Document
... apply because there is no auctioneer. Do you Agree or Disagree? Why or Why not? • The price of a given-quality personal computer is cheaper today than it was 5 years ago. Is this a result of Lower Demand ...
... apply because there is no auctioneer. Do you Agree or Disagree? Why or Why not? • The price of a given-quality personal computer is cheaper today than it was 5 years ago. Is this a result of Lower Demand ...
demanders
... consumer responds by purchasing more of this good, thus reducing the marginal utility. ...
... consumer responds by purchasing more of this good, thus reducing the marginal utility. ...
presentation source
... employ studies done by the Federal Trade Commission d. make sure you locate Internet information by using a search engine e. ask the National Industrial Conference Board for its latest study 267A(n) _____ is characterized by the researcher's altering one or more variables-such as price or package de ...
... employ studies done by the Federal Trade Commission d. make sure you locate Internet information by using a search engine e. ask the National Industrial Conference Board for its latest study 267A(n) _____ is characterized by the researcher's altering one or more variables-such as price or package de ...
Chapter 9: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
... Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition.” This exercise illustrates that a monopolistically competitive producer of blue jeans just breaks even in the long run after the demand for jeans increased in the short run. ...
... Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition.” This exercise illustrates that a monopolistically competitive producer of blue jeans just breaks even in the long run after the demand for jeans increased in the short run. ...
Ch 16 - Effective Marketing, 3e
... Review relationship between price and organizational objectives Relate demand to price Overview demand & cost considerations on pricing Differentiate price elasticity, inelasticity, and crosselasticity ...
... Review relationship between price and organizational objectives Relate demand to price Overview demand & cost considerations on pricing Differentiate price elasticity, inelasticity, and crosselasticity ...
Chapter 9: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
... Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition.” This exercise illustrates that a monopolistically competitive producer of blue jeans just breaks even in the long run after the demand for jeans increased in the short run. ...
... Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition.” This exercise illustrates that a monopolistically competitive producer of blue jeans just breaks even in the long run after the demand for jeans increased in the short run. ...
Price
... B) P = 12 , MR = 0 C) P = 8 , MR = -2 D) P = 4 , MR = -4 (8) Marginal revenue is positive whenever : A) demand is price-elastic . B) demand is price-inelastic . C) demand is unitary-elastic . D) a firm operates at a point on the lower half of a linear demand curve. (9) Suppose a monopolist produces ...
... B) P = 12 , MR = 0 C) P = 8 , MR = -2 D) P = 4 , MR = -4 (8) Marginal revenue is positive whenever : A) demand is price-elastic . B) demand is price-inelastic . C) demand is unitary-elastic . D) a firm operates at a point on the lower half of a linear demand curve. (9) Suppose a monopolist produces ...
B2B Chapter 12
... What proportion of cost is raw material or component parts? At different levels of product, how does cost vary? At what production levels can economies of scale be expected? Does our firm enjoy cost advantages over competition? How does the “experience effect” impact our cost projections? ...
... What proportion of cost is raw material or component parts? At different levels of product, how does cost vary? At what production levels can economies of scale be expected? Does our firm enjoy cost advantages over competition? How does the “experience effect” impact our cost projections? ...
20070722MEnotes
... I. Satisfaction received and limited budgets determine consumer demand. II. Utility analysis A. Law of diminishing marginal utility 1. Utility measures the want-satisfying power of a good or service. 2. Marginal utility is the additional or incremental satisfaction (utility) a consumer receives from ...
... I. Satisfaction received and limited budgets determine consumer demand. II. Utility analysis A. Law of diminishing marginal utility 1. Utility measures the want-satisfying power of a good or service. 2. Marginal utility is the additional or incremental satisfaction (utility) a consumer receives from ...
Chapter 1 Practice Exam Solutions
... being produced in a market system, its price falls; If “too little” is being produced, its price increases. The price remains stable only when a balance has been achieved between what producers are willing and able to produce and what consumers are willing and able to consume. That is, at the equili ...
... being produced in a market system, its price falls; If “too little” is being produced, its price increases. The price remains stable only when a balance has been achieved between what producers are willing and able to produce and what consumers are willing and able to consume. That is, at the equili ...
Econ 101 Exam Review 2 Answers
... 1. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of pizza if a hamburger place opens next door and the price of dough decreases? A. Price will fall and the effect on quantity is ambiguous. B. Price will rise and the effect on quantity is ambiguous C. Quantity will fall and the effect on pri ...
... 1. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of pizza if a hamburger place opens next door and the price of dough decreases? A. Price will fall and the effect on quantity is ambiguous. B. Price will rise and the effect on quantity is ambiguous C. Quantity will fall and the effect on pri ...
Principles of Microeconomics
... which he can do at a constant rate of 200 words per hour, and harvesting apples from the trees growing on his land, a task only he can perform. His return from harvesting apples depends on both the price of apples and the quantity of apples he harvests. For each hour Leroy spends picking apples, ...
... which he can do at a constant rate of 200 words per hour, and harvesting apples from the trees growing on his land, a task only he can perform. His return from harvesting apples depends on both the price of apples and the quantity of apples he harvests. For each hour Leroy spends picking apples, ...
The Cost Side of The Market - Ka
... which he can do at a constant rate of 200 words per hour, and harvesting apples from the trees growing on his land, a task only he can perform. His return from harvesting apples depends on both the price of apples and the quantity of apples he harvests. For each hour Leroy spends picking apples, ...
... which he can do at a constant rate of 200 words per hour, and harvesting apples from the trees growing on his land, a task only he can perform. His return from harvesting apples depends on both the price of apples and the quantity of apples he harvests. For each hour Leroy spends picking apples, ...
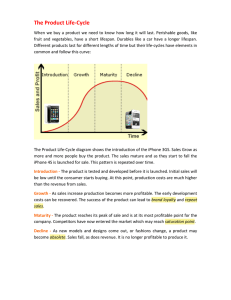
The Product Life-Cycle - NW 14-19
... more attractive. Continued advertising around the brand name will help to sustain sales. The marketing team may consider expanding its distribution, to reach more consumers. Maturity Competitors will usually have entered the market at this stage. If their products are as good but cheaper the com ...
... more attractive. Continued advertising around the brand name will help to sustain sales. The marketing team may consider expanding its distribution, to reach more consumers. Maturity Competitors will usually have entered the market at this stage. If their products are as good but cheaper the com ...
Factor Markets: Land, Labor, and Capital
... • Assume there’s a firm that is the largest supplier of jobs in town. This would be an example of monopsony. They’re going to use up the most factors, in this case, labor. • If it wants to hire more workers, it must offer higher wages to attract them. The higher wages go to all workers, not just tho ...
... • Assume there’s a firm that is the largest supplier of jobs in town. This would be an example of monopsony. They’re going to use up the most factors, in this case, labor. • If it wants to hire more workers, it must offer higher wages to attract them. The higher wages go to all workers, not just tho ...
In Search of Predatory Pricing
... and Plato calculates the resulting profit Each seller sees the other sellers only after both have entered their offers The buyers were then randomly ordered by Plato using a computerized subroutine under the assumption that demand was fully revealed Sellers were not told what the final period ...
... and Plato calculates the resulting profit Each seller sees the other sellers only after both have entered their offers The buyers were then randomly ordered by Plato using a computerized subroutine under the assumption that demand was fully revealed Sellers were not told what the final period ...