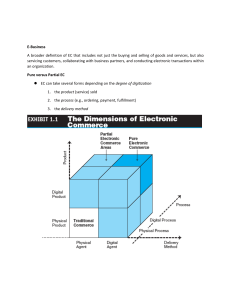
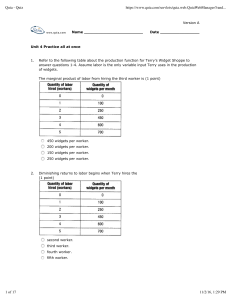
The Pan Paradigm of Business Analysis
... the aggregated want or desire to possess a good or service with purchasing power (money or affordability) necessary to make a legal transaction for the good or service. ...
... the aggregated want or desire to possess a good or service with purchasing power (money or affordability) necessary to make a legal transaction for the good or service. ...
Individual Writing Assignment 1
... 1. The microenvironment consists of entities that are “close to the company that affect its ability to serve its customers.” Examples of these entities in the microenvironment are the “company, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customer markets, competitors, and publics.” The company can influenc ...
... 1. The microenvironment consists of entities that are “close to the company that affect its ability to serve its customers.” Examples of these entities in the microenvironment are the “company, suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customer markets, competitors, and publics.” The company can influenc ...
Présentation Basic Principles of Competition_Dr Frederic Jenny
... 2) are perceived by consumers as fulfilling the same need, and ...
... 2) are perceived by consumers as fulfilling the same need, and ...
Lecture 20 Monopoly Price Discrimination
... to other buyers. q−1 q qM = q* Therefore, MR is always the and will stop only when p = MC. same as p and WTP. Social surplus is maximized,… So profits on that unit are P − MC. …but the monopoly gets all of The firm will continue to increase the surplus as producer surplus, sales as long ...
... to other buyers. q−1 q qM = q* Therefore, MR is always the and will stop only when p = MC. same as p and WTP. Social surplus is maximized,… So profits on that unit are P − MC. …but the monopoly gets all of The firm will continue to increase the surplus as producer surplus, sales as long ...
Course\EC\EC by KMV SY BBA ITM
... Technology that enables networked peer computers to share data and processing with each other directly; can be used in C2C, B2B, and B2C e-commerce. For example, in P2P application (Viber, WeChat, etc.), people can exchange music, photo, and other digitized goods electronically. ...
... Technology that enables networked peer computers to share data and processing with each other directly; can be used in C2C, B2B, and B2C e-commerce. For example, in P2P application (Viber, WeChat, etc.), people can exchange music, photo, and other digitized goods electronically. ...
Supply and Demand Curves
... of it. Electricity is an example: if power companies lower the price of electricity, consumers may be happy, but they probably won't use a lot more power in their homes, because they don't need much more than they already use. However, demand for luxury goods, such as restaurant meals, is extremely ...
... of it. Electricity is an example: if power companies lower the price of electricity, consumers may be happy, but they probably won't use a lot more power in their homes, because they don't need much more than they already use. However, demand for luxury goods, such as restaurant meals, is extremely ...
Marketing Plan - Silver Sage FFA
... research and present a marketing plan for an agricultural product, supply or service present the results of primary research involving the local community that provides a reasonable and logical solution to a marketing problem ...
... research and present a marketing plan for an agricultural product, supply or service present the results of primary research involving the local community that provides a reasonable and logical solution to a marketing problem ...
MRP - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... MRP of that resource equals its price. We would buy units of capital until the MRP of capital equals the price of capital MRP of capital = Price of capital MRP of capital Price of capital ...
... MRP of that resource equals its price. We would buy units of capital until the MRP of capital equals the price of capital MRP of capital = Price of capital MRP of capital Price of capital ...
Producer Choice - The Costs of Production
... total cost would rise if output were increased by one unit. The marginal cost always rises with the quantity of output. Average cost first falls as output increases and then rises. ...
... total cost would rise if output were increased by one unit. The marginal cost always rises with the quantity of output. Average cost first falls as output increases and then rises. ...
###The Marketing Mix - PowerPoint Presentation
... • The cost to make it • The amount of profit desired • Other objectives of the business • The price competitors charge • The price customers are willing to pay – Is there a high demand? – Is demand sensitive to changes in price? ...
... • The cost to make it • The amount of profit desired • Other objectives of the business • The price competitors charge • The price customers are willing to pay – Is there a high demand? – Is demand sensitive to changes in price? ...
Supply and Demand Infographic Supplemental Activity
... Supply and Demand Infographic Supplemental Activity Worksheet The concept of supply and demand is often called the heart and soul of economics. It is the foundation for much of what is studied in the field, and understanding how supply and demand affect the economy can help us to recognize economics ...
... Supply and Demand Infographic Supplemental Activity Worksheet The concept of supply and demand is often called the heart and soul of economics. It is the foundation for much of what is studied in the field, and understanding how supply and demand affect the economy can help us to recognize economics ...
The quantity demanded is the amount of a good that a buyer is
... Not always aggressive competition ...
... Not always aggressive competition ...
demand concepts - Cloudfront.net
... – Market competition promotes the general welfare, not because of any central plan but because of individual self-interests. • Market prices transmit information (signals) about scarcity and provide incentives for the most productive uses of Resources. – Response: A higher price encourages consumers ...
... – Market competition promotes the general welfare, not because of any central plan but because of individual self-interests. • Market prices transmit information (signals) about scarcity and provide incentives for the most productive uses of Resources. – Response: A higher price encourages consumers ...
Lecture slides Chap 5 and 7
... • Does the number of firms in an industry with constant marginal costs necessarily converge to infinity as the entry cost turns to zero? Explain. • Why are we interested in empirically estimating models of product differentiation? (After all, to understand the intensity of competition in the short r ...
... • Does the number of firms in an industry with constant marginal costs necessarily converge to infinity as the entry cost turns to zero? Explain. • Why are we interested in empirically estimating models of product differentiation? (After all, to understand the intensity of competition in the short r ...
Ch. 6: Market Research
... Ch. 6: Market Research • How do we choose a Target Market? – Multiple Target Markets can be chosen…However, its often best to choose the market with the __________point of __________ • Typically, these customers have a __________that ...
... Ch. 6: Market Research • How do we choose a Target Market? – Multiple Target Markets can be chosen…However, its often best to choose the market with the __________point of __________ • Typically, these customers have a __________that ...
A framework for analysing opportunities
... new product and surveying members of these markets to understand their purchasing behaviour relevant to such products ...
... new product and surveying members of these markets to understand their purchasing behaviour relevant to such products ...