No Slide Title
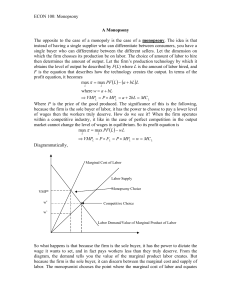
... » To produce more than this quantity implies that P < MC, which is not the most profitable decision. » To produce less than where P=MC, implies that P > MC, and the firm could increase profits by expanding output. ...
... » To produce more than this quantity implies that P < MC, which is not the most profitable decision. » To produce less than where P=MC, implies that P > MC, and the firm could increase profits by expanding output. ...
CH3Questions for Moodle
... ____ 5. If a need or want is particularly important or strong, a consumer might be willing to spend more money to satisfy it. ____ 6. If consumers believe there is only one product or brand that meets their needs, they will usually be willing to pay a higher price. ____ 7. When competition is intens ...
... ____ 5. If a need or want is particularly important or strong, a consumer might be willing to spend more money to satisfy it. ____ 6. If consumers believe there is only one product or brand that meets their needs, they will usually be willing to pay a higher price. ____ 7. When competition is intens ...
AP Microeconomics Syllabus
... consumer surpluses, the law of diminishing marginal utility, indifference curves, budget constraints, marginal rate of substitution, and cost-benefit analysis, isoquants, and isocosts. Part IV: Perfectly Competitive Markets & Economic Costs: Characteristics of Perfectly competitive markets, imperfec ...
... consumer surpluses, the law of diminishing marginal utility, indifference curves, budget constraints, marginal rate of substitution, and cost-benefit analysis, isoquants, and isocosts. Part IV: Perfectly Competitive Markets & Economic Costs: Characteristics of Perfectly competitive markets, imperfec ...
ECON 600 – Economics of Organizations and Management
... The firm maximizes profit so that marginal cost equals price. ...
... The firm maximizes profit so that marginal cost equals price. ...
PRICE
... The Price Elasticity of Demand • How sensitive are customers to changes in the price of a product? • Price elasticity of demand is a measure of the sensitivity of customers to changes in price. • Price elasticity of demand = Percentage change in quantity demanded / Percentage change in price ...
... The Price Elasticity of Demand • How sensitive are customers to changes in the price of a product? • Price elasticity of demand is a measure of the sensitivity of customers to changes in price. • Price elasticity of demand = Percentage change in quantity demanded / Percentage change in price ...
Chapter 9 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Firm sells DQ additional units of output, each at a price of P(Q), the output expansion effect Firm also has to lower price as dictated by the demand curve; reduces revenue earned from the original (Q-DQ) units of output, the price reduction effect Price-taking firm faces a horizontal demand curv ...
... Firm sells DQ additional units of output, each at a price of P(Q), the output expansion effect Firm also has to lower price as dictated by the demand curve; reduces revenue earned from the original (Q-DQ) units of output, the price reduction effect Price-taking firm faces a horizontal demand curv ...
S 11 Practice MC Test
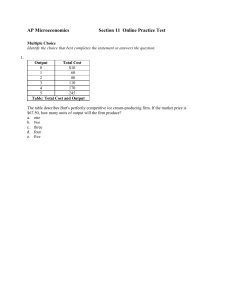
... c. monopoly may have economic profits in the long run, but in perfect competition economic profits are zero in the long run. d. perfect competition may have economic profits in the long run, but in monopoly economic profits are zero in the long run. e. monopoly produces where MR = MC, and a perfectl ...
... c. monopoly may have economic profits in the long run, but in perfect competition economic profits are zero in the long run. d. perfect competition may have economic profits in the long run, but in monopoly economic profits are zero in the long run. e. monopoly produces where MR = MC, and a perfectl ...
MicroEconomics
... commonly divided into four parts: allocation, distribution, stability, and growth. The study of allocation problems – what to produce and how much -, and the distribution problem – how real income is distributed among society’s members – are termed Microeconomic Theory. In microeconomics the major t ...
... commonly divided into four parts: allocation, distribution, stability, and growth. The study of allocation problems – what to produce and how much -, and the distribution problem – how real income is distributed among society’s members – are termed Microeconomic Theory. In microeconomics the major t ...
Smpfecba - University of Pittsburgh
... b. What profit or loss will the firm have if it operates where MR = MC? Does this profit or loss check with your decision on whether to produce or temporary shut down? T = TR - TC = 250(30) - 5,250 -100(30) - 2.5(30)2 = - 3,000. Yes, because the loss is less than the fixed cost, and therefore the f ...
... b. What profit or loss will the firm have if it operates where MR = MC? Does this profit or loss check with your decision on whether to produce or temporary shut down? T = TR - TC = 250(30) - 5,250 -100(30) - 2.5(30)2 = - 3,000. Yes, because the loss is less than the fixed cost, and therefore the f ...
Brief Outline - Fullerton College Staff Web Pages
... interdependence, collusive tendencies, incentive to cheat (232-233) kinked demand model, (234) Key Graph (235) cartel and other collusion, joint monopoly profits (236-238) price leadership (239) positive and negative effects of advertising (240-241) oligopoly and efficiency (241) Chapter 9 Pure Comp ...
... interdependence, collusive tendencies, incentive to cheat (232-233) kinked demand model, (234) Key Graph (235) cartel and other collusion, joint monopoly profits (236-238) price leadership (239) positive and negative effects of advertising (240-241) oligopoly and efficiency (241) Chapter 9 Pure Comp ...
AP Microeconomics Syllabus – Semester 1 Teacher Contact
... Each quarter grade will consist of a variety of activities, including daily activities and discussions, study guide questions/problems, hands on computer assignments, simulations, and chapter and unit assessments. Students should always be reading the material before discussed in class. Pop quizzes ...
... Each quarter grade will consist of a variety of activities, including daily activities and discussions, study guide questions/problems, hands on computer assignments, simulations, and chapter and unit assessments. Students should always be reading the material before discussed in class. Pop quizzes ...
Assigned Homework
... Draw diagrams carefully, paying attention to the kinds of relationships illustrated for you in the diagrams presented. For example, you should never draw a set of marginal and average cost curves where the MC intersects the AC at any point other than where AC is at a minimum. 1. Here are views of a ...
... Draw diagrams carefully, paying attention to the kinds of relationships illustrated for you in the diagrams presented. For example, you should never draw a set of marginal and average cost curves where the MC intersects the AC at any point other than where AC is at a minimum. 1. Here are views of a ...
Slide Set 3
... Normal Profit: The entrepreneur’s opportunity cost. It is equal to or greater than the maximum income an entrepreneur could have received employing his or her resources elsewhere. Normal Profit is included in the firm’s costs. Economic Profit: Profit that an entrepreneur makes over the Normal Profi ...
... Normal Profit: The entrepreneur’s opportunity cost. It is equal to or greater than the maximum income an entrepreneur could have received employing his or her resources elsewhere. Normal Profit is included in the firm’s costs. Economic Profit: Profit that an entrepreneur makes over the Normal Profi ...
Set 7 Perfect Competition
... firm increases its output from q1 to q2 and its profits become positive (P>AC). The industry is not in long run equilibrium because the firms are earning positive profits. 4. In the long run there will be entry, which will cause supply to increase from s to s1 in the graph above. Price will be drive ...
... firm increases its output from q1 to q2 and its profits become positive (P>AC). The industry is not in long run equilibrium because the firms are earning positive profits. 4. In the long run there will be entry, which will cause supply to increase from s to s1 in the graph above. Price will be drive ...
monopolistically competitive. - LMS
... • To sell one more unit of output will cost the price of the added message, k, divided by the marginal product of a dollar of advertising (DQ/DA). • If a radio message costs $1000, and if that message yields 5 new items sold, then the marginal cost of advertising is $200, ($1000 /marginal product of ...
... • To sell one more unit of output will cost the price of the added message, k, divided by the marginal product of a dollar of advertising (DQ/DA). • If a radio message costs $1000, and if that message yields 5 new items sold, then the marginal cost of advertising is $200, ($1000 /marginal product of ...