File
... If you have reached this page, you must have at least a reasonable understanding of the importance of voltage, current and resistance in electric circuits. However, there is more to it than that. Sometimes we have to be concerned about how much power is being consumed. Electrical Power is measured i ...
... If you have reached this page, you must have at least a reasonable understanding of the importance of voltage, current and resistance in electric circuits. However, there is more to it than that. Sometimes we have to be concerned about how much power is being consumed. Electrical Power is measured i ...
ADA4310-1 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... −95 dBc typical at 1 MHz, VOUT = 2 V p-p, G = +5, RLOAD = 50 Ω −69 dBc typical at 10 MHz, VOUT = 2 V p-p, G = +5, RLOAD = 50 Ω Power management and shutdown Control inputs CMOS level compatible ...
... −95 dBc typical at 1 MHz, VOUT = 2 V p-p, G = +5, RLOAD = 50 Ω −69 dBc typical at 10 MHz, VOUT = 2 V p-p, G = +5, RLOAD = 50 Ω Power management and shutdown Control inputs CMOS level compatible ...
2.2.3 Astable Circuits Word Document
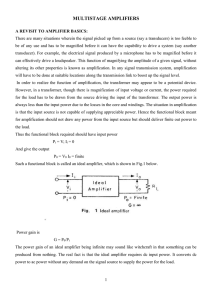
... Comparing this to the Schmitt characteristic reveals a different situation altogether. As VIN increases the voltage has to increase above 3V before the output voltage changes. Once the output has changed however, if the input is then decreased back to 3V, the output does not change back, as it would ...
... Comparing this to the Schmitt characteristic reveals a different situation altogether. As VIN increases the voltage has to increase above 3V before the output voltage changes. Once the output has changed however, if the input is then decreased back to 3V, the output does not change back, as it would ...
victor 6016a - AD INSTRUMENTS
... away from water to avoid electric shock and instrument damage. 2-2-3. Please do not measure before fixing the case and locking the screw. 2-2-4. Do not exceed maximum allowable input of any function when making measurement. 2-2-5. Do not apply voltage to terminal at Resistance Range. 2-2-6. Always s ...
... away from water to avoid electric shock and instrument damage. 2-2-3. Please do not measure before fixing the case and locking the screw. 2-2-4. Do not exceed maximum allowable input of any function when making measurement. 2-2-5. Do not apply voltage to terminal at Resistance Range. 2-2-6. Always s ...
S1-3-15 - Series vs. Parallel
... In this activity, you will construct your own series and parallel circuits and explore the current flow and the voltage differences in your circuits. You will use resistors as well as light bulbs in these circuits. Resistors and light bulbs both restrict the amount of current that can flow through t ...
... In this activity, you will construct your own series and parallel circuits and explore the current flow and the voltage differences in your circuits. You will use resistors as well as light bulbs in these circuits. Resistors and light bulbs both restrict the amount of current that can flow through t ...
asynchronous design in vlsi
... the clock. And above all the power dissipation is from that part of chip which is doing any computational problem. The Philips group designed an asynchronous digital compact cassette error detector which consumes 80% less power than the similar synchronous version. The AMULET group at Manchester Uni ...
... the clock. And above all the power dissipation is from that part of chip which is doing any computational problem. The Philips group designed an asynchronous digital compact cassette error detector which consumes 80% less power than the similar synchronous version. The AMULET group at Manchester Uni ...
ES100_Lecture 3
... • Calculate RN by setting all voltage sources to zero and current sources to open circuit but keeping all internal series and shunt resistances intact. Keep all dependent sources in the circuit like superposition theorem as well. You will, note that RN = RTh • Calculate IN by returning all sources t ...
... • Calculate RN by setting all voltage sources to zero and current sources to open circuit but keeping all internal series and shunt resistances intact. Keep all dependent sources in the circuit like superposition theorem as well. You will, note that RN = RTh • Calculate IN by returning all sources t ...
L1 N L2 - Smarthome
... Leviton warrants to the original consumer purchaser and not for the benefit of anyone else that this product at the time of its sale by Leviton is free of defects in materials and workmanship under normal and proper use for five years from the purchase date. Leviton’s only obligation is to correct s ...
... Leviton warrants to the original consumer purchaser and not for the benefit of anyone else that this product at the time of its sale by Leviton is free of defects in materials and workmanship under normal and proper use for five years from the purchase date. Leviton’s only obligation is to correct s ...
Angle Modulation by a Sinusoidal Signal
... FM demodulators are implemented by generating an AM signal Its amplitude is proportional to the instantaneous frequency of the FM signal, and then using an AM demodulator to recover the message signal. To implement the first step, i.e., to transform the FM signal into an AM signal, it is enough to ...
... FM demodulators are implemented by generating an AM signal Its amplitude is proportional to the instantaneous frequency of the FM signal, and then using an AM demodulator to recover the message signal. To implement the first step, i.e., to transform the FM signal into an AM signal, it is enough to ...
Document
... The human cardiovascular system consists of two circuits: pulmonary circulation which carries blood though the lungs, circulation which carries blood though the lungs and systemic circulation which carries blood to the organs The organs of the body are connected in parallel in the systemic circui ...
... The human cardiovascular system consists of two circuits: pulmonary circulation which carries blood though the lungs, circulation which carries blood though the lungs and systemic circulation which carries blood to the organs The organs of the body are connected in parallel in the systemic circui ...
AD7545A: CMOS 12-Bit Buffered Multiplying DAC Data Sheet (Rev C, 03/2000)
... C, U grades have a guaranteed maximum gain error of ± 1 LSB at +25°C, and in many applications it should be possible to dispense with gain trim resistors altogether. Capacitor C1 provides phase compensation and helps prevent overshoot and ringing when using high speed op amps. Note that all the circ ...
... C, U grades have a guaranteed maximum gain error of ± 1 LSB at +25°C, and in many applications it should be possible to dispense with gain trim resistors altogether. Capacitor C1 provides phase compensation and helps prevent overshoot and ringing when using high speed op amps. Note that all the circ ...
MAX9820 - Maxim Integrated
... from sources such as wireless and cellular phone networks. Although the RF radiation is out of the audio band, many signals, GSM signals in particular, contain bursts or modulation at audible frequencies. Most analog amplifiers demodulate the low-frequency envelope, adding noise to the audio signal. ...
... from sources such as wireless and cellular phone networks. Although the RF radiation is out of the audio band, many signals, GSM signals in particular, contain bursts or modulation at audible frequencies. Most analog amplifiers demodulate the low-frequency envelope, adding noise to the audio signal. ...
Sensitive radio-frequency measurements of a quantum dot by tuning
... measured with good sensitivity and bandwidth. Gate voltages are adjusted to the flank of one Coulomb peak at a point of maximum transconductance. With a modulation voltage now applied to a gate, Fig. 4(a) shows the sideband SNR as a function of f C for two different varactor settings. Again, the per ...
... measured with good sensitivity and bandwidth. Gate voltages are adjusted to the flank of one Coulomb peak at a point of maximum transconductance. With a modulation voltage now applied to a gate, Fig. 4(a) shows the sideband SNR as a function of f C for two different varactor settings. Again, the per ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.