MONOPOLY A (pure) monopolist is a sole supplier of the output of
... When a firm gets into the market ahead of others, it might be able to expand and reap economies of scale. It would be able to charge a lower price than its rivals. It would eat into the market share of its competitors who are forced to cut back production and shut down plants. Not able to compete, ...
... When a firm gets into the market ahead of others, it might be able to expand and reap economies of scale. It would be able to charge a lower price than its rivals. It would eat into the market share of its competitors who are forced to cut back production and shut down plants. Not able to compete, ...
ECO 335 Economics of Regulation and Antitrust Dr. David Loomis Department of Economics
... • Demanders - consumers wanting protection from monopoly or producers wanting protection from each other ...
... • Demanders - consumers wanting protection from monopoly or producers wanting protection from each other ...
Chapter 10 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
... In oligopoly there are fewer firms than in perfect competition or monopolistic competition, but more than in monopoly. Unlike perfectly or monopolistically competitive markets, there are barriers to entry and exit. ...
... In oligopoly there are fewer firms than in perfect competition or monopolistic competition, but more than in monopoly. Unlike perfectly or monopolistically competitive markets, there are barriers to entry and exit. ...
AP Economics Semester 1: Microeconomics Homework Check: 150
... Possibility Curve(Frontier), Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Positive, Normative, Economic Model, Ceteris Paribus, Absolute Advantage, Comparative Advantage, Specialization, Imports, Exports Graphs to Know: Circular Flow, PPC Assessments: - 1 Quiz (9/5/14) - Unit 1 Packet (9/9/14) ...
... Possibility Curve(Frontier), Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Positive, Normative, Economic Model, Ceteris Paribus, Absolute Advantage, Comparative Advantage, Specialization, Imports, Exports Graphs to Know: Circular Flow, PPC Assessments: - 1 Quiz (9/5/14) - Unit 1 Packet (9/9/14) ...
ECON 2010-200 Principles of Microeconomics
... exams. A small percentage of the final grade will be determined by performance in a game, and by some data collection exercises to be given out in class. ...
... exams. A small percentage of the final grade will be determined by performance in a game, and by some data collection exercises to be given out in class. ...
PART 2
... a) 110,000 TL profit. b) 50,000 TL profit. c) 50,000 TL losses. d) 0 TL . 2) Which of the following is correct about marginal and average products? a) When the marginal product is increasing, the average product must be increasing. b) When the marginal product exceeds the average product, the averag ...
... a) 110,000 TL profit. b) 50,000 TL profit. c) 50,000 TL losses. d) 0 TL . 2) Which of the following is correct about marginal and average products? a) When the marginal product is increasing, the average product must be increasing. b) When the marginal product exceeds the average product, the averag ...
Quiz 6 Solutions
... C) the marginal benefit of consumers for each level of consumption. D) none of these. Answer: C 2) Assume extra benefits in a market are equal to $75 while extra costs are equal to $54. What can be said about economic efficiency? A) Economic efficiency has not been reached, more needs to be produced ...
... C) the marginal benefit of consumers for each level of consumption. D) none of these. Answer: C 2) Assume extra benefits in a market are equal to $75 while extra costs are equal to $54. What can be said about economic efficiency? A) Economic efficiency has not been reached, more needs to be produced ...
Monopolistic Competition
... As always, the profit-maximizing rate of output is achieved by producing the quantity where MR = MC. ...
... As always, the profit-maximizing rate of output is achieved by producing the quantity where MR = MC. ...
Deriving the Long-Run Market Supply Curve
... nature of costs in that industry. Costs in industries are characterized by increasing, constant, or decreasing costs, depending on the behavior of long-run costs as firms enter the industry in response to increased demand. To understand how to derive a market supply curve, consider first an industry ...
... nature of costs in that industry. Costs in industries are characterized by increasing, constant, or decreasing costs, depending on the behavior of long-run costs as firms enter the industry in response to increased demand. To understand how to derive a market supply curve, consider first an industry ...
Assignment 2
... MC(Q) = 200 b. How many bakers will John hire to make 25 tons of donuts? Q = 2KL 25= 2(1)(L) L = 12.5 4. (5 marks) A monopolist can produce at constant average and marginal costs of AC = MC = 6. It faces a market demand curve given by Q = 54 – P and MR = 54 – 2Q. a) Calculate the profit-maximizing ...
... MC(Q) = 200 b. How many bakers will John hire to make 25 tons of donuts? Q = 2KL 25= 2(1)(L) L = 12.5 4. (5 marks) A monopolist can produce at constant average and marginal costs of AC = MC = 6. It faces a market demand curve given by Q = 54 – P and MR = 54 – 2Q. a) Calculate the profit-maximizing ...
Unit 1: Going Into Business For Yourself
... – People can choose what products to buy – People can choose to own private property – People are free to start a legal business and compete with other businesses – Also known as Capitalism or a Market Economy ...
... – People can choose what products to buy – People can choose to own private property – People are free to start a legal business and compete with other businesses – Also known as Capitalism or a Market Economy ...
Practice Questions on Perfect Competition
... Consider a perfectly competitive market in the short run. Assume that market demand is P 100 4QD and market supply is P=Qs. Denoting firm level quantity by q, assume TC=50+4q+2q2 so that MC=4+4q. a) What is the market equilibrium price and quantity? b) How many firms are in the industry in the s ...
... Consider a perfectly competitive market in the short run. Assume that market demand is P 100 4QD and market supply is P=Qs. Denoting firm level quantity by q, assume TC=50+4q+2q2 so that MC=4+4q. a) What is the market equilibrium price and quantity? b) How many firms are in the industry in the s ...
Profit maximization in different market structures In the cappuccino
... “Market power” also known as “pricing power” is defined in the managerial literature as the ability of an individual firm to vary its price while still remaining profitable or as the firm’s ability to charge the price above its MC. ...
... “Market power” also known as “pricing power” is defined in the managerial literature as the ability of an individual firm to vary its price while still remaining profitable or as the firm’s ability to charge the price above its MC. ...
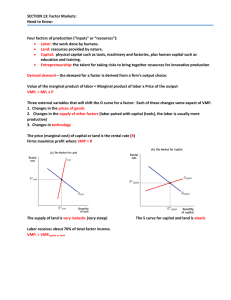
SECTION 13: Factor Markets: Need to Know: Four factors of production (“inputs” or “resources”):
... Entrepreneurship: the talent for taking risks to bring together resources for innovative production ...
... Entrepreneurship: the talent for taking risks to bring together resources for innovative production ...
AP Micro Concepts
... Production is the creation of utility. Four Factors of Production Economists vs. Accountants Total Revenue Explicit Costs Implicit Costs Economic Costs Economic Profit Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (Graph) Total Product and Marginal Product: 3 Stages of returns (Graph) Stage I: ...
... Production is the creation of utility. Four Factors of Production Economists vs. Accountants Total Revenue Explicit Costs Implicit Costs Economic Costs Economic Profit Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (Graph) Total Product and Marginal Product: 3 Stages of returns (Graph) Stage I: ...
ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
... number; their products are standardized to some extent; their size makes new entry very difficult; there is much nonprice competition; there is little, if any, price competition; while there may be no collusion, there does seem to be much price leadership. (c) Kansas wheat farm: pure competition. Th ...
... number; their products are standardized to some extent; their size makes new entry very difficult; there is much nonprice competition; there is little, if any, price competition; while there may be no collusion, there does seem to be much price leadership. (c) Kansas wheat farm: pure competition. Th ...