Price - Dicle Yurdakul
... New-Product Development Process New-Product Strategy Idea Generation Idea Screening Business Analysis Development Test Marketing ...
... New-Product Development Process New-Product Strategy Idea Generation Idea Screening Business Analysis Development Test Marketing ...
The price is right: price, equilibrium, elasticity, and incentives
... The goal is to find the equilibrium price. The point at which the quantity of a good or service that buyers demand is equal to the quantity that sellers are supplying. ...
... The goal is to find the equilibrium price. The point at which the quantity of a good or service that buyers demand is equal to the quantity that sellers are supplying. ...
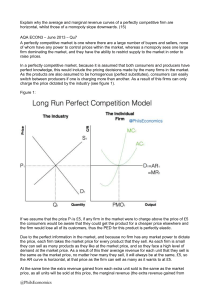
AQA ECON3 – June 2013 – Q7 – Model Answer
... If we assume that the price P1 is £5, if any firm in the market were to charge above the price of £5 the consumers would be aware that they could get the product for a cheaper price elsewhere and the firm would lose all of its customers, thus the PED for this product is perfectly elastic. Due to the ...
... If we assume that the price P1 is £5, if any firm in the market were to charge above the price of £5 the consumers would be aware that they could get the product for a cheaper price elsewhere and the firm would lose all of its customers, thus the PED for this product is perfectly elastic. Due to the ...
Price Elasticity of Demand
... Competition Pricing – Charge similar prices to other firms. Example petrol ...
... Competition Pricing – Charge similar prices to other firms. Example petrol ...
Retail Pricing Strategies
... compromising on prices. The common factor that is common to all such retail formats in India and anywhere across the world is that they cater only to their limited markets and cannot expand beyond a certain point. Despite the vast benefits that it offers, the EDLP policy, however, is not for every r ...
... compromising on prices. The common factor that is common to all such retail formats in India and anywhere across the world is that they cater only to their limited markets and cannot expand beyond a certain point. Despite the vast benefits that it offers, the EDLP policy, however, is not for every r ...
Chapter 10 – Pricing, understanding and capturing
... The market consists of many buyers and sellers who trade over a range of prices rather than a single market price A range of prices occurs because sellers can differentiate their offers to buyers Sellers try to develop differentiated offers for different customer segments and, in addition to p ...
... The market consists of many buyers and sellers who trade over a range of prices rather than a single market price A range of prices occurs because sellers can differentiate their offers to buyers Sellers try to develop differentiated offers for different customer segments and, in addition to p ...
CONTENT TEACHING OUTLINE Unit D: Marketing a Small
... (positively or negatively) in their buying power alter their spending habits in response to those changes. An individual who is laid off from his/her job will not tend to spend a great deal of money on non-essential items due to the uncertainty of his/her economic future. Government regulation: Asid ...
... (positively or negatively) in their buying power alter their spending habits in response to those changes. An individual who is laid off from his/her job will not tend to spend a great deal of money on non-essential items due to the uncertainty of his/her economic future. Government regulation: Asid ...
practice chapter 9
... A firm is a ______ when it can sell as much as it wants at some given price P, but nothing at any higher price. A. Monopoly B. Oligopoly C. Price taker D. Price setter A firm that is a price taker faces a perfectly ______ demand curve. A. Horizontal B. Vertical C. Inelastic D. Convex A price-taking ...
... A firm is a ______ when it can sell as much as it wants at some given price P, but nothing at any higher price. A. Monopoly B. Oligopoly C. Price taker D. Price setter A firm that is a price taker faces a perfectly ______ demand curve. A. Horizontal B. Vertical C. Inelastic D. Convex A price-taking ...
Homework 1
... -1. This means that a 1% rise in prices results in a less than 1% decline in demand which means that a price rise will increase revenue. At higher prices, demand becomes more elastic and raising prices above 10 results in bigger declines in demand offsetting higher prices and reducing revenue. 5. Be ...
... -1. This means that a 1% rise in prices results in a less than 1% decline in demand which means that a price rise will increase revenue. At higher prices, demand becomes more elastic and raising prices above 10 results in bigger declines in demand offsetting higher prices and reducing revenue. 5. Be ...
Sports and Entertainment Marketing
... • Example : UGG Boots only releasing limited amount of sparkly UGG boots at Nordstrom and their stores ...
... • Example : UGG Boots only releasing limited amount of sparkly UGG boots at Nordstrom and their stores ...
ECONOMICS
... the weather, etc. can create demand for goods and services (very quickly, at times). Producers can raise prices to lower demand for goods and services or producers cannot raise prices and cause a shortage of goods and services ...
... the weather, etc. can create demand for goods and services (very quickly, at times). Producers can raise prices to lower demand for goods and services or producers cannot raise prices and cause a shortage of goods and services ...
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing
The usage and pricing of gasoline (or petrol) results from factors such as crude oil prices, processing and distribution costs, local demand, the strength of local currencies, local taxation, and the availability of local sources of gasoline (supply). Since fuels are traded worldwide, the trade prices are similar. The price paid by consumers largely reflects national pricing policy. Some regions, such as Europe and Japan, impose high taxes on gasoline (petrol); others, such as Saudi Arabia and Venezuela, subsidize the cost. Western countries have among the highest usage rates per person. The largest consumer is the United States, which used an average of 368 million US gallons (1.46 gigalitres) each day in 2011.