Supply and Demand
... Quantity demanded--it is the amount that will be purchased at a specific P. Demand--it is a schedule of quantities of goods and services that will be purchased at various prices at a specified time, all other things held constant. ...
... Quantity demanded--it is the amount that will be purchased at a specific P. Demand--it is a schedule of quantities of goods and services that will be purchased at various prices at a specified time, all other things held constant. ...
3: Demand and Supply
... Demand • A Change in Demand Quantity of the good that people plan to buy changes at each and every price Shift of demand curve. When demand increases, – QD increases at each and every price – the demand curve shifts rightward. ...
... Demand • A Change in Demand Quantity of the good that people plan to buy changes at each and every price Shift of demand curve. When demand increases, – QD increases at each and every price – the demand curve shifts rightward. ...
department of economics - Faculty of Business and Economics
... competitive and monopoly markets the more elastic is demand relative t o supply or marginal cost. With a monopoly industry, no-more than a half of the marginal cost reduction contributed by e-commerce will be passed forward to buyers. For some industries e-commerce improves the extra information a n ...
... competitive and monopoly markets the more elastic is demand relative t o supply or marginal cost. With a monopoly industry, no-more than a half of the marginal cost reduction contributed by e-commerce will be passed forward to buyers. For some industries e-commerce improves the extra information a n ...
Managerial Economics - Unit 3: Perfect Competition, Monopoly and
... A firm’s pricing market power depends on its competitive environment. In perfectly competitive markets, firms have no market power. They are “price takers.” They make decisions based on the market price, which ...
... A firm’s pricing market power depends on its competitive environment. In perfectly competitive markets, firms have no market power. They are “price takers.” They make decisions based on the market price, which ...
When a consumer is able and willing to buy a good or service, he or
... Disequilibrium occurs when: • a. quantity supplied and quantity demanded are not equal • b. prices are higher than quantity supplied • c. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded • d. there is neither excess supply nor excess demand ...
... Disequilibrium occurs when: • a. quantity supplied and quantity demanded are not equal • b. prices are higher than quantity supplied • c. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded • d. there is neither excess supply nor excess demand ...
Test 2 practice MCQ (Answers are at the end) 1. If the demand for
... Suppose that a 10 percent increase in the price of normal good Y causes a 20 percent increase in the quantity demanded of normal good X. The coefficient of cross elasticity of demand is: A. negative and therefore these goods are substitutes. B. negative and therefore these goods are complements. C. ...
... Suppose that a 10 percent increase in the price of normal good Y causes a 20 percent increase in the quantity demanded of normal good X. The coefficient of cross elasticity of demand is: A. negative and therefore these goods are substitutes. B. negative and therefore these goods are complements. C. ...
Managerial Economics - Unit 3 - Johannes Kepler University Linz
... A firm’s pricing market power depends on its competitive environment. In perfectly competitive markets, firms have no market power. They are “price takers.” They make decisions based on the market price, which ...
... A firm’s pricing market power depends on its competitive environment. In perfectly competitive markets, firms have no market power. They are “price takers.” They make decisions based on the market price, which ...
bonus case 2-2
... the city government responsible, or the state government, or the federal government? There have been major natural disasters throughout the world in recent years, and the results have been much the same. Many people die; others lose their homes and jobs. Almost always, citizens try to help, but the ...
... the city government responsible, or the state government, or the federal government? There have been major natural disasters throughout the world in recent years, and the results have been much the same. Many people die; others lose their homes and jobs. Almost always, citizens try to help, but the ...
Answers
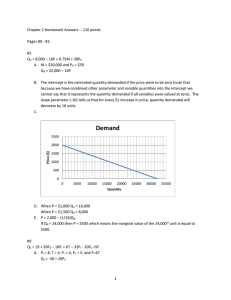
... A. M = $30,000 and PR = $50 Qd = 32,000 – 16P B. The intercept is the estimated quantity demanded if the price were to be zero (note that because we have combined other parameter and variable quantities into the intercept we cannot say that it represents the quantity demanded if all variables were v ...
... A. M = $30,000 and PR = $50 Qd = 32,000 – 16P B. The intercept is the estimated quantity demanded if the price were to be zero (note that because we have combined other parameter and variable quantities into the intercept we cannot say that it represents the quantity demanded if all variables were v ...
EC 170: Industrial Organization
... • With monopoly setting price or quantity first makes no difference • In oligopoly it matters a great deal – nature of price competition is much more aggressive the quantity competition ...
... • With monopoly setting price or quantity first makes no difference • In oligopoly it matters a great deal – nature of price competition is much more aggressive the quantity competition ...
ManEc 300 Day 1 -Bryson
... ManEc 300, Day 5 Review Questions from Session 4 What problems of information flow does the firm have in its planning? What is brittleness? When can the firm not rely on organizational routine for proper functioning of productive processes? How do economies of scale and scope affect the firm’s coor ...
... ManEc 300, Day 5 Review Questions from Session 4 What problems of information flow does the firm have in its planning? What is brittleness? When can the firm not rely on organizational routine for proper functioning of productive processes? How do economies of scale and scope affect the firm’s coor ...
Document
... – Shutdown: firm stops producing the good but still pays fixed costs – Exit: firm leaves the industry entirely and no longer faces any costs ...
... – Shutdown: firm stops producing the good but still pays fixed costs – Exit: firm leaves the industry entirely and no longer faces any costs ...
Costs 5.2
... production as volume changes. Starting from a few meals and customers, Con’s Kitchen can improve its efficiency and decrease its average variable cost per meal as it increases its volume (product). But, if we expand too much, the average variable cost starts to rise as more employees start to ge ...
... production as volume changes. Starting from a few meals and customers, Con’s Kitchen can improve its efficiency and decrease its average variable cost per meal as it increases its volume (product). But, if we expand too much, the average variable cost starts to rise as more employees start to ge ...
Equilibrium price
... 2. Which type of economy are economic decisions based on customs and habits of the past? 3. Which type of economy does the government control all aspects of production? 4. Which type of economy do individuals and firms have the freedom to produce what they want? ...
... 2. Which type of economy are economic decisions based on customs and habits of the past? 3. Which type of economy does the government control all aspects of production? 4. Which type of economy do individuals and firms have the freedom to produce what they want? ...
Assignment 4 Marketing
... Consumers are grouped by a common geographic aspect, they could be cities, regions, countries, postal codes and the list goes on. With this information business can specifically meet the needs of the region, say for example you are selling winter jackets in Alaska or trying to sell beach wear in Mia ...
... Consumers are grouped by a common geographic aspect, they could be cities, regions, countries, postal codes and the list goes on. With this information business can specifically meet the needs of the region, say for example you are selling winter jackets in Alaska or trying to sell beach wear in Mia ...
Supply
... • Assessing the best level of output can be done by determining when marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. • Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one more unit. • Marginal revenue is the additional income from selling one more unit of a good; sometimes equal to price. • Simply, th ...
... • Assessing the best level of output can be done by determining when marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. • Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one more unit. • Marginal revenue is the additional income from selling one more unit of a good; sometimes equal to price. • Simply, th ...
Marketing - BA Dresden
... as well as too expensively. While the goal of marketing is to create a maximum satisfaction for the consumer, it is not always the cheapest price that does that. In general, the importance of the price will depend on the competition and on the market the product or service is aimed at. Consumers usu ...
... as well as too expensively. While the goal of marketing is to create a maximum satisfaction for the consumer, it is not always the cheapest price that does that. In general, the importance of the price will depend on the competition and on the market the product or service is aimed at. Consumers usu ...
Chapter 7
... A multidomestic marketing strategy is used by multinational firms that have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business. ...
... A multidomestic marketing strategy is used by multinational firms that have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business. ...