Chapter 24
... • So every point on the one-firm supply curve that lies to the right of the intersection of the two-firm supply curve and the line determined by p* cannot be consistent with the LR equilibrium. • As the number of firms gets larger, the supply curve becomes flatter. So we cannot be very far from p* ...
... • So every point on the one-firm supply curve that lies to the right of the intersection of the two-firm supply curve and the line determined by p* cannot be consistent with the LR equilibrium. • As the number of firms gets larger, the supply curve becomes flatter. So we cannot be very far from p* ...
AP Micro Problem Set 3 Production Costs and Perfect Competition
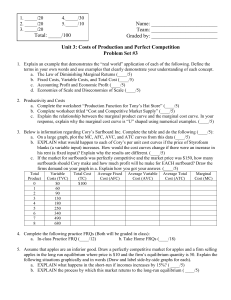
... 1. Explain an example that demonstrates the “real world” application of each of the following. Define the terms in your own words and use examples that clearly demonstrate your understanding of each concept. a. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (____/5) b. Fixed Costs, Variable Costs, and Tota ...
... 1. Explain an example that demonstrates the “real world” application of each of the following. Define the terms in your own words and use examples that clearly demonstrate your understanding of each concept. a. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (____/5) b. Fixed Costs, Variable Costs, and Tota ...
HL monopoly
... industry, it has developed a cost advantage over potential entrants. It might use this advantage to cut prices if and when new suppliers enter the market, moving away from short run profit maximisation objectives - but designed to inflict losses on new firms and protect its market position in the lo ...
... industry, it has developed a cost advantage over potential entrants. It might use this advantage to cut prices if and when new suppliers enter the market, moving away from short run profit maximisation objectives - but designed to inflict losses on new firms and protect its market position in the lo ...
Chapter 9
... The main cause of monopolies is barriers to entry – other firms cannot enter the market. Three sources of barriers to entry: 1. A single firm controls a key resource. 2. The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce the good. 3. Natural monopoly: a single firm can produce the ent ...
... The main cause of monopolies is barriers to entry – other firms cannot enter the market. Three sources of barriers to entry: 1. A single firm controls a key resource. 2. The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce the good. 3. Natural monopoly: a single firm can produce the ent ...
Theory of Markets
... • Increase in the price of a another good would result in an inward shift of the supply curve of the related good ...
... • Increase in the price of a another good would result in an inward shift of the supply curve of the related good ...
Chapter 9 – Profit maximization
... existence of economies of scale over the entire relevant range of output. a larger firm will always be able to produce output at a lower cost than could a smaller firm. only a single firm can survive in a longrun equilibrium. ...
... existence of economies of scale over the entire relevant range of output. a larger firm will always be able to produce output at a lower cost than could a smaller firm. only a single firm can survive in a longrun equilibrium. ...
Slide 1
... Selection of price and output Shut down decision in short run. Entry and exit behavior. Predicting the effects of a change in demand, technological advance, or change in cost. Efficiency of perfect competition ...
... Selection of price and output Shut down decision in short run. Entry and exit behavior. Predicting the effects of a change in demand, technological advance, or change in cost. Efficiency of perfect competition ...
Goal 8 PPT
... conglomerates that include businesses in different countries • Trusts – large monopolies (anti-trust laws ban these) ...
... conglomerates that include businesses in different countries • Trusts – large monopolies (anti-trust laws ban these) ...
large number of firms
... • One of the primary characteristics of purely competitive markets is that they are efficient. • Competition within these markets keeps both prices and production costs low. • Firms must use all inputs—land, labor, organizational skills, machinery and equipment—to their best advantage. • Prices that ...
... • One of the primary characteristics of purely competitive markets is that they are efficient. • Competition within these markets keeps both prices and production costs low. • Firms must use all inputs—land, labor, organizational skills, machinery and equipment—to their best advantage. • Prices that ...
Two
... products. 6. The welfare loss due to monopoly refers to the fact that monopolists are able to make profits by taking consumer surplus from the consumers. 7. An externality is said to occur when marginal private cost is not equal to marginal social cost. 8. If there is a positive externality in the p ...
... products. 6. The welfare loss due to monopoly refers to the fact that monopolists are able to make profits by taking consumer surplus from the consumers. 7. An externality is said to occur when marginal private cost is not equal to marginal social cost. 8. If there is a positive externality in the p ...
Homework #5 - Iowa State University Department of Economics
... 19) Small pizza parlors exist in just about every town. Anyone can open a pizza parlor, and the pizzas from one parlor typically have different tastes and sizes than pizzas from another parlor. Thus, the pizza industry is an example of A) monopoly. B) oligopoly. C) monopolistic competition. D) perfe ...
... 19) Small pizza parlors exist in just about every town. Anyone can open a pizza parlor, and the pizzas from one parlor typically have different tastes and sizes than pizzas from another parlor. Thus, the pizza industry is an example of A) monopoly. B) oligopoly. C) monopolistic competition. D) perfe ...
Lecture 19 Review Questions
... 14. What the (profit maximizing) firm's output if it is operating in a monopolistically comptetitive market with demand and costs given in the ...
... 14. What the (profit maximizing) firm's output if it is operating in a monopolistically comptetitive market with demand and costs given in the ...
1 - JustAnswer
... 4. The invention of the assembly line provided Ford Motor Company with an incredible advantage over its competitors. This method of production may have made Henry Ford a monopolist but competition never quite vanished. Based on your knowledge of market forms, which form was more suitable to describe ...
... 4. The invention of the assembly line provided Ford Motor Company with an incredible advantage over its competitors. This method of production may have made Henry Ford a monopolist but competition never quite vanished. Based on your knowledge of market forms, which form was more suitable to describe ...
Perfect Competition & Monopoly
... different prices in each market segment To price-discriminate • The firm must identify consumer groups/classes with different downward-sloping demand curves • The firm must be able to prevent consumers of one class from reselling its product to the consumers of another class; no intermarket redistri ...
... different prices in each market segment To price-discriminate • The firm must identify consumer groups/classes with different downward-sloping demand curves • The firm must be able to prevent consumers of one class from reselling its product to the consumers of another class; no intermarket redistri ...
Chpt 8 PP
... common monopolies? Local monopolies are more common real-world approximations of the model than national or world market monopolies ...
... common monopolies? Local monopolies are more common real-world approximations of the model than national or world market monopolies ...
Oligopoly - Cornell University
... Other firms may be able to produce the good or service but choose not to enter the market or are barred from it. Firms are price makers. Some pharmaceuticals ...
... Other firms may be able to produce the good or service but choose not to enter the market or are barred from it. Firms are price makers. Some pharmaceuticals ...