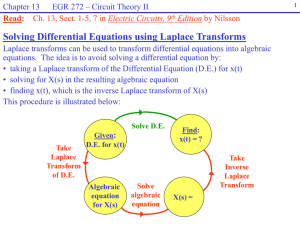
Chapter 13 – Circuit Analysis using Laplace Transforms
... • Transfer functions are always defined with zero initial condition (or zero initial stored energy). Therefore, VC(0) = IL(0) = 0, so the voltage sources in the models for capacitors and inductors disappear. • Y(s) and X(s) typically represent voltages or currents. • The input and the output must be ...
... • Transfer functions are always defined with zero initial condition (or zero initial stored energy). Therefore, VC(0) = IL(0) = 0, so the voltage sources in the models for capacitors and inductors disappear. • Y(s) and X(s) typically represent voltages or currents. • The input and the output must be ...
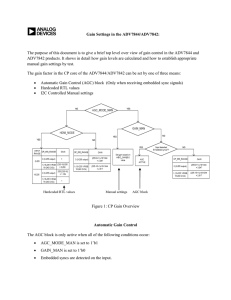
Gain Settings in the ADV7844/ADV7842:
... The AGC of the CP takes measurements of the signal on channel A. The AGC measures the depth of this synchronization pulse and compares it against a target value. It then determines an appropriate gain value for all three channels. Hard Coded RTL Values Hard coded RTL values have being calculated to ...
... The AGC of the CP takes measurements of the signal on channel A. The AGC measures the depth of this synchronization pulse and compares it against a target value. It then determines an appropriate gain value for all three channels. Hard Coded RTL Values Hard coded RTL values have being calculated to ...
Document
... • The frequency will change randomly due to fluctuations in the rate of matter accretion • In LMXB a clustering of frequencies is observed, though the exact rotation frequency is not known • Possibility to apply coherent methods over short time period (few hours) (Vecchio, GWDAW10) ...
... • The frequency will change randomly due to fluctuations in the rate of matter accretion • In LMXB a clustering of frequencies is observed, though the exact rotation frequency is not known • Possibility to apply coherent methods over short time period (few hours) (Vecchio, GWDAW10) ...
Bsc_ElexPassIstAndII.. - Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya
... General theory of feedback, classification of feedback, closed loop gain, open loop gain and return difference, stabilization of gain, Negative feedback in amplifier, Effect of negative feedback on gain, non linear distortion, Band width, Noise, Input and output impedance, Topologies of feedback. Po ...
... General theory of feedback, classification of feedback, closed loop gain, open loop gain and return difference, stabilization of gain, Negative feedback in amplifier, Effect of negative feedback on gain, non linear distortion, Band width, Noise, Input and output impedance, Topologies of feedback. Po ...
Current Mode Compensation Article
... error can manifest itself as a sub-harmonic oscillation of the current loop in the time domain at duty cycles above 50%. Slope compensation is the well-known technique of adding a ramp to the sensed inductor current to obviate the risk of this sub-harmonic oscillation. Figure 2 illustrates how a tur ...
... error can manifest itself as a sub-harmonic oscillation of the current loop in the time domain at duty cycles above 50%. Slope compensation is the well-known technique of adding a ramp to the sensed inductor current to obviate the risk of this sub-harmonic oscillation. Figure 2 illustrates how a tur ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.