DIYstompboxes.com » Tubes for dummies
... The cathode resistor, plate resistor and grid resistor, determine the biasing of the tube stage. The cathode bypass cap controls the degree of bass reduction - generally 25uF passes all frequencies - commonly used in Fender amps, 1uF less, .68uF is used in Marshall amps. A capacitor can be placed in ...
... The cathode resistor, plate resistor and grid resistor, determine the biasing of the tube stage. The cathode bypass cap controls the degree of bass reduction - generally 25uF passes all frequencies - commonly used in Fender amps, 1uF less, .68uF is used in Marshall amps. A capacitor can be placed in ...
Multi-loop Circuits and Kirchoff`s Rules
... battery, the situation is trickier. If all the batteries are part of one branch they can be combined into a single equivalent battery. Generally, the batteries will be part of different branches, and another method has to be used to analyze the circuit to find the current in each branch. Circuits li ...
... battery, the situation is trickier. If all the batteries are part of one branch they can be combined into a single equivalent battery. Generally, the batteries will be part of different branches, and another method has to be used to analyze the circuit to find the current in each branch. Circuits li ...
SP483E 数据资料DataSheet下载
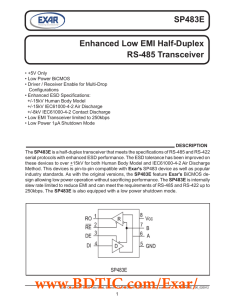
... Method. This devices is pin-to-pin compatible with Exar's SP483 device as well as popular industry standards. As with the original versions, the SP483E feature Exar's BiCMOS design allowing low power operation without sacrificing performance. The SP483E is internally slew rate limited to reduce EMI ...
... Method. This devices is pin-to-pin compatible with Exar's SP483 device as well as popular industry standards. As with the original versions, the SP483E feature Exar's BiCMOS design allowing low power operation without sacrificing performance. The SP483E is internally slew rate limited to reduce EMI ...
Non-inverting amplifier
... Typical values : a few V/ms A sine wave of amplitude A and frequency f requires a slew rate of ...
... Typical values : a few V/ms A sine wave of amplitude A and frequency f requires a slew rate of ...
Active Filters
... inductors (RLC networks). To minimize distortion in the filter characteristic, it is desirable to use inductors with high quality factors (remember the model of a practical inductor includes a series resistance), however these are difficult to implement at frequencies below 1 kHz. ...
... inductors (RLC networks). To minimize distortion in the filter characteristic, it is desirable to use inductors with high quality factors (remember the model of a practical inductor includes a series resistance), however these are difficult to implement at frequencies below 1 kHz. ...
Silicon photonics-wireless interface ICs for micro-/millimeter
... shown in Fig. 2(a) is the simplest because RAU does not have to perform any signal processing except O/E, E/O conversion and amplification. However, the bandwidth of photonic devices should be high enough to handle RF signals, which can be challenging especially for millimeter-wave applications. The ...
... shown in Fig. 2(a) is the simplest because RAU does not have to perform any signal processing except O/E, E/O conversion and amplification. However, the bandwidth of photonic devices should be high enough to handle RF signals, which can be challenging especially for millimeter-wave applications. The ...
CW4301569573
... 1, where as if the Vp is at a potential less than the Vn , the output of the comparator is at logic 0. If Vp > Vn, then Vo= logic 1. If Vp < Vn, then Vo= logic 0. In UDSM (Ultradeep Submicrometer) CMOS Technologies, Analog circuit have the drawback of low power supply voltage when threshold voltage ...
... 1, where as if the Vp is at a potential less than the Vn , the output of the comparator is at logic 0. If Vp > Vn, then Vo= logic 1. If Vp < Vn, then Vo= logic 0. In UDSM (Ultradeep Submicrometer) CMOS Technologies, Analog circuit have the drawback of low power supply voltage when threshold voltage ...
15-W FILTER-FREE STEREO CLASS
... Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operations of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to abso ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operations of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to abso ...
HAMTRONICS® TA51 VHF FM EXCITER: INSTALLATION
... e. Install metal can output transistor Q8 on the board with the bottom of the transistor can 1/32" above the ground plane. Since the case of the transistor is the collector, it is necessary to prevent shorting to the board. Do not use any material as a spacer under the board. Proper operation requir ...
... e. Install metal can output transistor Q8 on the board with the bottom of the transistor can 1/32" above the ground plane. Since the case of the transistor is the collector, it is necessary to prevent shorting to the board. Do not use any material as a spacer under the board. Proper operation requir ...
DigiSat III LCD
... LNBFs. The only qualification is that the LNBF must be down-converting to an I.F. Frequency of 900~2200 Mhz (which is typical of most LNBFs). The Digisat III looks at the entire spectrum of signals received from the LNBF and gives an overall summation of the signal. It is not transponder / frequency ...
... LNBFs. The only qualification is that the LNBF must be down-converting to an I.F. Frequency of 900~2200 Mhz (which is typical of most LNBFs). The Digisat III looks at the entire spectrum of signals received from the LNBF and gives an overall summation of the signal. It is not transponder / frequency ...
Exam 3--PHYS 102--S14
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these statements is always true? a. resistors in parallel have the same voltage b. the equivalent resistance of resistors in parallel is bigger than any one of the resistors c. the sum of the potentials for re ...
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these statements is always true? a. resistors in parallel have the same voltage b. the equivalent resistance of resistors in parallel is bigger than any one of the resistors c. the sum of the potentials for re ...
SSM2402/SSM2412 Dual Audio Analog Switches Data Sheet (Rev. A)
... R1 and R2. The advantage of this configuration is that the attenuator current does not have to flow through the switches. The disadvantage is that the output is undefined during the switching period, which can be several milliseconds. ...
... R1 and R2. The advantage of this configuration is that the attenuator current does not have to flow through the switches. The disadvantage is that the output is undefined during the switching period, which can be several milliseconds. ...
Signal Level Control (AGC)
... •AGC voltage is proportional to signal strength. •Even weak RF signals will produce some control voltage. •This when applied to RF amplifier will tend to reduce its gain. •Hence, RF amplifier is not fed any AGC voltage till the signal strength attains a predetermined level. ...
... •AGC voltage is proportional to signal strength. •Even weak RF signals will produce some control voltage. •This when applied to RF amplifier will tend to reduce its gain. •Hence, RF amplifier is not fed any AGC voltage till the signal strength attains a predetermined level. ...
AN113 - Power Conversion, Measurement and Pulse Circuits
... determines battery voltage by injecting current into the battery and measuring resultant clamp voltage (again, see Reference 5). Figure 17 shows battery simulator response (trace B) to trace A’s monitor current pulse into the output. Closed loop control and the 680µF capacitor limit simulator output ...
... determines battery voltage by injecting current into the battery and measuring resultant clamp voltage (again, see Reference 5). Figure 17 shows battery simulator response (trace B) to trace A’s monitor current pulse into the output. Closed loop control and the 680µF capacitor limit simulator output ...
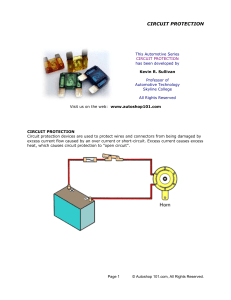
Circuit Protection
... current condition. A fusible link is usually four (4) wire sizes smaller than the circuit that it is protecting. The insulation of a fusible link is a special nonflammable material. This allows the wire to melt, but the insulation to remain intact for safety. Some fusible links have a tag at one end ...
... current condition. A fusible link is usually four (4) wire sizes smaller than the circuit that it is protecting. The insulation of a fusible link is a special nonflammable material. This allows the wire to melt, but the insulation to remain intact for safety. Some fusible links have a tag at one end ...
AD8428 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AD8428 is one of the fastest instrumentation amplifiers available. The circuit architecture is designed for high bandwidth at high gain. The AD8428 uses a current feedback topology for the initial preamplifier gain stage of 200, followed by a difference amplifier stage of 10. This architecture r ...
... The AD8428 is one of the fastest instrumentation amplifiers available. The circuit architecture is designed for high bandwidth at high gain. The AD8428 uses a current feedback topology for the initial preamplifier gain stage of 200, followed by a difference amplifier stage of 10. This architecture r ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.